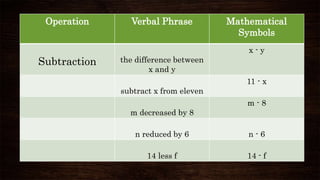
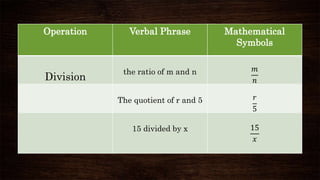
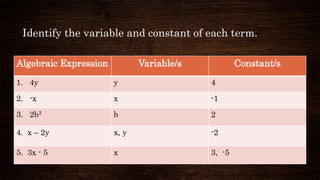
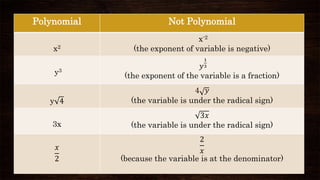
This document discusses algebraic expressions and polynomials. It defines key terms like variables, constants, and operations. It provides examples of algebraic expressions and identifies the variables and constants. It also defines polynomials as expressions with whole number exponents and restrictions. Examples are given to classify expressions as polynomials or not. The document also discusses classifying polynomials by number of terms and degree.