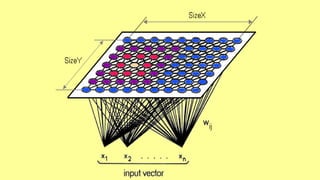
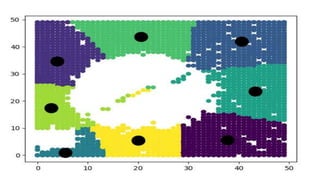
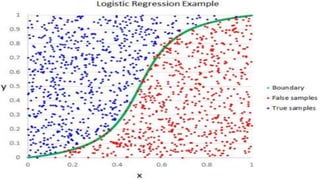
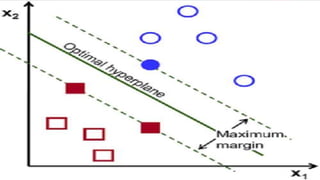
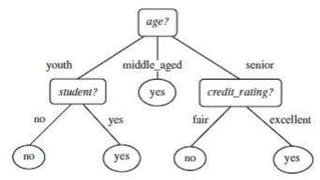
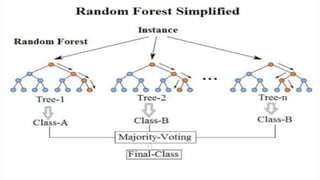
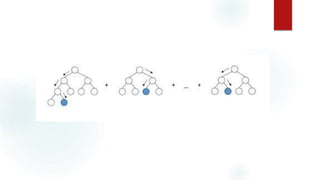
The document discusses several machine learning algorithms: Kohonen's self-organizing map (SOM) which reduces dimensionality; K-means clustering which groups similar data points; logistic regression which classifies data using probabilities; support vector machines (SVM) which find optimal separating hyperplanes; C4.5 decision trees which classify using a question-answer tree structure; random forests which create many decision trees; gradient boosting decision trees which iteratively adjust weights; and K-nearest neighbors (KNN) which classifies based on closest training examples. For each algorithm, it provides a brief overview of the approach and key steps or equations involved.