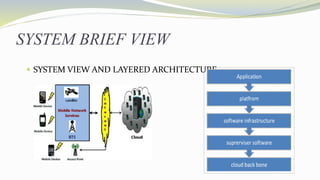
The document discusses a proposed efficient and secure framework for mobile cloud computing that addresses key issues like data ownership, privacy, and resource management for smartphones. It outlines a modular design consisting of six components that optimize execution decisions based on resource usage and network conditions, utilizing AES encryption for enhanced security during data transfer to the cloud. The framework aims to dynamically offload resource-intensive application strategies while minimizing energy consumption and maximizing performance.