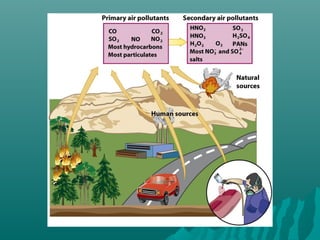
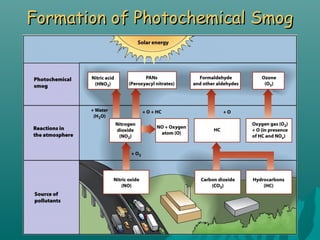
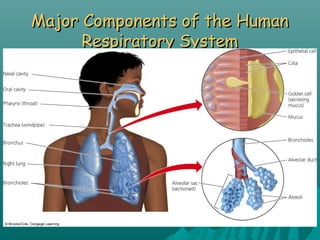
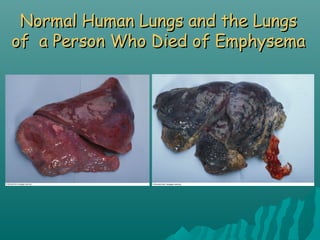
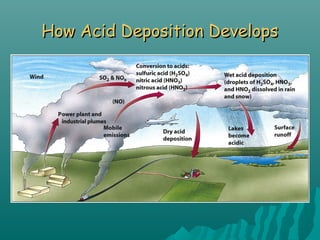
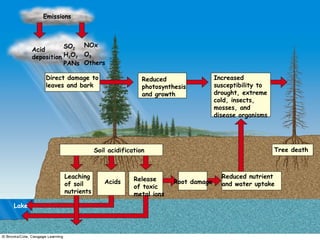
This document discusses air pollution and its causes, effects, and methods of control. It begins by describing the composition of the atmosphere and how air pollution occurs from both natural and human sources. The major classes of air pollutants are identified as particulate matter, nitrogen oxides, sulfur oxides, carbon oxides, hydrocarbons, and ozone. Transportation and industry are cited as the main sources of outdoor air pollution. The health effects of air pollution and methods to control pollution through emissions standards and regulations are also examined.