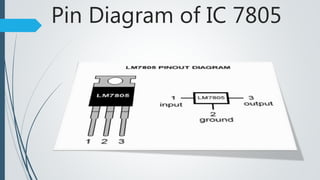
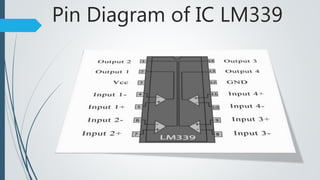
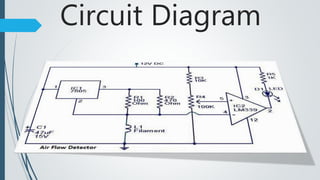
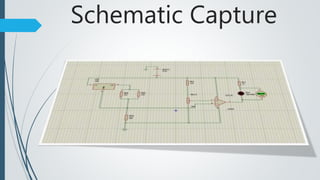
This document presents a design for an air flow detector circuit. The circuit uses the variable resistance of an incandescent light bulb filament when exposed to different air flow rates. An op-amp comparator circuit compares the filament resistance to a reference voltage and lights an LED if air flow is detected. The circuit could be used to monitor airflow in applications like electronics cooling, HVAC systems, clean rooms, and laboratory equipment to detect failures or issues.