This document discusses aluminium and its alloys. Key points include:
- Aluminium is a lightweight metal that is abundant, corrosion resistant, and highly conductive. It is extracted from bauxite via electrolysis.
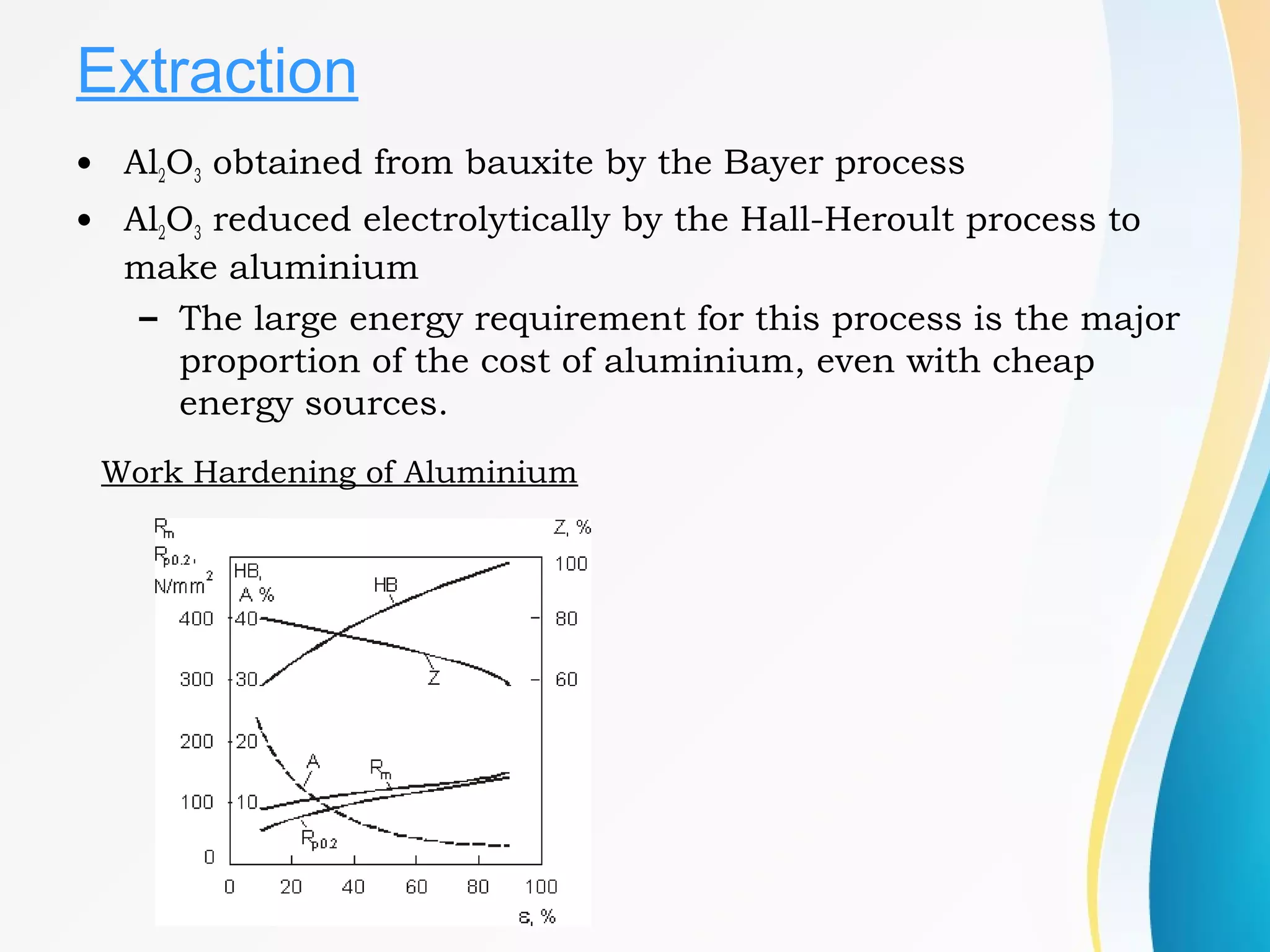
- Aluminium alloys include heat treatable alloys like duralumin that can be strengthened via precipitation hardening as well as non heat-treatable alloys.
- Common fabrication methods for aluminium include casting, rolling, extrusion, and welding. Various heat treatments can further influence the properties of aluminium alloys.
- Applications of aluminium alloys span transportation, infrastructure, packaging, and more due to its combination of properties like strength, conductivity, and corrosion resistance