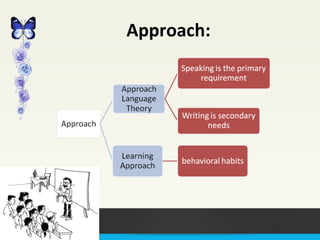
The Audio Lingual Method (ALM) is a language teaching method introduced in the US in the 1940s that focuses on speaking and listening skills. It emphasizes imitation, memorization of dialogues, and uses of drills. While ALM improved speaking abilities, it was criticized for ignoring reading and writing skills. The method also lost popularity in the 1950s when linguist Noam Chomsky questioned its theoretical foundations. ALM is still used in some contexts in Pakistan to help students memorize lessons and improve English speaking, though it has disadvantages if used as the sole method of instruction.