Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX
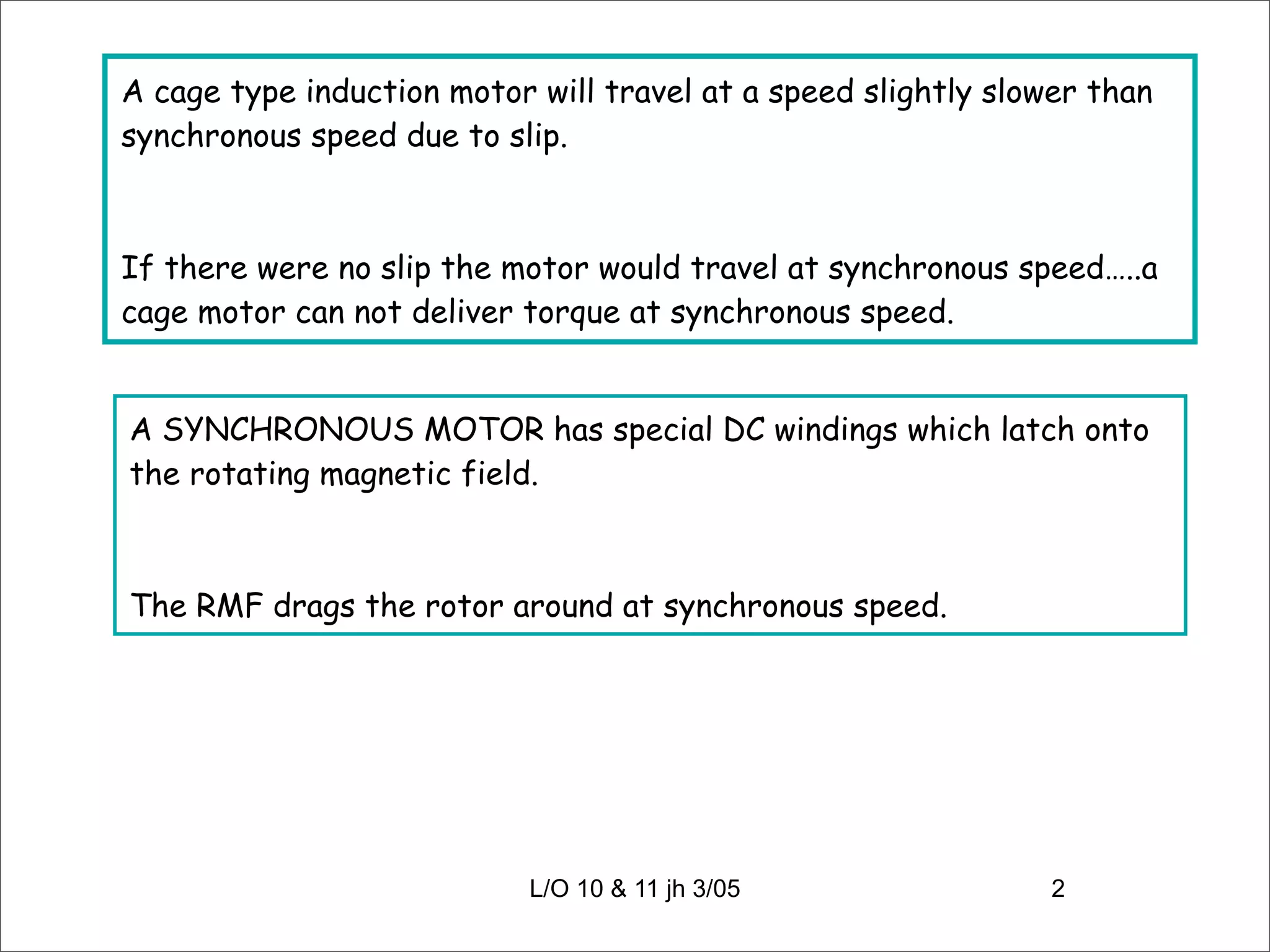













































1) Synchronous motors and alternators operate based on the same principles - they have a rotor that is synchronized to rotate at the same speed as the rotating magnetic field in the stator. 2) Alternators produce voltage through the interaction of a magnetic field and a conducting coil moving through this field. They require a conducting path, magnetic field, and relative motion between the two to generate an electromotive force (EMF). 3) Synchronous machines can operate in parallel by ensuring their frequencies, voltages, phase sequences, and synchronization are identical to share load demand. Proper synchronization is critical for parallel operation.














































