This document describes power allocation methods for secured communication in wireless relay networks. It discusses a system model with one source, three decode-and-forward relays, one destination, and one eavesdropper node. The destination sends artificial jamming noise to the relays to confuse the eavesdropper. Four jamming power allocation methods are introduced: fixed allocation, rate optimal allocation, outage optimal allocation, and statistical optimal allocation. Rate optimal allocation aims to maximize the destination's secrecy rate while minimizing outage probability. Outage optimal allocation chooses power based on source-relay and relay-destination channel state information to minimize outage probability of the secrecy rate.

![R. Revathi, S. Sinthuja, Dr.N.Manoharan and N.Rajendiran
http://www.iaeme.com/IJARET/index.asp 136 editor@iaeme.com
Cite this Article: R. Revathi, S. Sinthuja, Dr.N.Manoharan and N.Rajendiran,
Allocation of Power In Relay Networks For Secured Communication.
International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering and Technology,
6(8), 2015, pp. 135-144.
http://www.iaeme.com/IJARET/issues.asp?JType=IJARET&VType=6&IType=8
1. INTRODUCTION
Security plays an essential role in numerous wireless relay network applications. Due
to broadcast the messages through a wireless medium, receiving secured information
at the destination node in presence of possible eavesdroppers is of increasing
importance. A relay network is performed well means to satisfy the conditions of
higher reliability, higher data rate and a secured communication system. Wireless
relay network is used to help increase the rate of communication between the
transmitter and the receiver. The motivation of these relay networks is to provide
secure data access with anytime and anywhere. When implement the wireless devices,
power consumption have taken an important role. Therefore, power allocation is one
of the important issues in wireless communication technology, to overcome this
problem by using various power allocation methods. Wireless information theoretic
security was proposed in [1]. This paper considers a two channels are main channel
and wireless wiretap channel.
This encryption method provides the less security in a network. Collaborative
relay beam forming with perfect CSI Optimum and distributed implementation was
proposed in [2]. The optimal power allocation at the relays has been analyzed in
different strategies are partial CSI allocation, full CSI allocation and eavesdropper
node CSI allocation.
Secure wireless communication via cooperation was proposed in [3]. In an
optimal beam forming scheme is used to minimize the jamming power consumption
and also maintain a maximum secured communication in a relay network.
Cooperative communications based decode and forward relay is considered here.
Outage probability based power distribution between data and artificial noise for
physical layer security was proposed in [4]. It provides the security in physical layer,
communicating with many sources, one relay and one destination node was performed
here. Consider two types of broadcasting strategies are spatial beam forming and
noise forwarding techniques. This technique is used to minimize the outage
probability in the network and also improve the quality of service at the destination
node.
Consider the two beam forming techniques are optimal beam forming and robust
beam forming design was discussed in [5]. Optimal beam forming is performed well
in the presence of perfect CSI, and it is used iterative algorithm to obtain the
maximum secrecy rate. Robust beam forming schemes are investigated, when the
imperfect CSI is present at the node. The two hop wireless relay networks of half
duplex communication with different optimal power allocation schemes under the
Rayleigh fading channel was investigated in [6]-[8]. Here single relay is used, which
acts as an Amplify and forward relay protocol manner. Consider an Amplify and
forward relay strategies, to amplify the communication data and forwarded to the
destination. To maintain a secure communication against the eavesdropper node, relay
transmits the code words to confuse the eavesdropper node. The outage probability
and ergodic capacity was investigated in [9]. The partial band allocation provides the
less secrecy rate when the outage probability achieved the level of zero.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ijaret0608012-160426081417/75/ALLOCATION-OF-POWER-IN-RELAY-NETWORKS-FOR-SECURED-COMMUNICATION-2-2048.jpg)
![Allocation of Power In Relay Networks For Secured Communication
http://www.iaeme.com/IJARET/index.asp 137 editor@iaeme.com
Flat fading half duplex system is considered where multiple input and multiple
output pairs communicate with the help of an Amplify and forward relay was
investigated in [10]. In a channel state information available at the destination, to
transmit the more number of data streams based on the linear precoding schemes
through a conventional relay system. A cooperative communication network consists
of a one source, one relay node and multiple eavesdropper system was discussed in
[11]. Cooperative networks are used to transmit the intended noise to the jammer
node. Here node cooperation is developed for achieving security in a relay network.
Jamming techniques which generate an intended interference at the imperfect user
node in order to diminish the outage probability of the related link appear to be a
motivating approach for practical applications [12]. Optimal power allocation for
recuperating the amplify-and-forward relaying network is proposed in [15]. Secure
communications via cooperating base stations was proposed. An addition of the work
offered in [16] for cooperative ad-hoc environments with jamming. [14] In difference,
where only one relay node is preferred to pledge security, here the problem
considered involves the selection of a relay and a jammer node.
The objective of this paper is discussed below.
Minimizing the optimal jamming power with a fixed objective secrecy rate.
Maximizing the secrecy rate with convinced power constraints.
To find the excellent optimal power allocation by utilizing the method of JPA.
In our proposed work, we consider a two hop wireless relay networks in the
occurrence of an imperfect channel user with multiple decode-and-forward relaying
protocol. To achieve the maximum data received at the destination, we consider a
Quadrature phase shift keying modulation technique. [15] Here different types of
jamming power allocation methods are used to achieve a maximum security level in a
network.
The remaining paper is illustrated as follows: section II describe the system model
and channel capacity, section III discusses the cooperative jamming schemes, section
IV gives the numerical results with discussions and Conclusions are drawn in section
V.
2. SYSTEM MODEL AND CHANNEL CAPACITY
Here, we discuss the system model and channel capacity of the two hop wireless relay
networks system to achieve a maximum security level in a network.
2.1. System Model
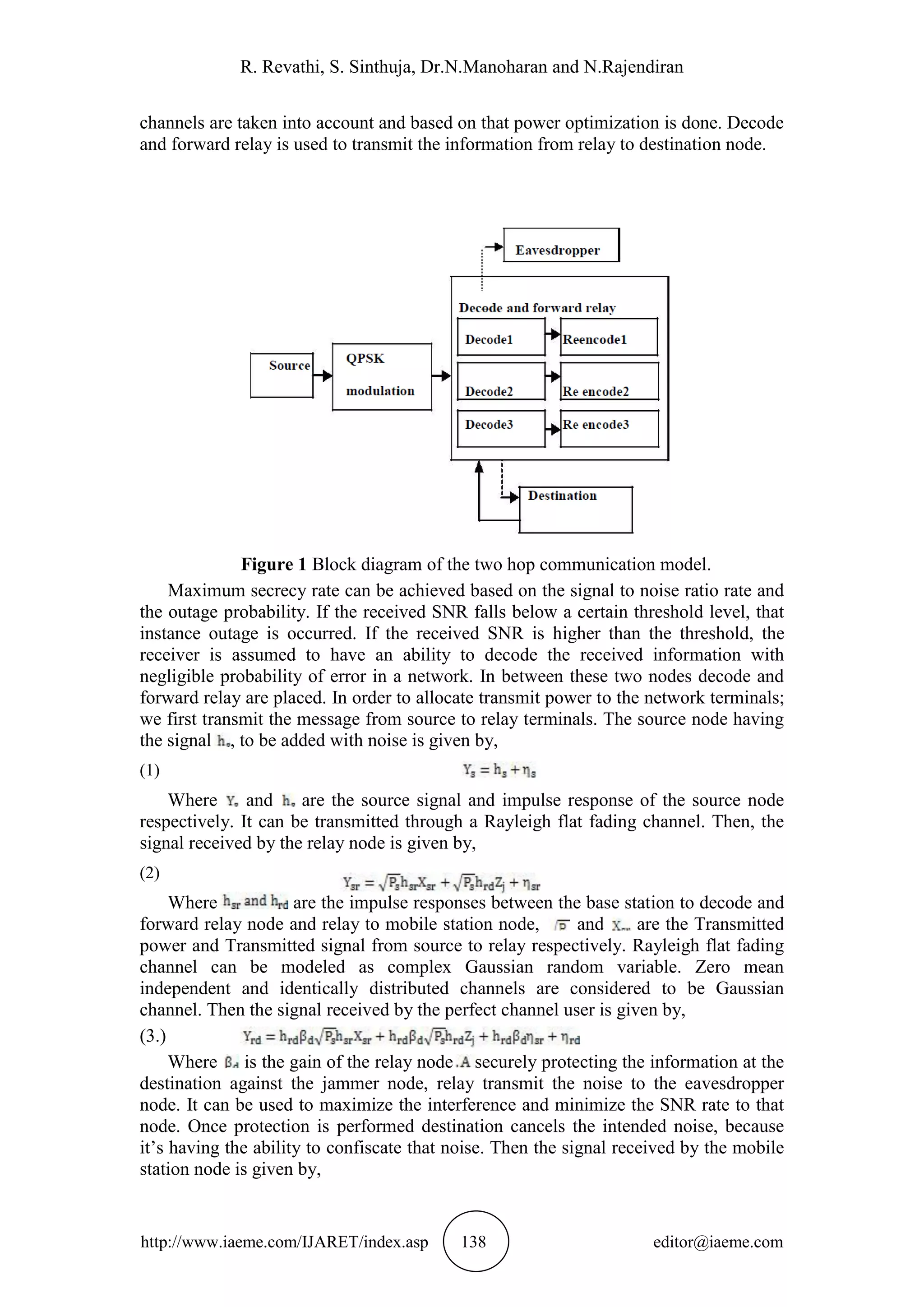
Consider a two-hop four terminal wireless relay networks system consisting of single
source node S, single destination node D, one eavesdropper node E terminal and three
decode and forward relay protocol as shown in Fig. 1. In this communication model
all nodes are assumed to be half duplex transmission. So relay cannot be transmits and
receive the information simultaneously. There is no direct communication link
between the source to destination and source to eavesdropper node. Here the relay
node transmits the source messages in a decode-and-forward fashion to the perfect
channel user node. While transmitting the messages from source to relay node, that
instant jammer intercept and try to capture that relay node messages. To avoid that
jammer node interception, the destination sends an intended noise to the relay node,
through a cooperative jamming communication. Power allocation is done for this
network using different jamming power allocation scheme in which, noise allocated to](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ijaret0608012-160426081417/75/ALLOCATION-OF-POWER-IN-RELAY-NETWORKS-FOR-SECURED-COMMUNICATION-3-2048.jpg)
![Allocation of Power In Relay Networks For Secured Communication
http://www.iaeme.com/IJARET/index.asp 139 editor@iaeme.com
(4)
Where the minus operator in the above equation is referred to as relay only
transmits if decoded correctly, otherwise it can be idle and if the source to destination
and source to relay link is strength less link means, than that performance is restricted.
The decode and forward relay provides the received signal by a factor that is inversely
proportional to the received power, which is given by,
Then the signal received by the imperfect channel user is given by,
(5)
Where , is the impulse response of the relay node to imperfect channel user
node and is considered as artificial jamming noise.
2.2. Decode and forward relay protocol
In decode-and-forward relaying protocol, while transmitting the message from
source to relay node, the received signal at the relay node, it first decoded that
received messages by using Viterbi decoding Algorithm and re encodes after it can be
forwarded to the destination. In that procedure noise is decoded at the relay node,
instead of by using amplify and forward relay protocol, it only amplifies the source
message without any decoding and encoding procedure. A Viterbi decoding
Algorithm procedure is shown in below.
Algorithm 1: Finding an decoded information Initialization:
Step 1: Set time t = 0, initial state of PM – 0, and all other PM - ∞.
Step 2: Increase time by 1, t = i+1.
Step 3: Evaluate BM for each branch,
Step 4: Compute PM[s, i+1], based on the ACS procedure
Step 5: End: map the decoded sequence, otherwise go back to step1.
A Viterbi algorithm consists of three parts they are branch metric, path metric and
trace back calculation. In a path metric calculation depends on the procedure of ACS
(Add, Compare and Select). The distance between the transmitted input pair of bits
and received pair of bits is referred as branch metric calculation.
The expression for decode-and-forward relay is given by
(6)
Where the minus operator in the above equation is referred to as relay only
transmits if decoded correctly, otherwise it can be idle and if the source to destination
and source to relay link is strength less link means, than that performance is restricted.
The decode and forward relay provides the received signal by a factor that is inversely
proportional to the received power, which is given by,
(7)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ijaret0608012-160426081417/75/ALLOCATION-OF-POWER-IN-RELAY-NETWORKS-FOR-SECURED-COMMUNICATION-5-2048.jpg)


![Allocation of Power In Relay Networks For Secured Communication
http://www.iaeme.com/IJARET/index.asp 143 editor@iaeme.com
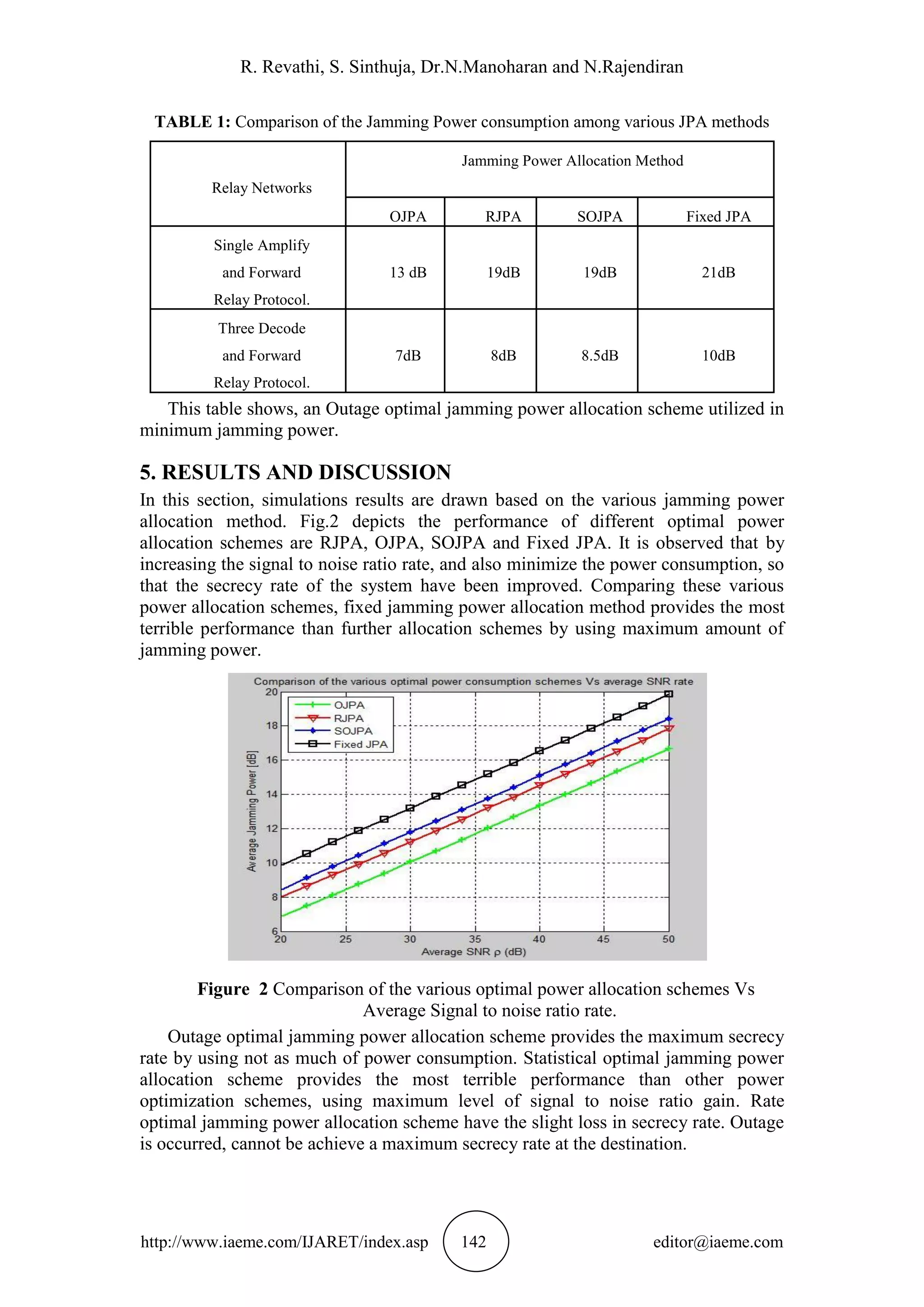
Figure 3 Comparison of the maximum achievable data rates among different JPA methods.
Fig.3 shows the maximum data rate received at the perfect channel user node. It
can be observed that by using decode and forward relay protocol offers superior
performance, instead of by using amplify and forward relay protocol provides the
moderate secrecy rate. Because Amplify and forward relaying protocol, without have
a decoding and encoding procedure.
5. CONCLUSION
This paper has studied the analysis of various optimal power allocation methods with
maximum secrecy consideration. The proposed scheme achieves a one source node,
three decode and forward relay node, single jammer node and single perfect channel
user node to exploit the security level against the jammer node. Maximum secrecy
rate was achieved by using decode and forward relay protocol. Outage optimal
jamming power allocation scheme provides the maximum secrecy rate by using not as
much of power consumption. To get better the secrecy rate modulation was performed
by using Quadrature phase shift keying modulation scheme. It is clear from the
observation that for superior values of the signal to noise ratio and the power
consumption was minimized. This work can be additionally extended by escalating
the relay nodes and also the system can be additionally improved with different
modulation techniques. Secured transmission is a most important concern in wireless
relay networks, such as military network and mobile phone wallet applications.
REFERENCES
[1] M. Bloch, J. Barros, M.R.D. Rodriques, and S.W. McLaughlin, Wireless
information theoretic security, IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory, 54(6), pp. 2515--
2534, Jun.2008.
[2] G. Zheng, K. Wong, A. Paulraj, and B. Ottersten, Collaborative- relay
beamforming with perfect CSI: Optimum and distributed implementation,
IEEE Signal Process Letters, 16(4), Apr.2009.
[3] L. Dong, Z. Han, A. Petropulu, and H.V. Poor, Secure wireless
communications via cooperation, in Proc. 46th Annual. Allerton Conf.
Commun., Control and computing, Monticello, IL, Sept. 2008.
[4] N. Romero-Zurita, M. Ghogho, and D. McLernon, Outage probability based
power distribution between data and artificial noise for physical layer
security, IEEE Signal Process. Lett, 19(2), pp. 71–74, Feb. 2012.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ijaret0608012-160426081417/75/ALLOCATION-OF-POWER-IN-RELAY-NETWORKS-FOR-SECURED-COMMUNICATION-9-2048.jpg)
![R. Revathi, S. Sinthuja, Dr.N.Manoharan and N.Rajendiran
http://www.iaeme.com/IJARET/index.asp 144 editor@iaeme.com
[5] Junwei Zhang and Mustafa Cenk Gursoy, Collaborative Relay Beamforming
for secrecy, IEEE International Conference on Communications, Jun. 2010.
[6] S. Goel and R. Negi, Guaranteeing secrecy using artificial noise, IEEE Trans.
Wireless Commun., 7(6), pp.2180-2189, Jun.2008.
[7] S. Adams, D. Goeckel, Z. Ding, D. Towsley and K. Leung, Multi-user
diversity for secrecy in wireless networks, in Proc. Information Theory and
Applications Workshop (ITA), Feb. 2010.
[8] A. Mukherjee and A.L. Swindlehurst, Robust beamforming for security in
MIMO wiretap channels with imperfect CSI, IEEE Trans. Signal Process,
59(1), pp. 351-361, Jan. 2011.
[9] W.C. Liao, T.H. Chang, W.K. Ma, and C.Y. Chi, Qos-based transmit
beamforming in the presence of eavesdroppers: An optimized artificial noise
aided approach, IEEE Trans. Signal Process, 59(3), pp.1202–1216,
Mar.2011.
[10] Z. Ding, K. Leung, D.L. Goeckel, and D. Towsley, On the application of
cooperative transmission to secrecy communications, IEEE J. Sel. Areas
commun, 30(2), pp.359-368, Feb.2012.
[11] J. Li, A.P. Petropulu, and S. Weber, on cooperative relaying schemes for
wireless physical layer security, IEEE Trans. Signal Process, 59(10), pp.
4985-4997, Oct. 2011.
[12] L. Dong, Z. Han, A.P. Petropulu, and H.V. Poor, Improving wireless physical
layer security via cooperating relays, IEEE Trans. Signal Process, 58(3),
pp.1875-1888, Mar.2010.
[13] Pimal Khanpara. A Review on Fuzzy Logic Based Routing In Ad Hoc
Networks, International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering &
Technology (IJARET), 5(5), 2014, pp. 75 - 81.
[14] Taha Abdelshafy Abdelhakim Khalaf. Optimal Decoding For Wireless Relay
Networks With Decode-And-Forward Cooperation Protocol, International
Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering & Technology
(IJECET), 5(5), 2014, pp. 75 - 81.
[15] C. Jeong, I.M. Kim, and D.I. Kim, Joint secure beamforming design at the
source and the relay for an amplify and forward MIMO untrusted relay
system, IEEE Trans. Signal Process 60(1), pp.310-325, Jan.2012.
[16] O. Simeone and P. Popovski. Secure communications via cooperating base
stations, IEEE Commun. Lett, 12, pp.188-190, Mar.2008.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ijaret0608012-160426081417/75/ALLOCATION-OF-POWER-IN-RELAY-NETWORKS-FOR-SECURED-COMMUNICATION-10-2048.jpg)