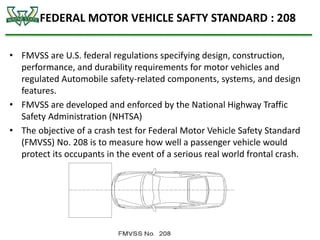
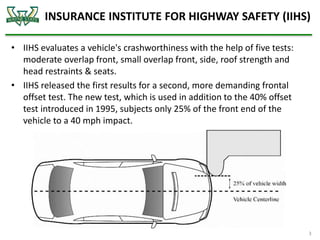
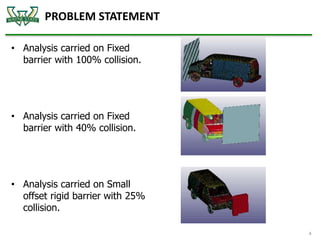
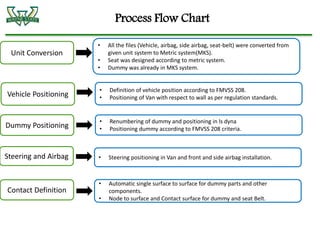
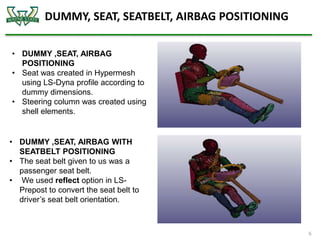
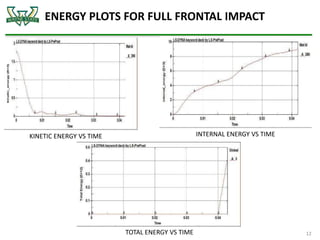
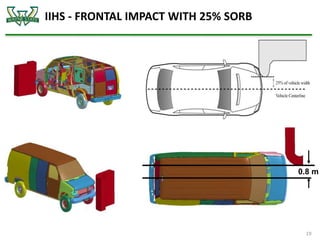
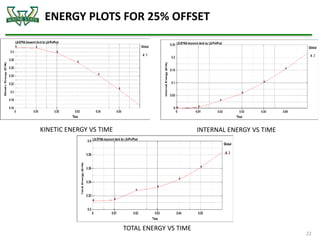
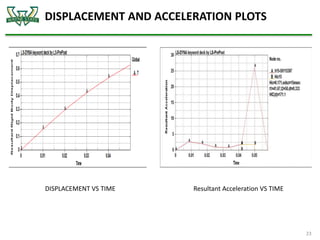
The document discusses the analysis of crashworthiness and occupant protection under the federal motor vehicle safety standard (FMVSS) 208, focusing on frontal impact tests conducted by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) and the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS). It outlines methods used for simulating various collision scenarios, including fixed barrier tests and offset impacts, as well as the effects of safety features like airbags and seatbelts on injury risk. The findings emphasize the importance of side airbags and seatbelt positioning in enhancing passenger safety during crashes.