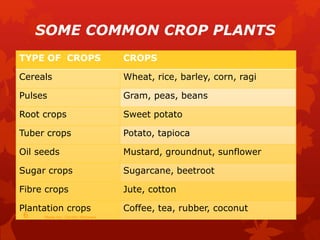
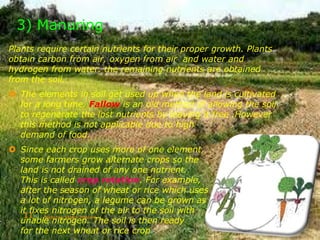
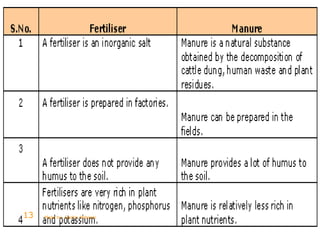
This document discusses the key aspects of agriculture. It defines agriculture as the science dealing with the growth of plants and animals for human use. The main components of agriculture discussed are cultivation of soil, growing and harvesting of crops, horticulture, and animal husbandry. The document then covers various crop types including cereals, pulses, root crops, tuber crops, oilseeds, sugar crops, and plantation crops. It also discusses rabi and kharif crops. The major steps in crop production outlined are preparation of soil, sowing seeds, manuring, irrigation, weeding, crop protection, harvesting, and storage.