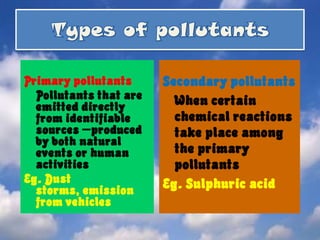
This document summarizes various types of air pollution including smog, acid rain, the greenhouse effect, and holes in the ozone layer. It discusses sources of air pollution such as volcanoes, decaying organic matter, and emissions from human activities like burning fossil fuels. The main types of air pollutants are primary pollutants emitted directly and secondary pollutants formed from chemical reactions. Indoor air pollution from activities like smoking can also be harmful. Air pollution affects human health in both short and long term ways. Solutions proposed include using cleaner fuels, reducing energy use, and controlling industrial and vehicle emissions.