This document discusses various types of incentive plans used to motivate employees. It defines incentive plans as performance incentive plans (PIPs) that encourage employees to exceed expectations. Some key incentive plans discussed include:
- Bonus incentives that reward employees for specific tasks or projects completed.
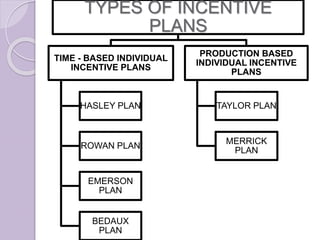
- Production-based individual incentive plans like the Taylor Plan and Merrick Plan that tie pay to productivity levels.
- Time-based individual incentive plans like the Halsey Plan, Rowan Plan, Emerson Plan, and Bedaux Plan that provide bonuses based on time saved or points earned.
- Merrick's Differential Piece-Rate System that uses three piece rates to distinguish pay for beginner, average,