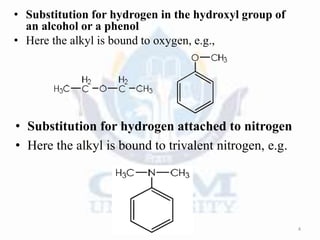
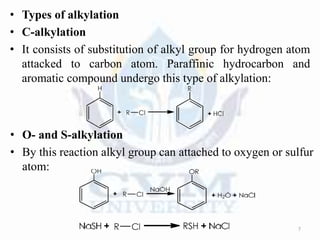
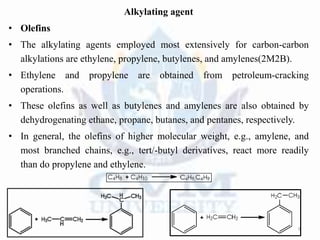
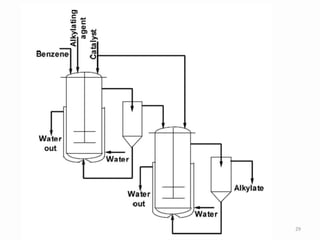
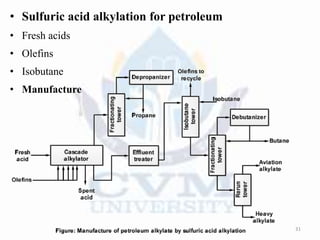
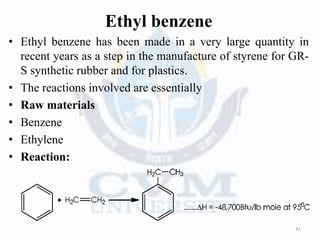
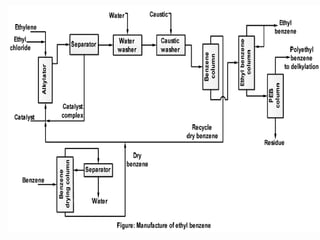
Alkylation is the introduction of an alkyl group into an organic compound by substitution or addition. There are six main types of alkylation depending on what is substituted - hydrogen, hydroxyl, nitrogen, addition to tertiary nitrogen, bonding to metals, or miscellaneous additions. Common alkylating agents used are olefins, alcohols, alkyl halides, alkyl sulfates, aralkyl halides, and arylsulfonic alkyl esters. The effect of alkylation depends on the compound but can impact properties like volatility, solubility, toxicity, and physiological activity. Common reactors for alkylation include tubular, stirred cascade, and column types. Sulfuric acid is commonly used as a catalyst for pet





































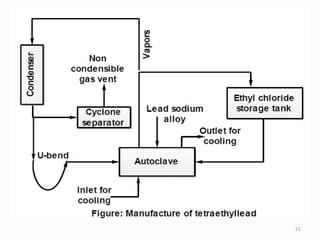
![• Tetraethyllead (TEL)[Pb(C2H5)4]
• Tetraethyllead is widely used for the prevention of
knocking in high-compression gasoline engines,
0.04% TEL being as efficient in this respect as 25%
benzene.
• In order to prevent the deposition of lead in the
exhaust sections of the engine, 3-parts by volume of
TEL are mixed with 2-parts of ethylene bromide
(CH2BrCH2Br) or a mixture of ethylene bromide and
ethylene chloride.
• The ethylene halide converts the lead oxide formed
during the combustion into the volatile lead halide. 47](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/alkylation-200201071120/85/Alkylation-47-320.jpg)