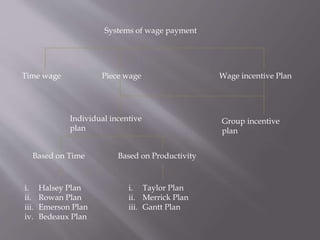
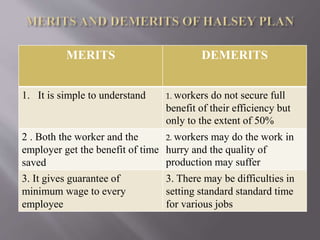
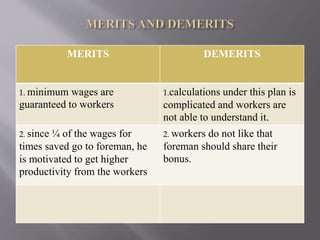
The document discusses different types of incentive plans used to motivate workers, including individual and group plans. Individual plans can be time-based or production-based, setting standards for time to complete tasks or units of output. Group plans reward cooperation and teamwork. Specific incentive plans discussed include Halsey, Rowan, Emerson, Bedeaux, Taylor, Merrick, and Gantt plans, outlining their mechanics for determining wages based on standards and incentives for efficiency.