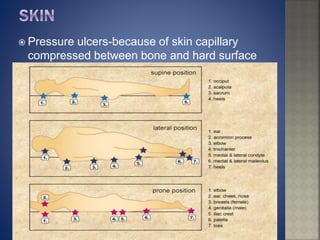
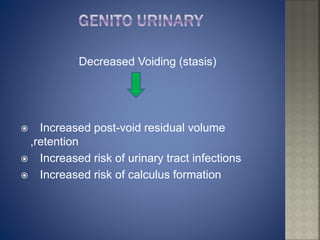
Bed rest and immobilization can lead to serious physical, physiological, and psychological consequences if prolonged. It can cause muscle atrophy, bone loss, joint stiffness, decreased lung function, urinary problems, nutritional deficiencies, depression, and increased risk of infections and pressure ulcers. Prolonged inactivity negatively impacts nearly every body system and functional ability if the individual is not given adequate exercise and range of motion.