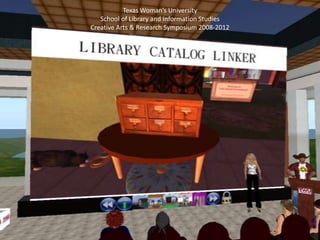
Valerie Hill is an adjunct instructor and librarian who focuses her research on adopting virtual worlds for education and librarianship. Her presentation discusses emerging trends in virtual and digital media based on constructivism and adult learning theory, including apps, MOOCs, augmented reality, digital content curation, and serious gaming. She provides examples of virtual exhibits, conferences, and a certificate program on virtual worlds. Hill advocates balancing tradition with innovation and values interactive, problem-based learning that actively engages adult learners.



































![Bibliography
Antiquity Texas. (2010). http://antiquitytexas.wordpress.com/about-2/ [accessed December 15, 2012]
Dalgarno, Barney, and Mark J. W. Lee. (2010). What are the learning affordances of 3-D virtual environments? British Journal of Educational
Technology 41, (1) (01): 10-32.
Dewey, John. (1916). Democracy and education. The Free Press, New York.
Dresang, Eliza T. (2005). The information-seeking behavior of youth in the digital environment. Library Trends 54, (2): 178-196.
Farley, Kathryn, Michael Nitsche, Jay Bolter and Blair MacIntyre. (2009). Augmenting Creative Realities: The Second Life Performance Project.
Leonardo 42, no. 1: 96-7.
Hecher, M. M., Möstl, R. R., Eggeling, E. E., Derler, C. C., &Fellner, D. W. (2011). 'Tangible Culture' - Designing virtual exhibitions on multi-
touch devices. Information Services & Use, 31(3/4), 199-208.
Hew, KheFoon, and Wing Sum Cheung. (2010). Use of three-dimensional (3-D) immersive virtual worlds in K-12 and higher education settings:
A review of the research. British Journal of Educational Technology 41, (1) (01): 33-55.
Hill, Valerie, and Hyuk-Jin Lee. (2009). Libraries and immersive learning environments unite in second life. Library Hi Tech 27, (3): 338-56.
Hill, Valerie. (2011) “Virtual tornado hits the library”, Learning Technology IEEE, 13 (4), 42-45.
Huang, H. (2002). Toward constructivism for adult learners in online learning environments. British Journal Of Educational Technology, 33(1),
27.
Jamaludin, Azilawati, Yam San Chee, and Caroline Mei Lin Ho. (2009). Fostering argumentative knowledge construction through enactive role
play in second life. Computers & Education 53, (2) (9): 317-29.
Klomp, R. W., Spitalnick, J. S., &Reissman, D. B. (2011).Virtual Classroom Immersion Training.T+D, 65(1), 38-43.
Malcom Knowles. (2007). Adult Learning Theory and Principles.
http://www.qotfc.edu.au/resource/index.html?page=65375 [accessed December 15, 2012]
Lateef, F. (2010). Simulation-based learning: Just like the real thing. Journal Of Emergencies, Trauma & Shock, 3(4), 348-352.
Plutchak, T. Scott. (2007). The Librarian: Fantastic Adventures in the Digital World. Serials, 20(2), 87-91.
Slone, Debra. (2009). A Methodology for Measuring Usability Evaluation Skills Using the Constructivist Theory and the Second Life Virtual
World. Journal of Usability Studies, 4 (4) 178-188.
Stanziola, J. (2008). What will be the needs of library, museum and archives users in the next 10 years? research implications. Library &
Information Research, 32(100), 13-19.
SylaiouStyliani, LiarokapisFotis, Kotsakis Kostas, PatiasPetros, (2009). Virtual museums, a survey and some issues for consideration. Journal of
Cultural Heritage, 10 (4): 520-528.
Taouabit Boland, I. (2009). Efficacy of the 3D Multi-User Virtual Environment (MUVE) Second Life for learning in cognitive constructivist and
social constructivist activities. Ph.D. diss., Capella University.
Teeuwisse, Jo. (2012). http://www.ghostsofhistory.co.uk/who-are-we/bio/ [accessed December 15, 2012]
TRP360. (2012). http://www.trp360.com/ [accessed December 15, 2012]
Vygotsky, Lev. (1978). Mind in society Harvard University Press, Cambridge.
Webber, Sheila and Diane Nahl. (2011). Sustaining Learning for LIS through use of a Virtual World. IFLA Journal (37)(1): 5-15.
Zemke , Ron and Susan. (1995). http://setur.khi.is/fullordinsfraedsla/NoN/Itarefni/Zemke_WhatDoWeKnow.pdf [accessed December 15,
2012]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/alisehillteachingmethodssigjan2013rev-130129182111-phpapp02/85/Librarianship-Embraces-Virtual-Media-39-320.jpg)
