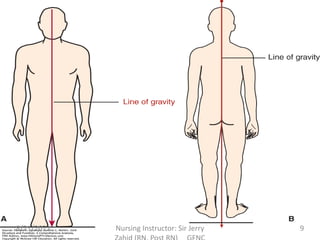
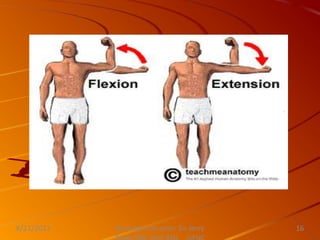
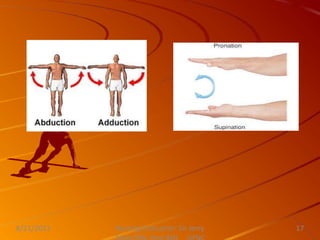
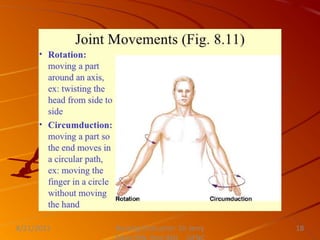
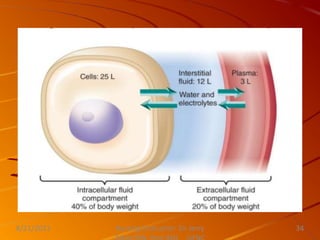
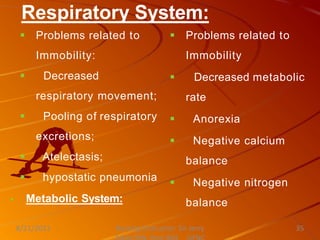
This document discusses activity, exercise patterns, mobility, immobility, and their effects on the body. It begins by defining terms like mobility, joint mobility, and body mechanics. It then discusses the benefits of exercise and factors that affect mobility. Various types of exercises are described, including isotonic, isometric, aerobic, and anaerobic exercises. The document concludes by covering the effects of immobility, such as disuse osteoporosis, atrophy, and cardiovascular problems.