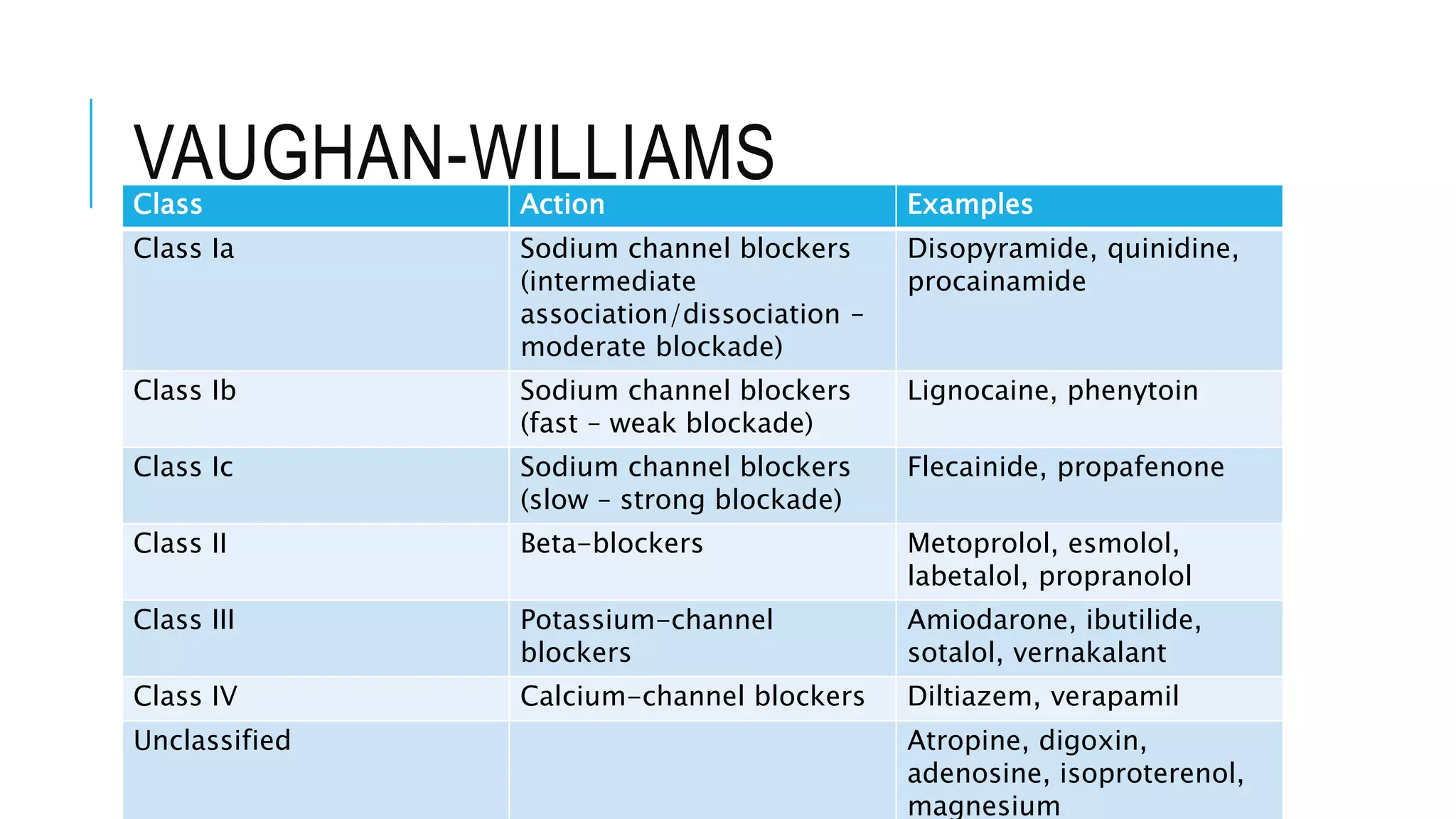
Class I antiarrhythmics include sodium channel blockers that are classified as Class Ia, Ib, or Ic based on their binding properties and effects. Class Ia drugs like procainamide have intermediate binding and prolong the action potential. Class Ib drugs like lignocaine have fast binding and decrease action potential duration. Class Ic drugs like flecainide have slow, strong binding and do not change action potential duration. Class II drugs are beta blockers that decrease sympathetic stimulation. Class III drugs are potassium channel blockers that prolong the refractory period like amiodarone and sotalol. They carry a risk of QT prolongation. Amiodarone has multiple mechanisms of action and a long half



















![AMIODARONE
Adverse reactions to IV dosing
Bradycardia, hypotension and phlebitis
Infusion rates should not exceed 30mg/min and total daily doses not exceed 2.2g
Amiodarone precipitates in saline
Dose adjustments only required for severe hepatic dysfunction
Adverse reactions
Cardiovascular – Sinus bradycardia (5% with oral), Torsades (<1%), thrombophlebitis, AV
nodal block, hypotension (16% with IV) [may be due to infusion rate or IV solution
emulsifier polysorbate 80]
CNS – Gait and movement disorders, paraesthesias, peripheral neuropathy or dizziness
GI - Nausea, vomiting, anorexia, constipation (10-33%)
Hepatic – Raised LFT (in 15-50%), monitor at baseline and 6 monthly
Pulmonary – 2-7% incidence. Often reversible pulmonary fibrosis, eosinophilia,
interstitial pneumonia, allergic alveolitis. Monitor baseline PFT’s and repeat CXR annually
Thyroid - Hypothyroidism (4-22%), hyperthyroidism (3-10%) monitor 3-6 monthly
Ocular corneal deposits](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/antiarrhythmics-200116235816/75/Antiarrhythmics-21-2048.jpg)