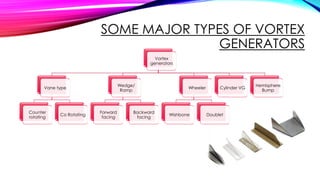
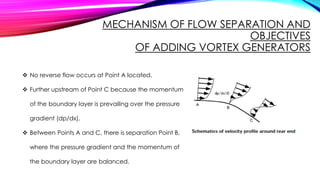
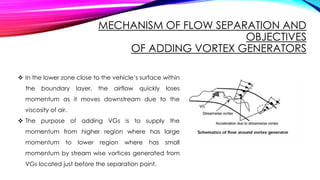
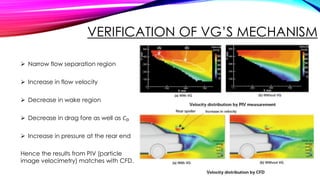
This document discusses the optimization of vortex generators (VGs) applied to the roof end of a sedan vehicle to reduce aerodynamic drag. It presents 6 group members who studied installing bump-shaped VGs upstream of the flow separation point. Computational fluid dynamics simulations and particle image velocimetry experiments showed that optimized VGs reduced the drag coefficient by 0.006 by generating streamwise vortices that delayed flow separation. VGs increase surface pressure over the rear window and trunk area, narrowing the wake region and flow separation point. VGs are commonly used on vehicles worldwide to improve fuel efficiency and vehicle performance.