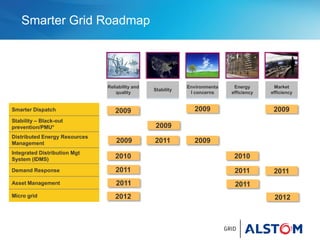
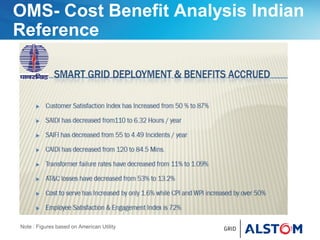
This document provides an overview of ALSTOM's smart grid solutions. It discusses their e-terra product suite which includes solutions for distribution management (e-terradistribution), energy management (e-terraplatform), and markets management (e-terramarkets). It also outlines their roadmap for developing solutions for stability and blackout prevention, distributed energy resource management, and demand response. The document then discusses specific products within the e-terra suite like their distribution management system, asset condition monitoring systems, and distributed energy resource management systems. It concludes by discussing ALSTOM's vision of enabling demand side resources to function as virtual power plants through their demand response management system, DRBizNet.