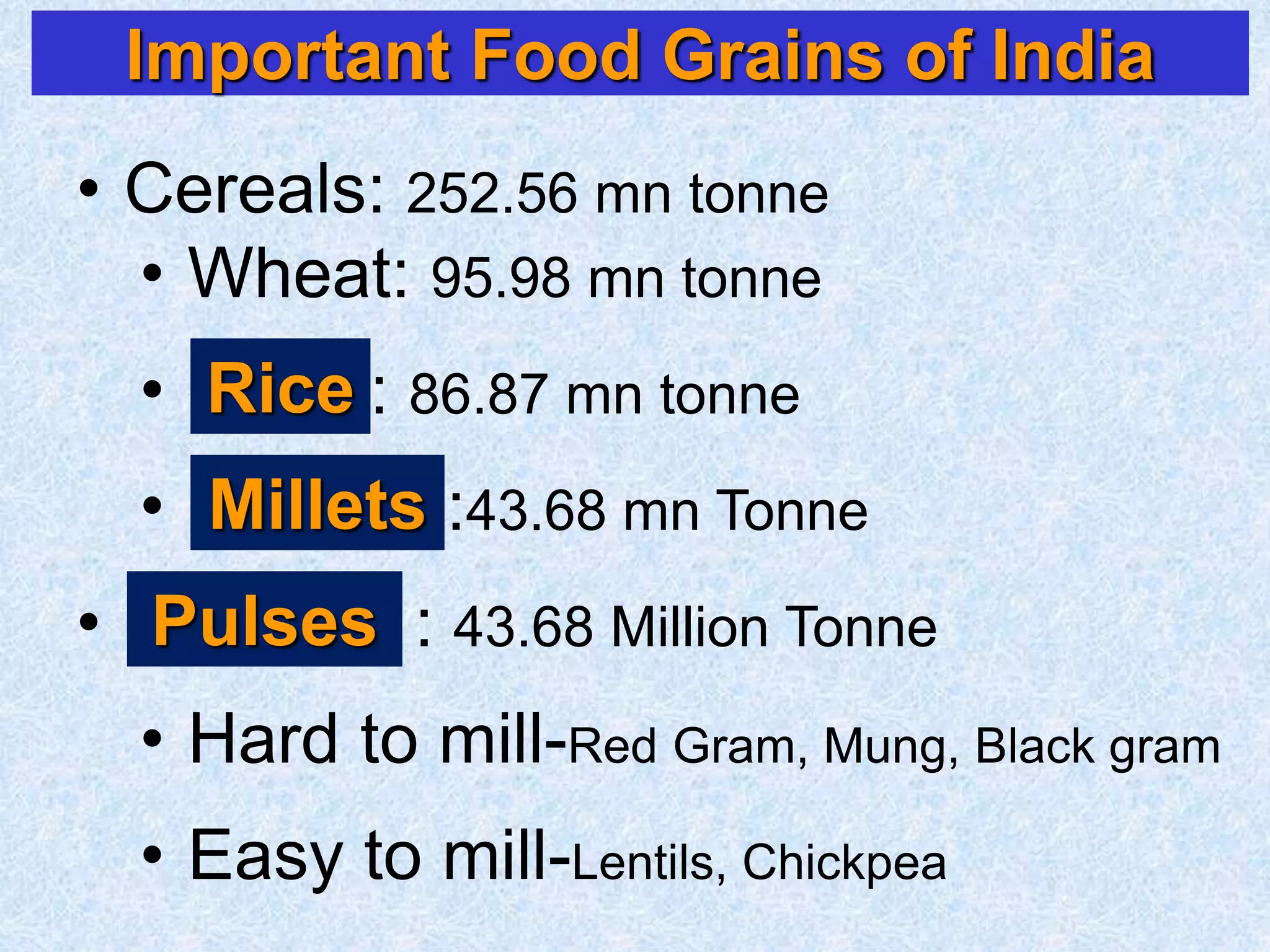
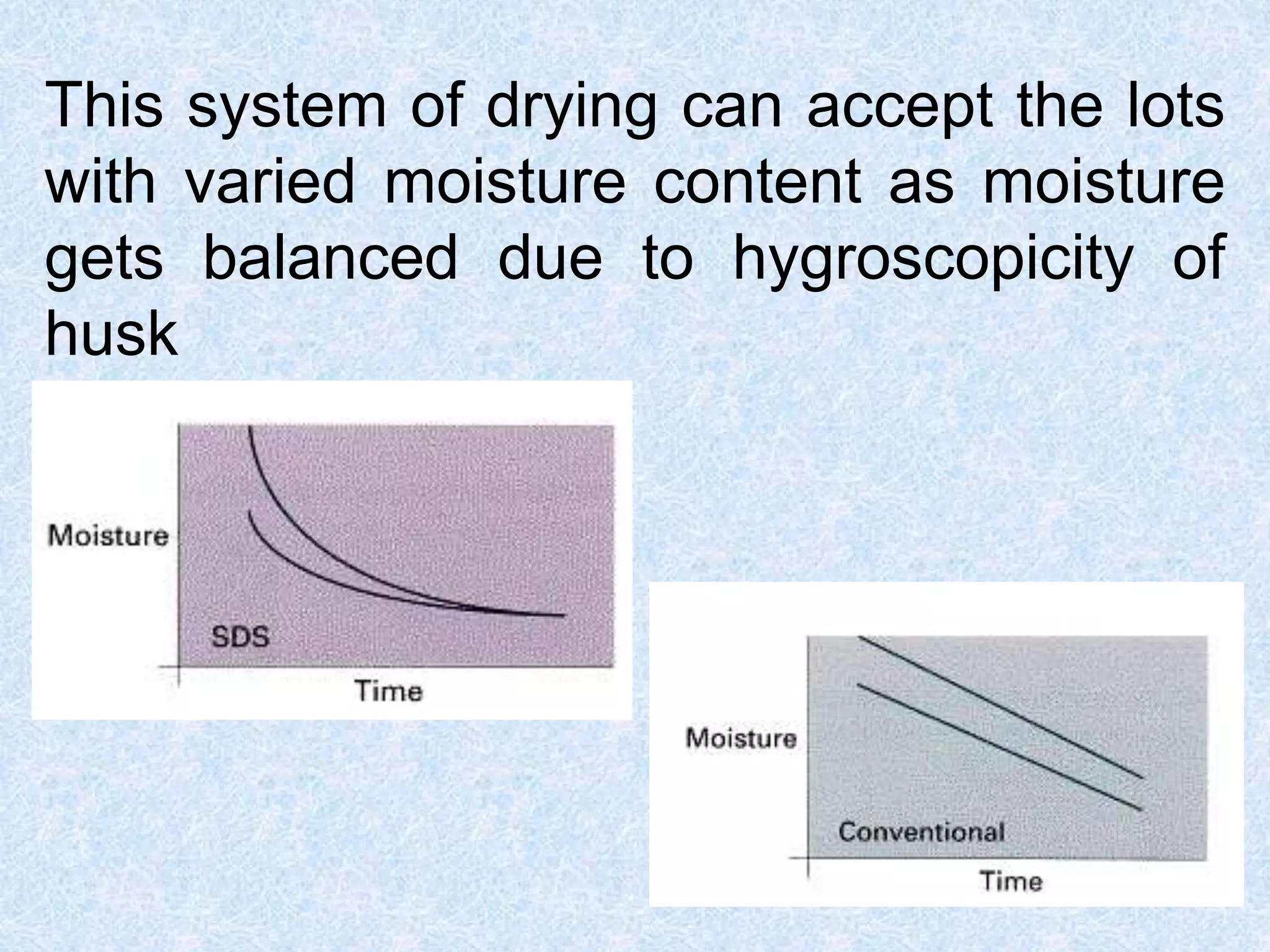
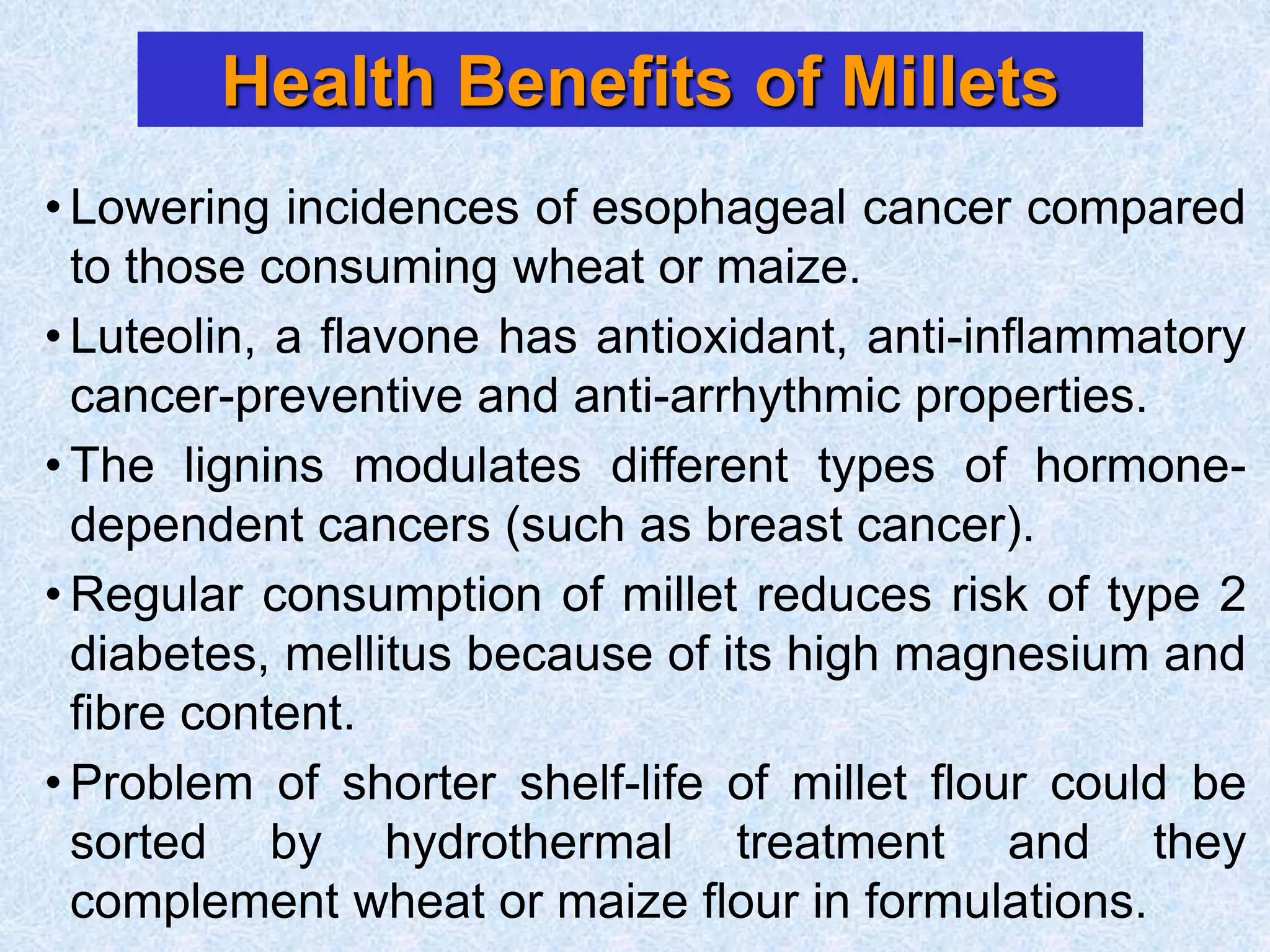
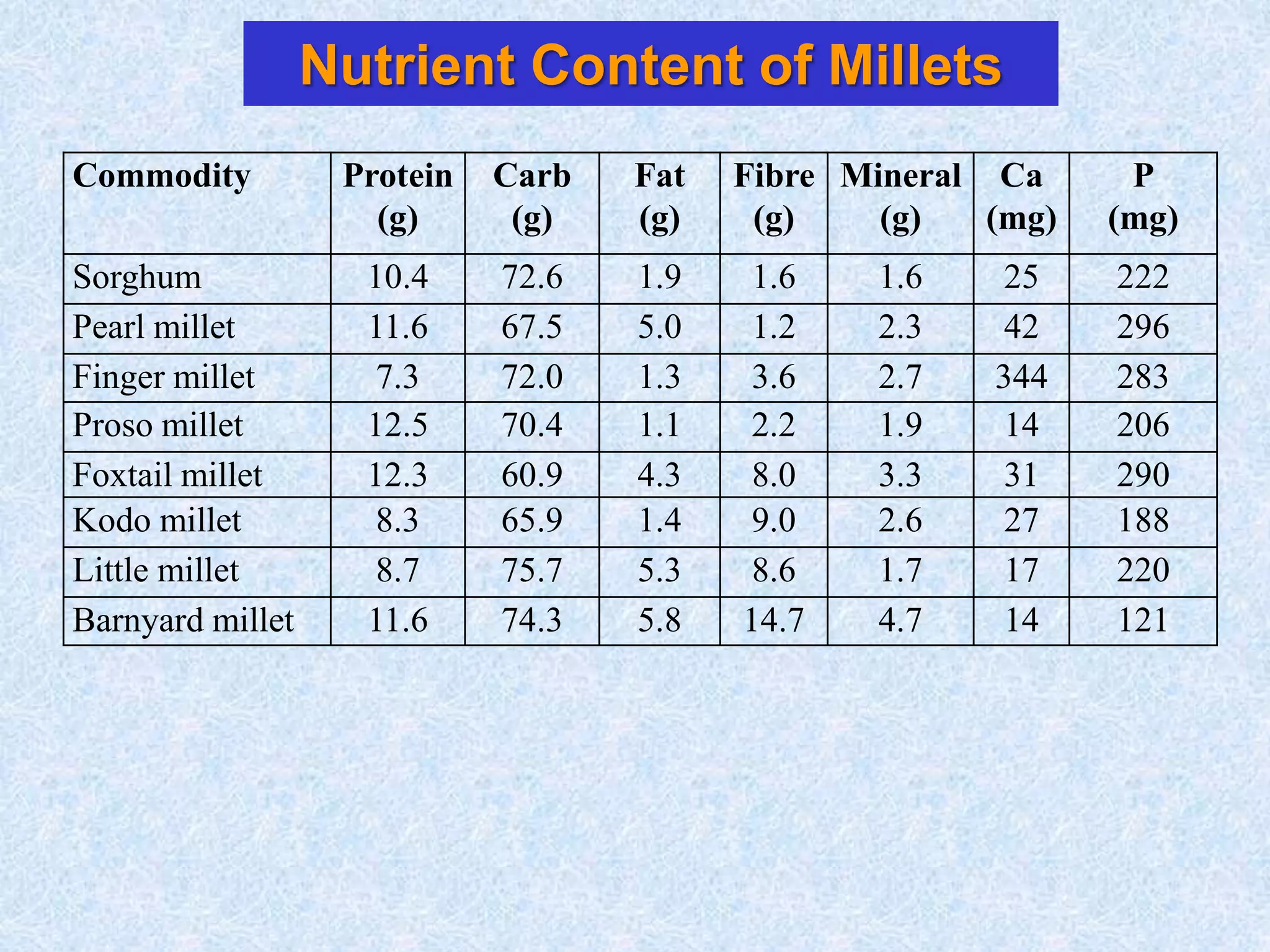
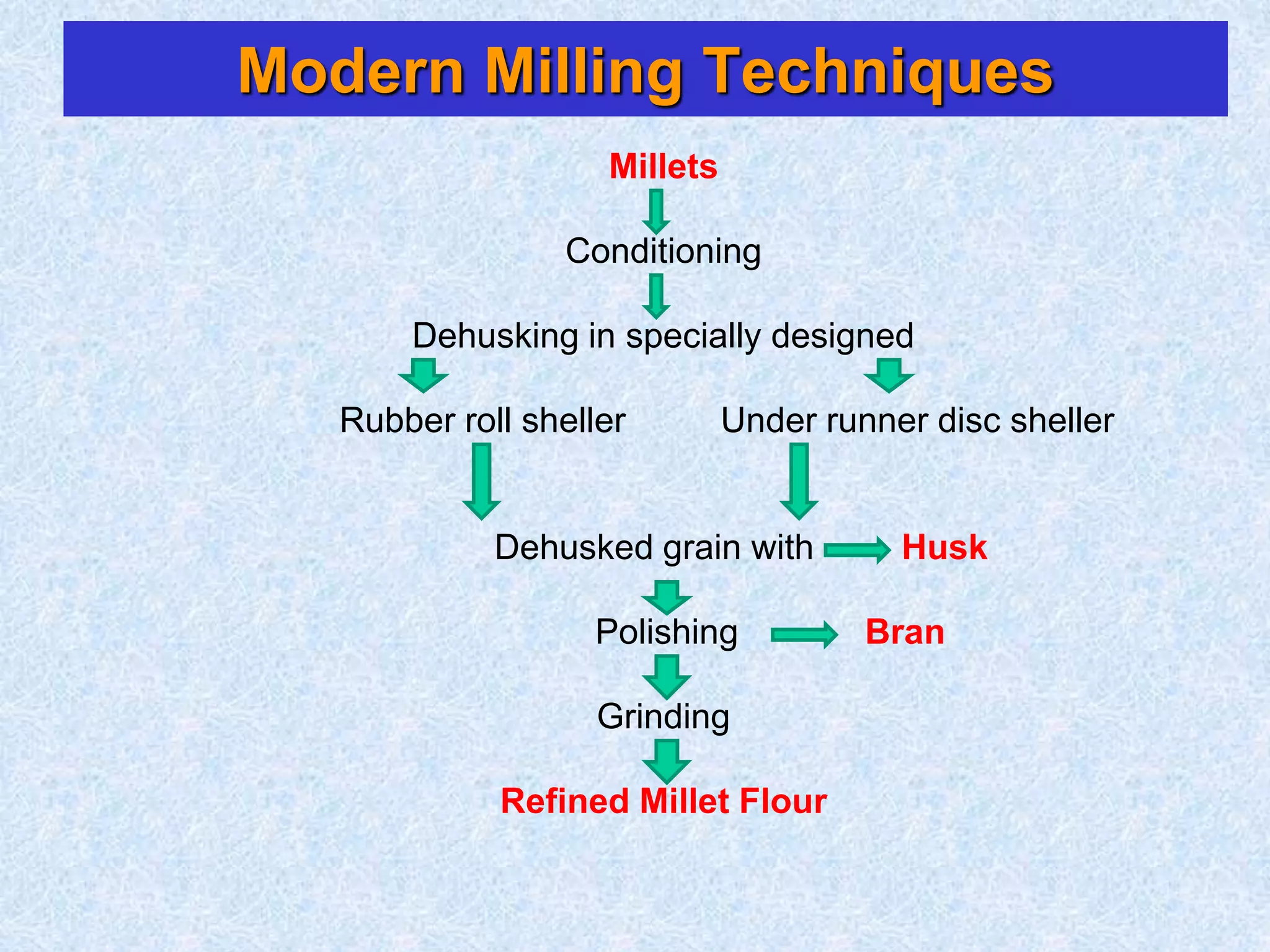
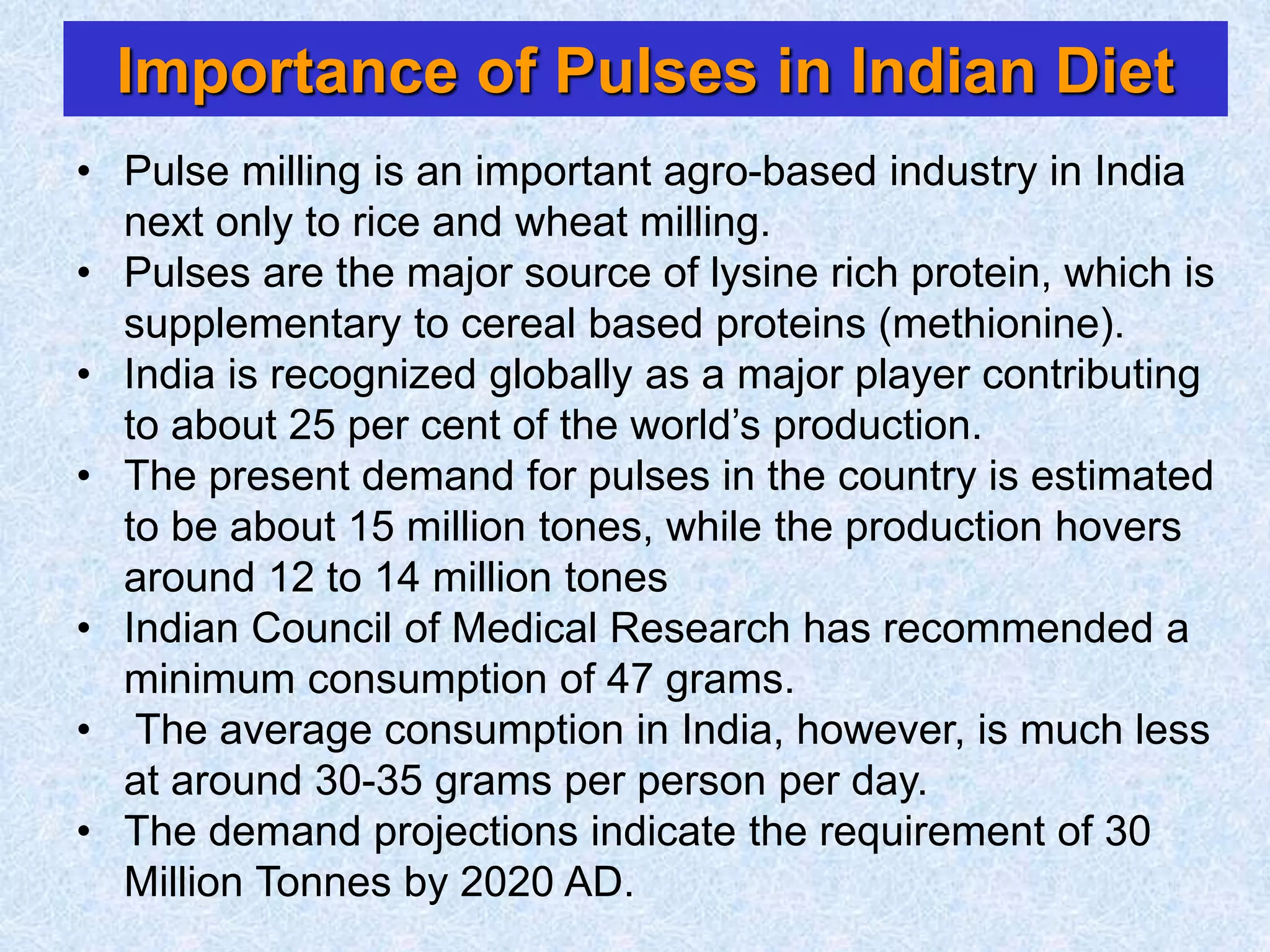
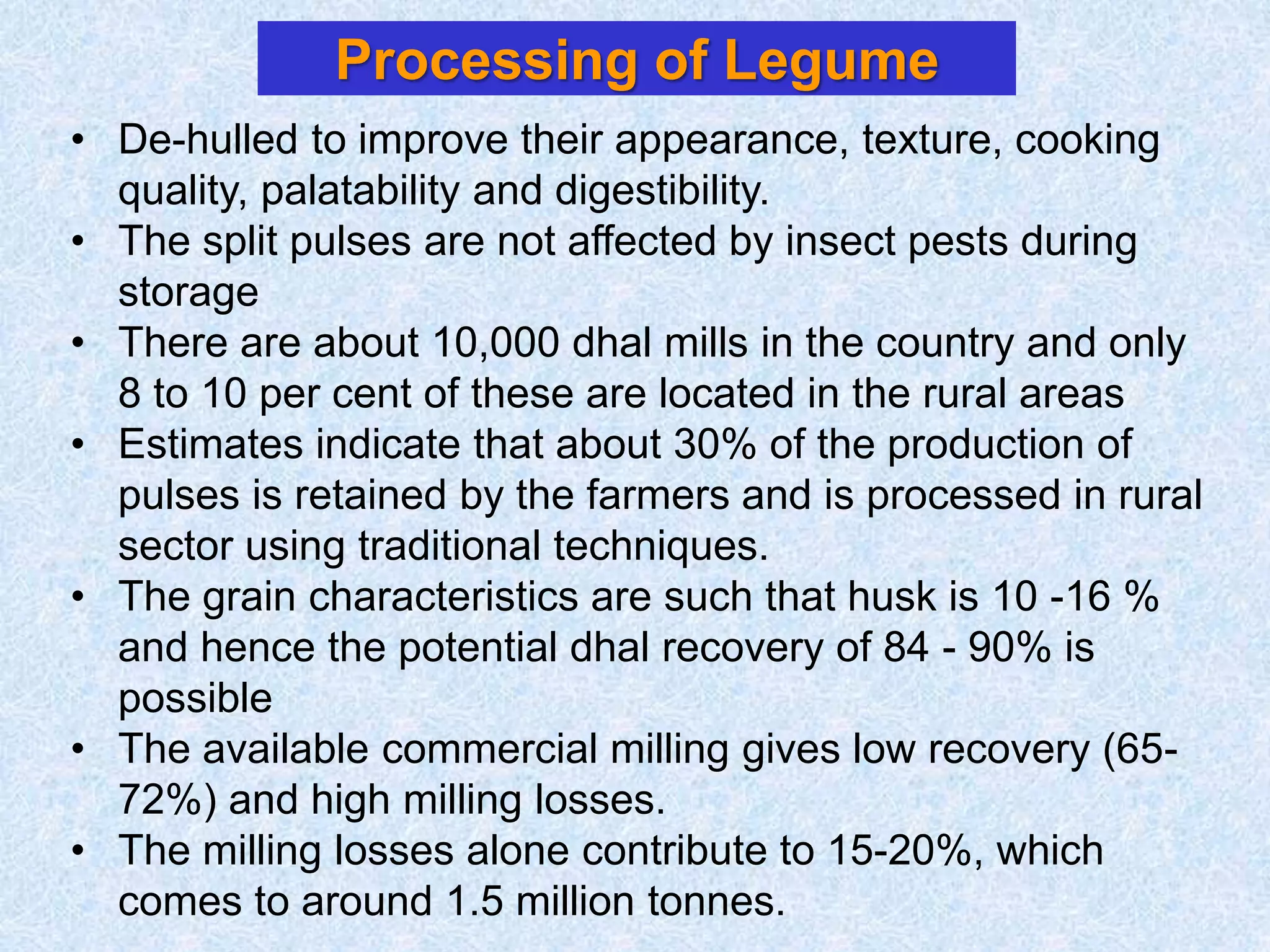
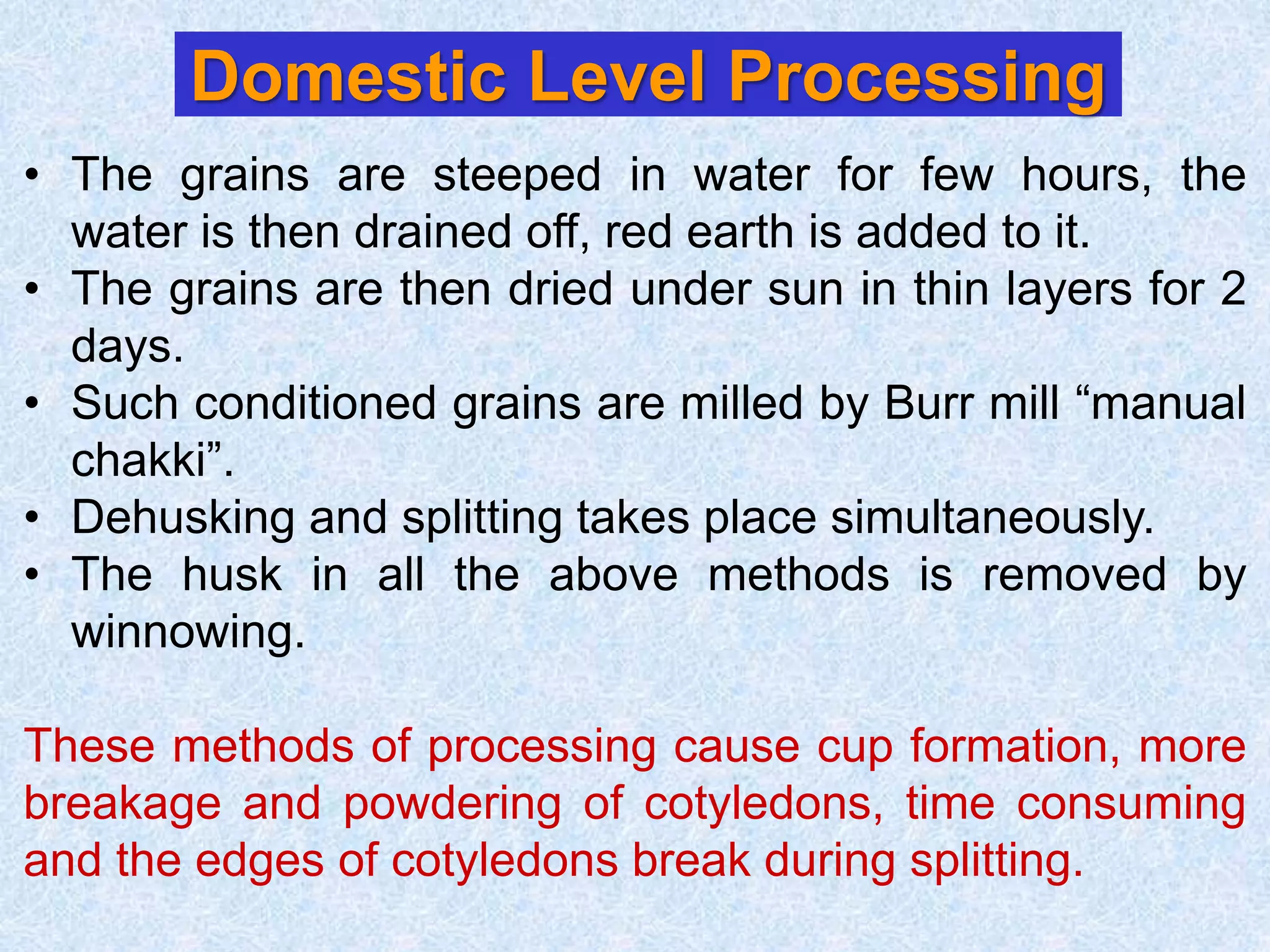
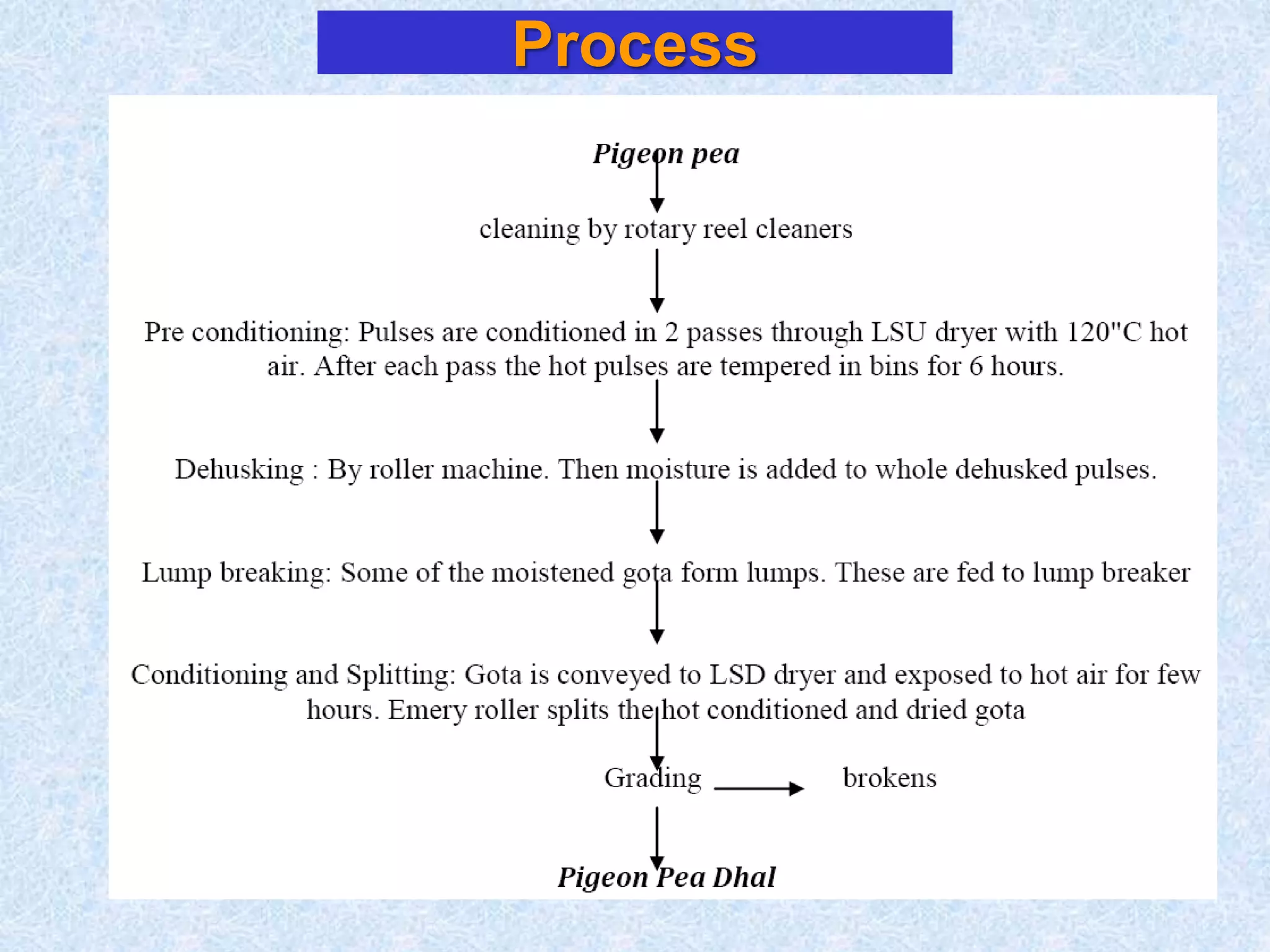
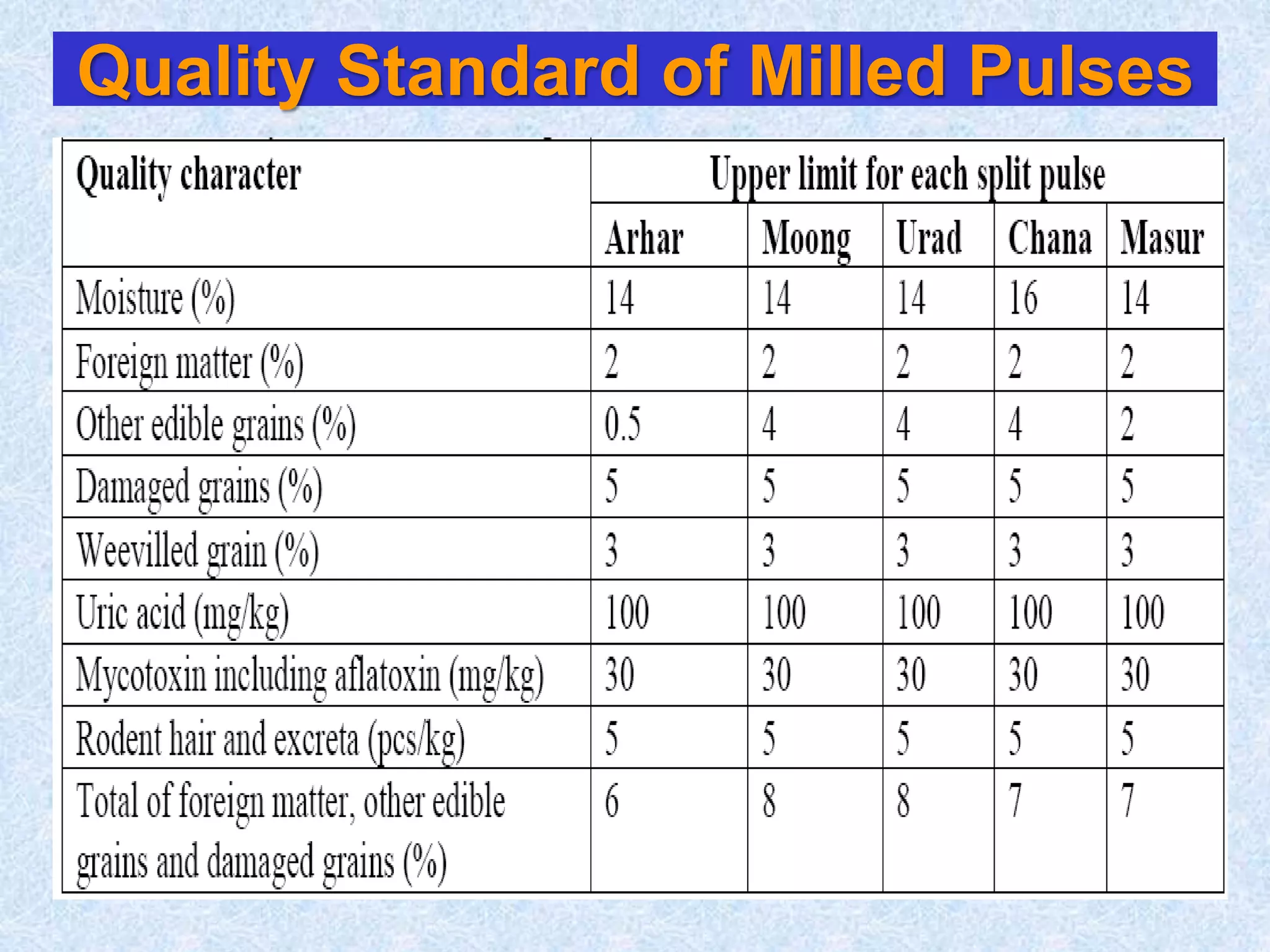
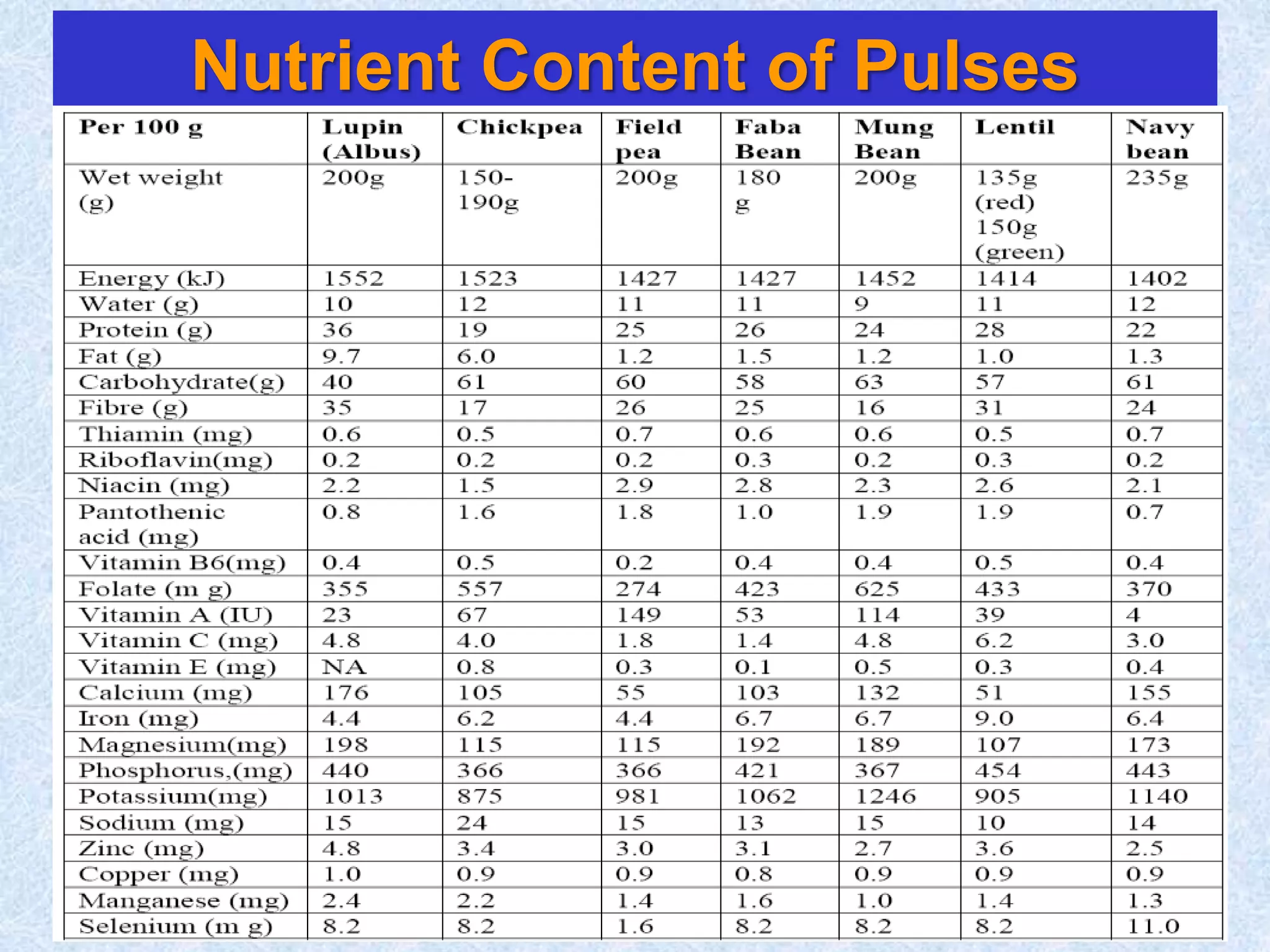
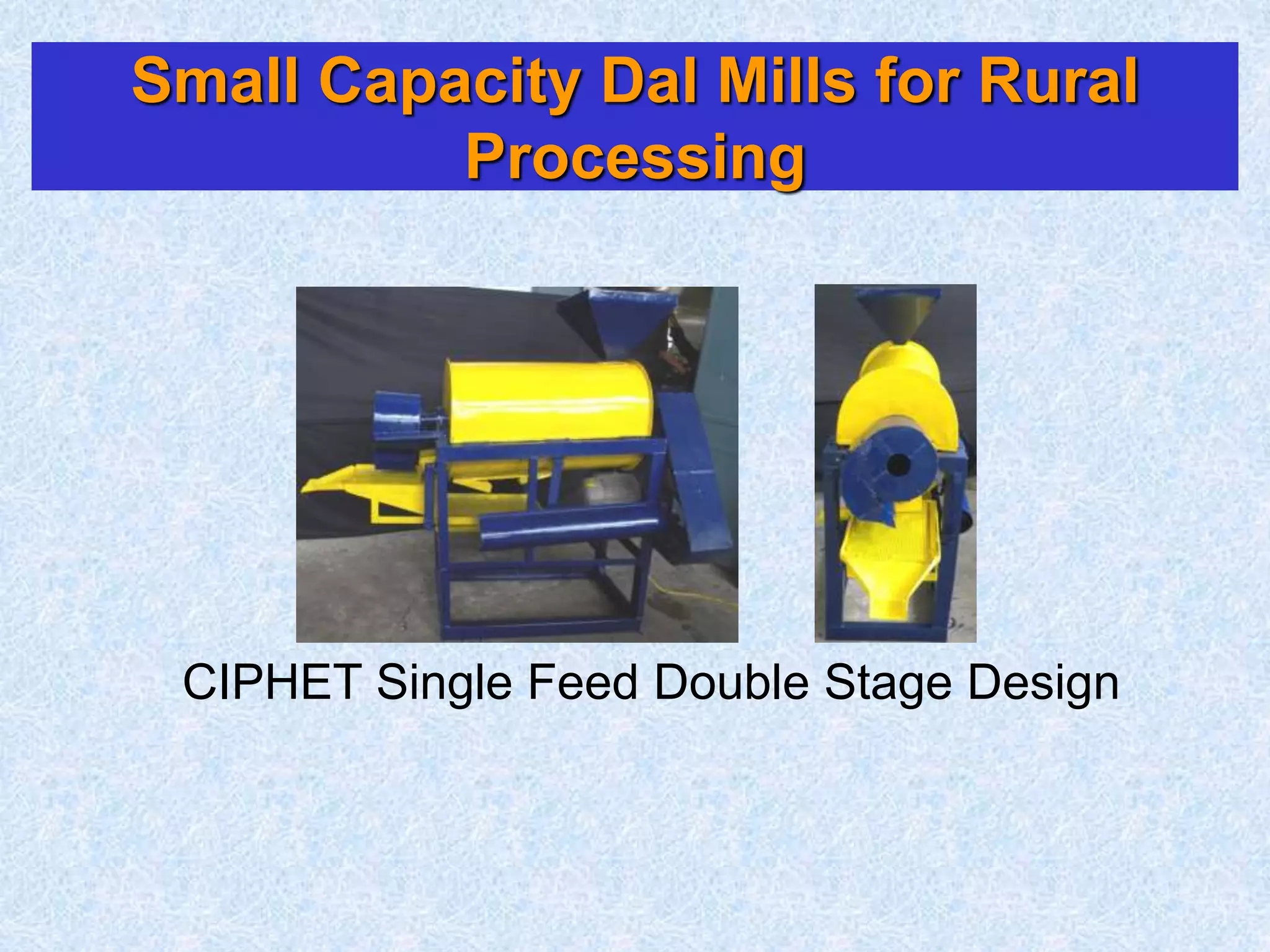
This document discusses various topics related to processing of food grains in India. It provides statistics showing that India's major food grains are cereals like wheat, rice, and millets, as well as pulses. It then covers health benefits and recent trends in processing for some of these crops. For rice, it discusses soft drying, curing, bio-polishing, and various rice-based bakery and snack products. It also summarizes processing techniques and opportunities for millets and pulses in India.