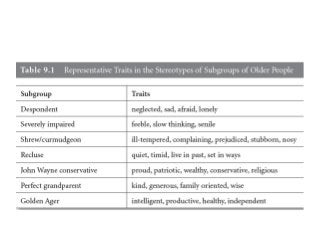
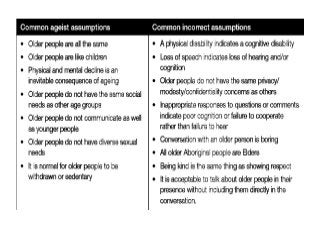
Ageism refers to stereotyping, prejudice, and discrimination against individuals based on their age. There are three main components of ageism: cognitive (beliefs and stereotypes about older people), affective (prejudicial attitudes), and behavioral (discriminatory practices). Ageism occurs at personal, institutional, and societal levels and can be intentional or unintentional. It negatively impacts older adults' self-esteem, participation in society, and access to quality services. While ageism is prevalent, discrimination in old age must be addressed by challenging negative stereotypes, promoting intergenerational contact, and changing policies that marginalize older groups.