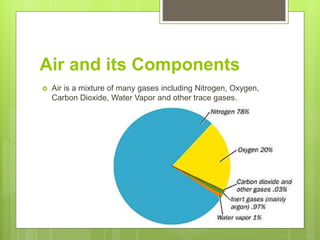
This document discusses air pollution, its causes, effects, and potential solutions. It defines air pollution as any change in the atmosphere's composition from harmful gases. The main causes are burning fossil fuels which release gases like SO2 and NOx, vehicular emissions, agricultural activities, waste disposal, and chemical usage. The effects include respiratory illnesses, global warming, acid rain, eutrophication, and ozone layer depletion. Solutions proposed are increasing public transportation and clean energy adoption, as well as reducing waste and conserving resources.