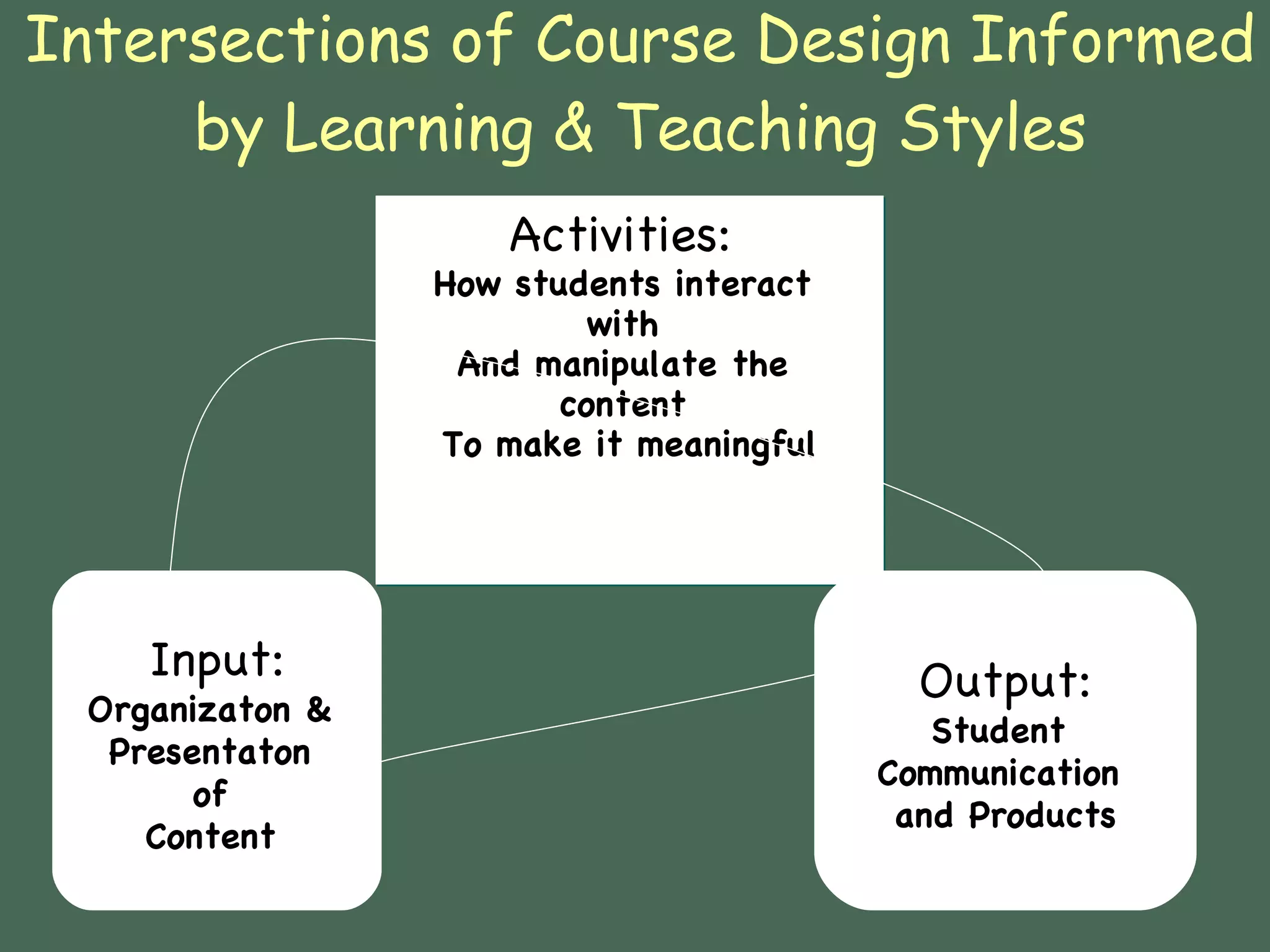
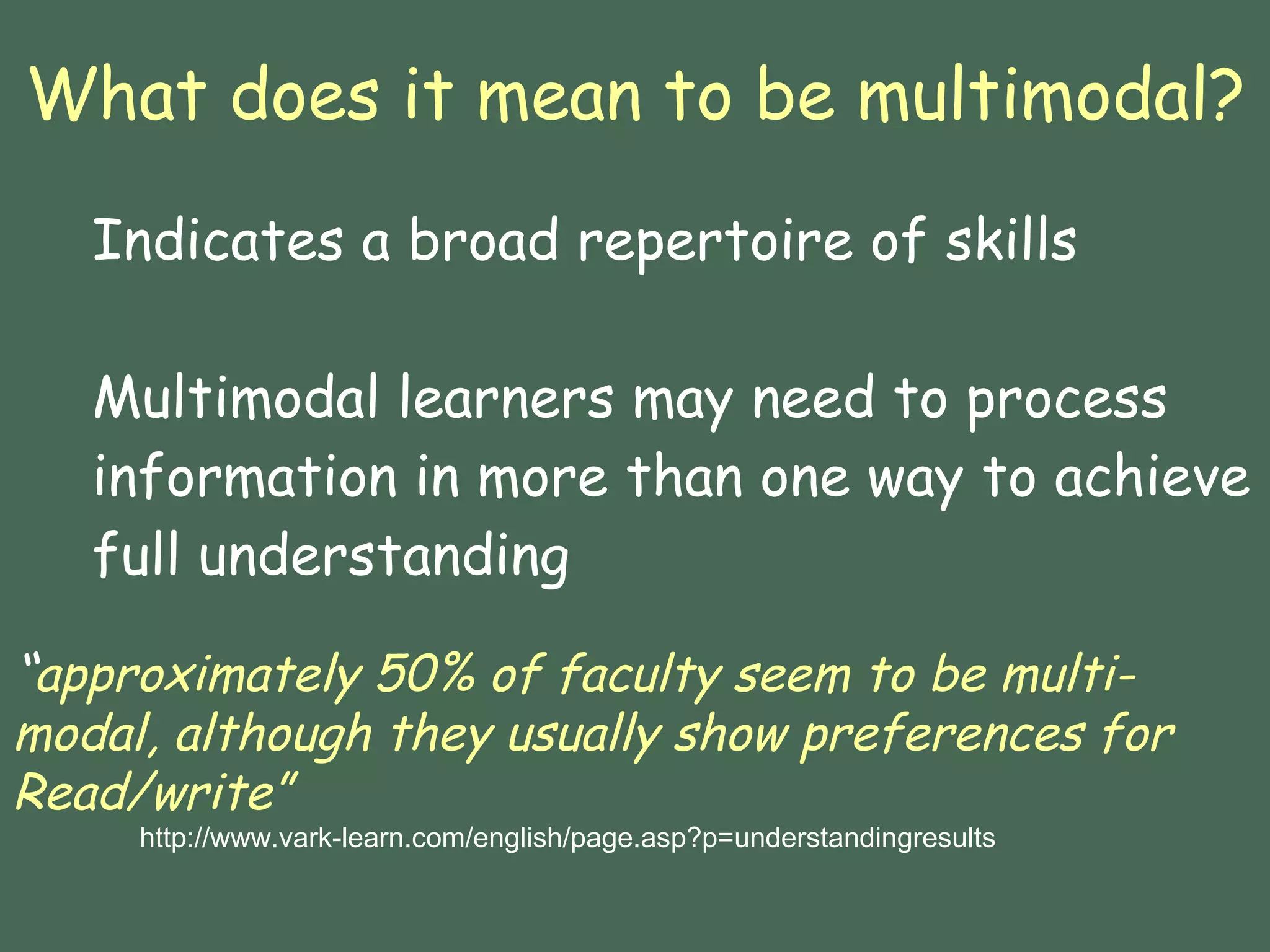
This document discusses how learning styles can inform the design of online courses. It provides an overview of several learning style models, including Grasha's teaching styles, Gardner's multiple intelligences, Felder-Silverman learning styles, and VARK learning styles. The Felder-Silverman model categorizes students as active/reflective, sensing/intuitive, visual/verbal, and sequential/global learners. The document gives tips for designing online content and activities to engage different types of learners based on their preferred styles. It provides examples of exemplary online courses that incorporate varied instructional strategies, activities, and tools to appeal to diverse learning preferences.
![Taking Learning Styles Online Nancy G. Abney, Instructor & Program Manager UAB Graduate School Professional Development Program [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/takinglearningstylesonlinenancyabneyjsa-12549775665687-phpapp01/75/Taking-Learning-Styles-Online-1-2048.jpg)















![Taking Learning Styles Online Nancy G. Abney, Instructor & Program Manager UAB Graduate School Professional Development Program [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/takinglearningstylesonlinenancyabneyjsa-12549775665687-phpapp01/75/Taking-Learning-Styles-Online-19-2048.jpg)