- Amiodarone is a class III antiarrhythmic agent with alpha, beta, sodium, potassium, and calcium channel blocking properties. It is indicated for ventricular and atrial dysrhythmias.
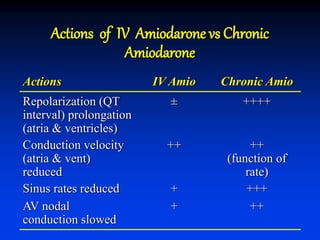
- Amiodarone has a long half-life, can be used in patients with kidney failure on dialysis, is generally well tolerated even in advanced heart failure, and has a very low risk of torsades de pointes.
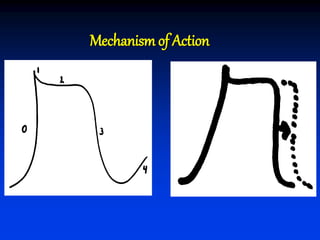
- The mechanism of action of amiodarone includes prolonging the action potential duration and effective refractory periods while also having anti-sympathetic effects through alpha and beta receptor blockade.