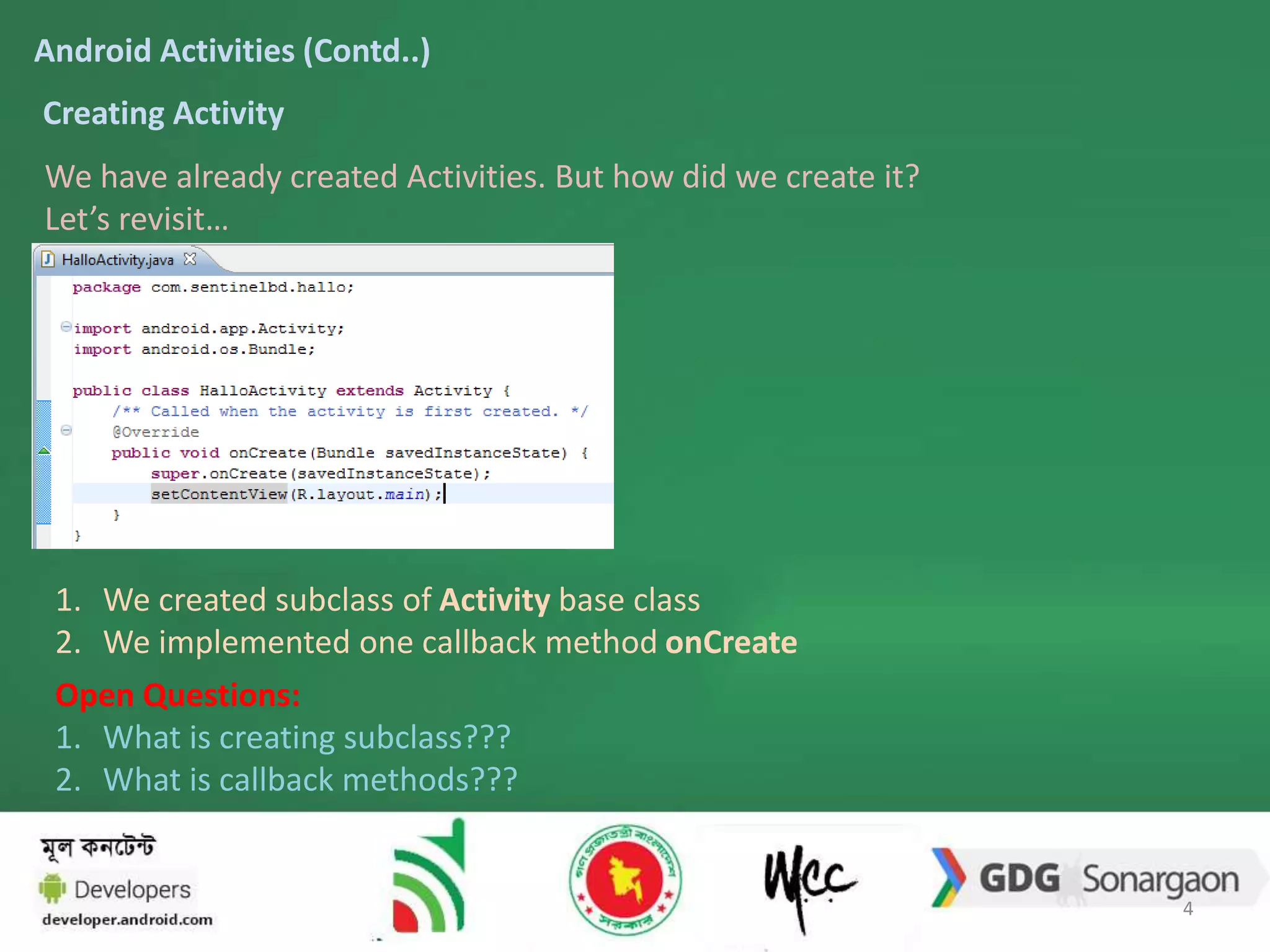
1. The document discusses Android activities, which provide interactive screens for users to perform tasks. Activities are created by subclassing the Activity base class and implementing callback methods like onCreate.
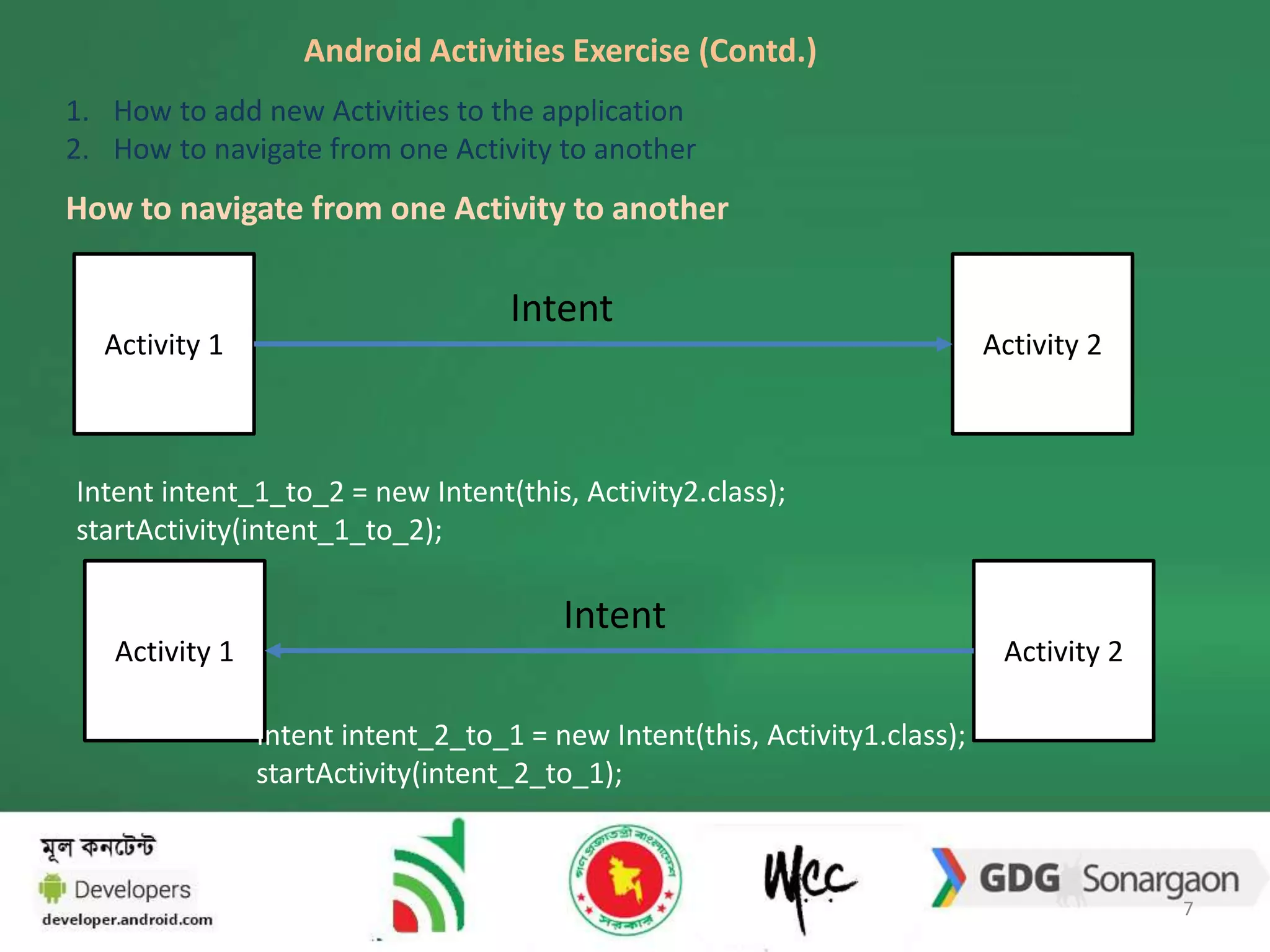
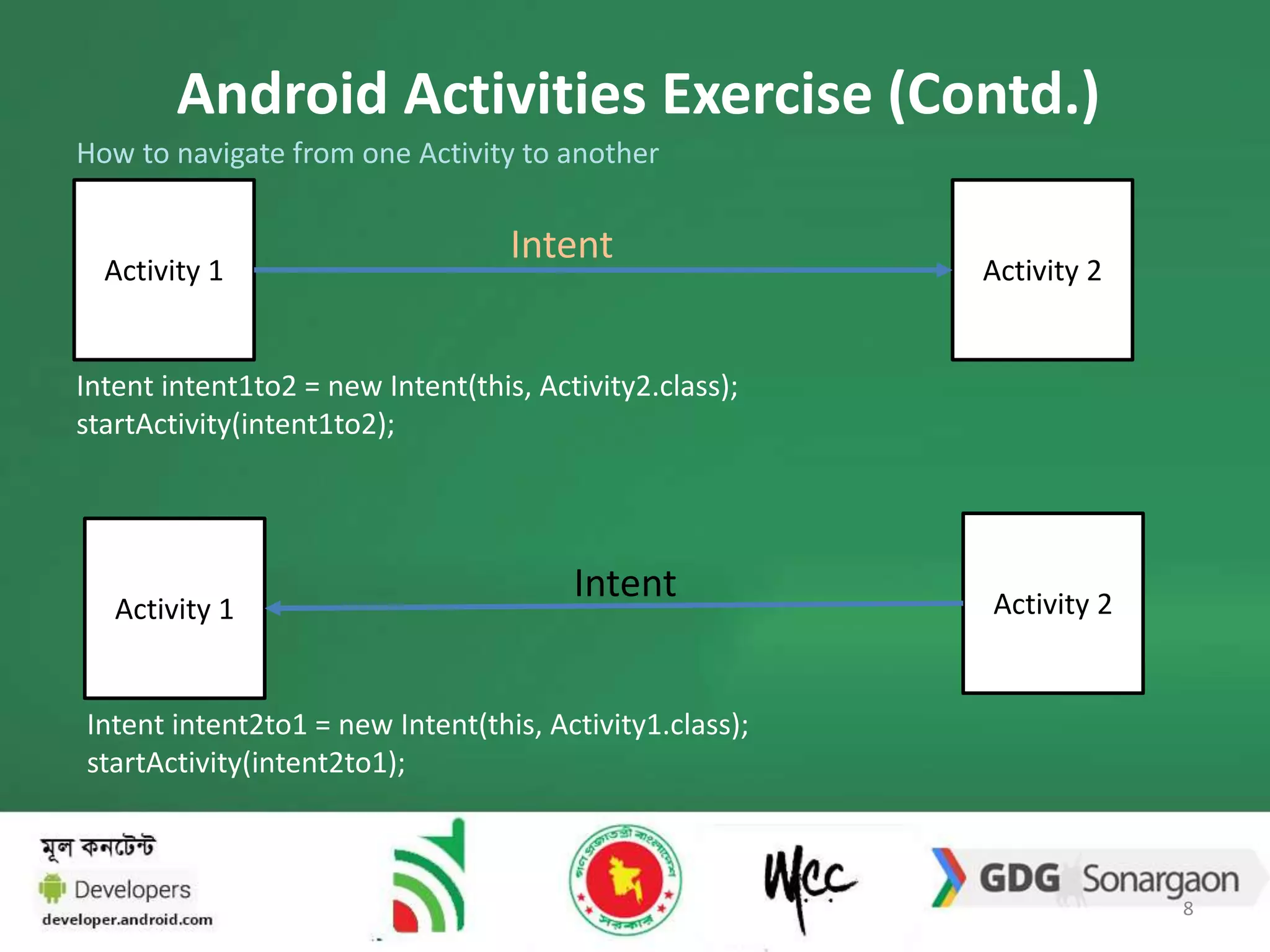
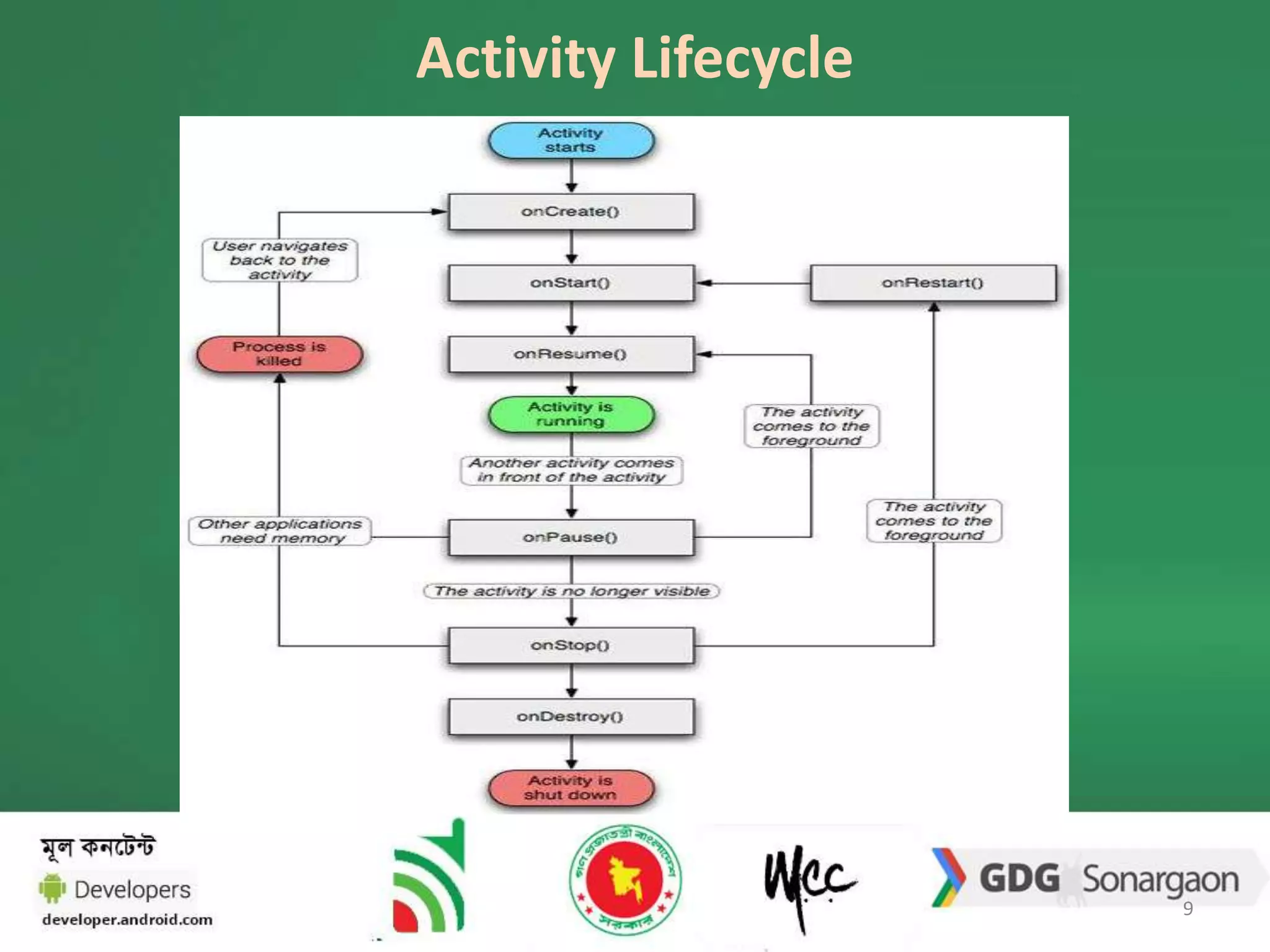
2. The document also discusses how to navigate between activities using intents, and how activities transition through various lifecycle states like onStart and onStop. An example app with registration and login activities is provided to demonstrate navigation between activities.
3. The document explains how to use shared preferences to store persistent data in Android applications. Shared preferences can be accessed via the PreferenceManager and values can be read and written by getting and putting values with keys. An example demonstrates reading a value set in a previous app session.