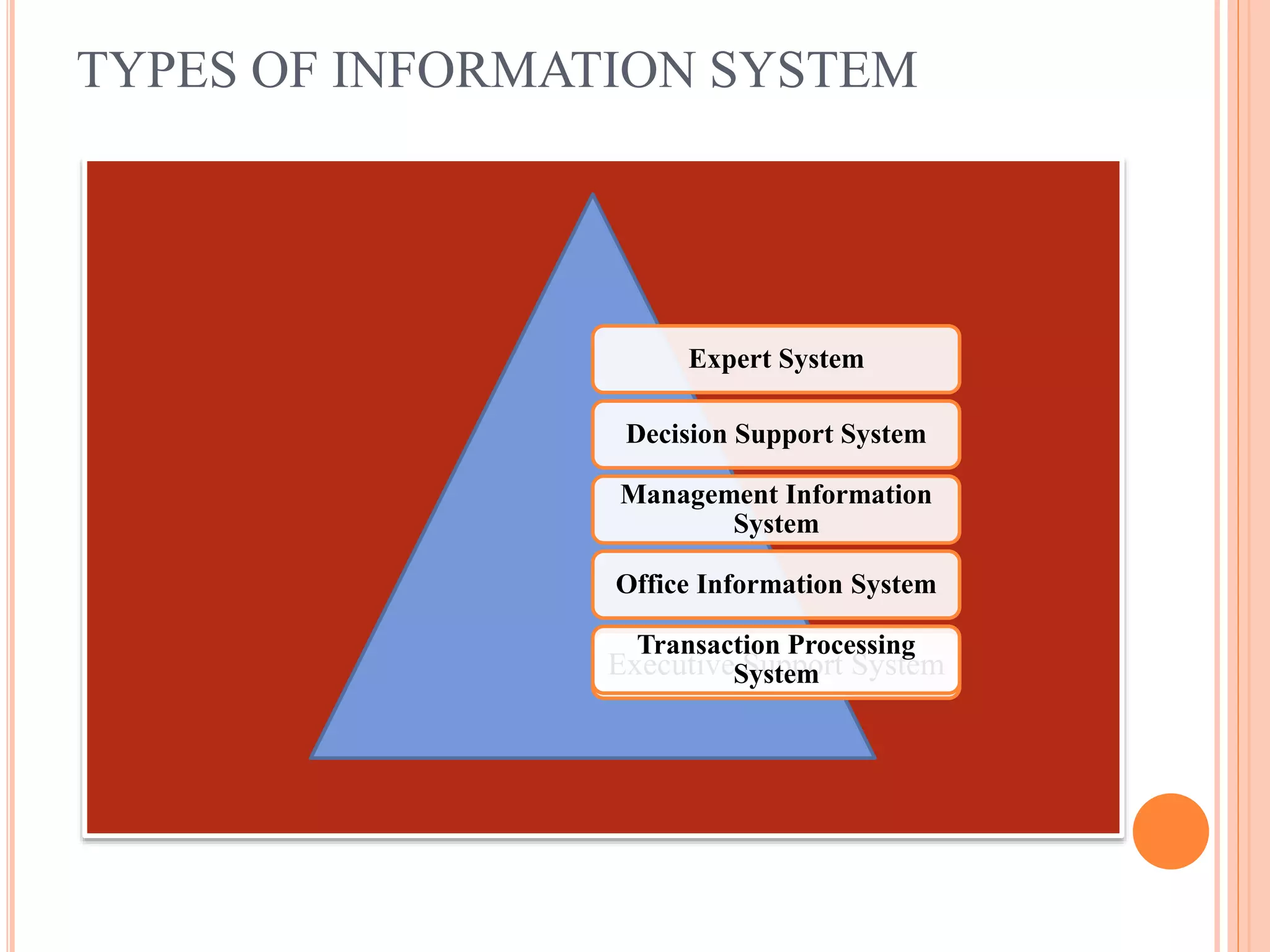
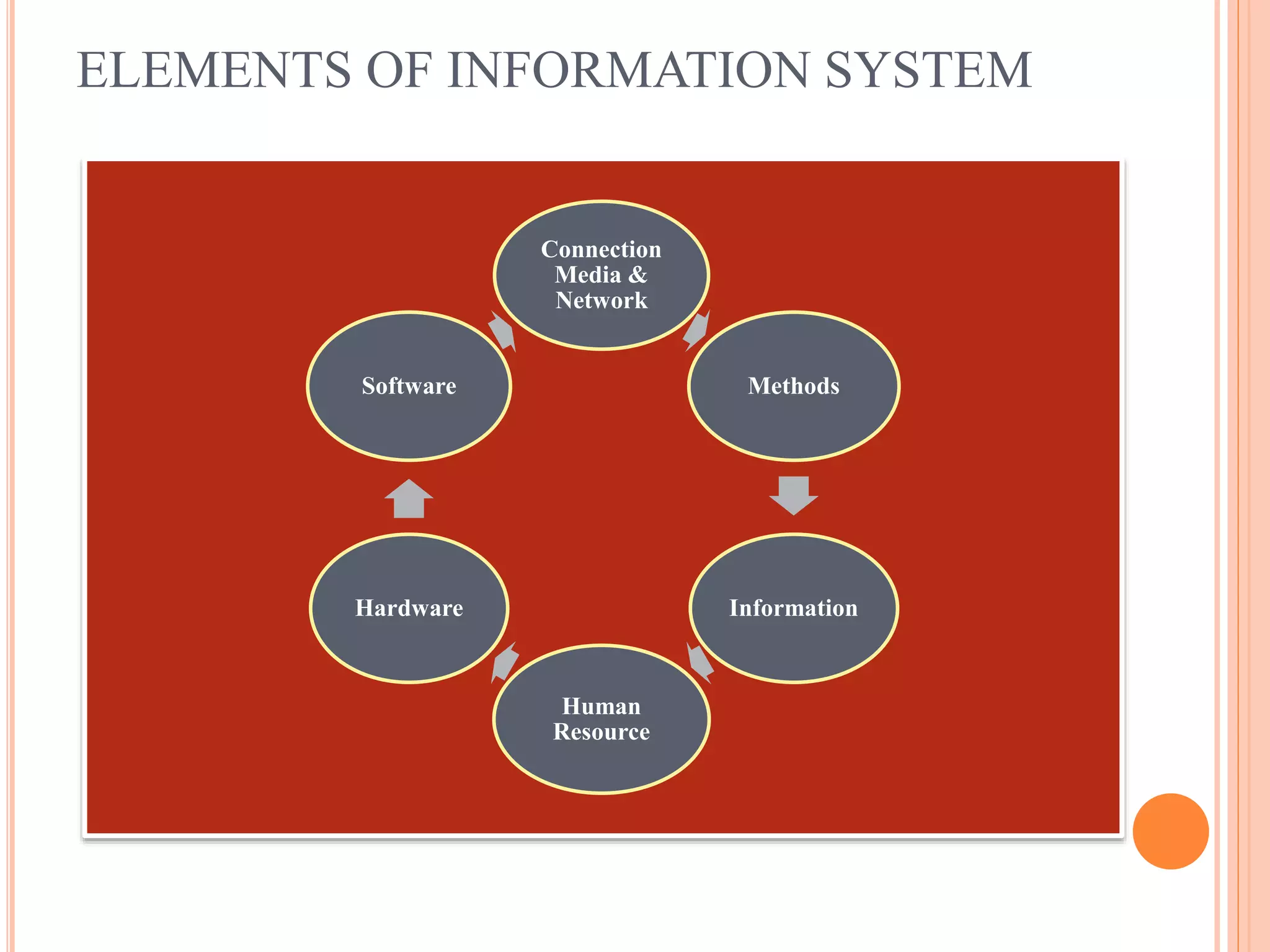
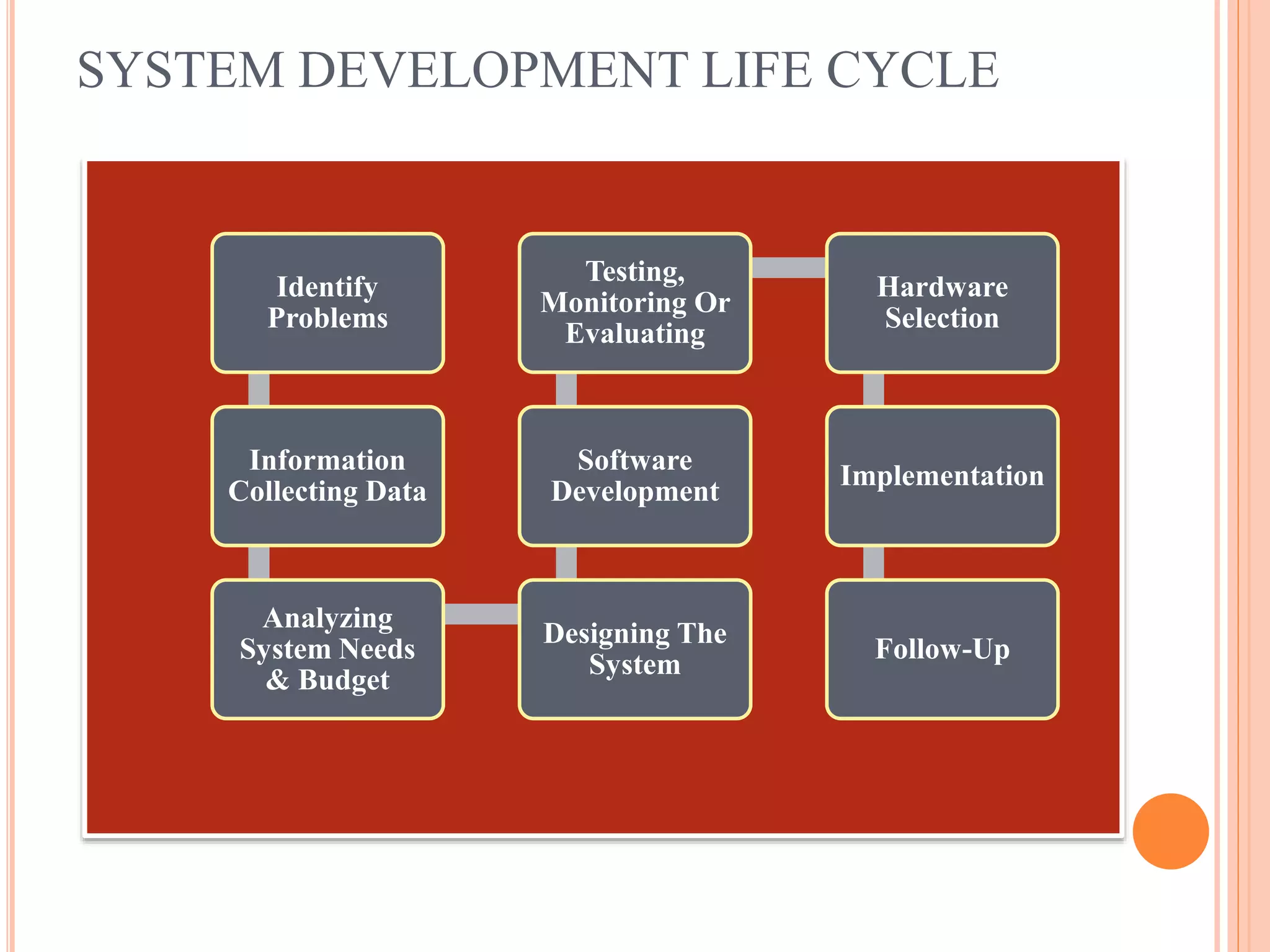
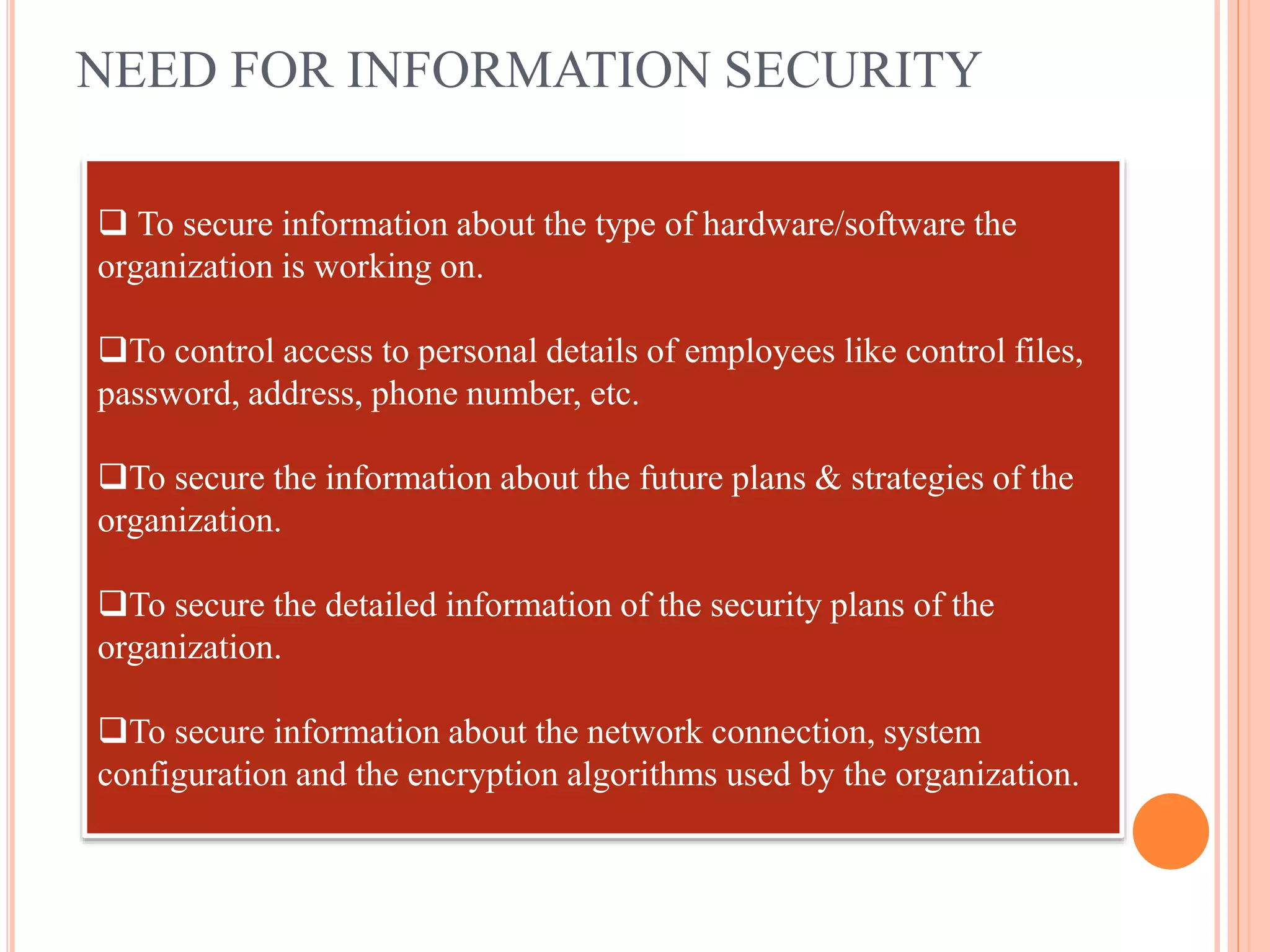
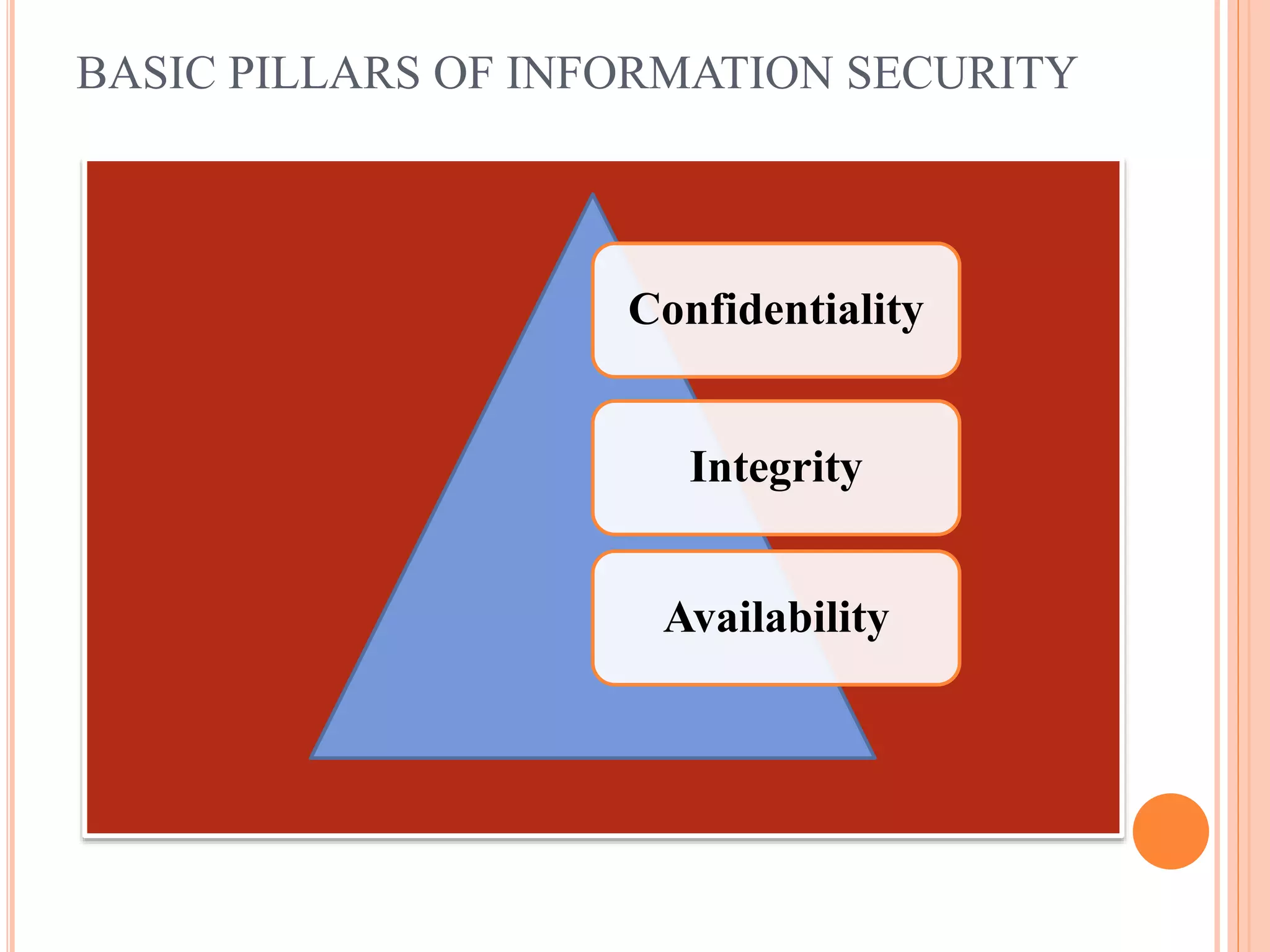
The document provides an overview of information systems and information security, defining their roles and components in organizational management. It highlights the need for data collection, security measures, and risk analysis to safeguard information while emphasizing various types of information systems, their development, and the significance of cyber security. Key elements discussed include the system development life cycle, threats to information systems, and the importance of ensuring confidentiality, integrity, and availability.