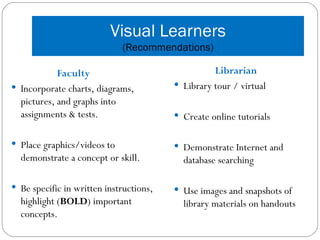
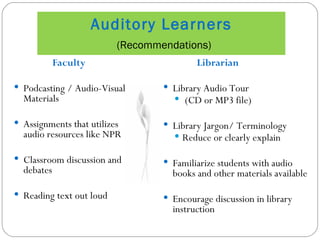
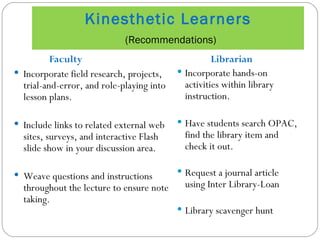
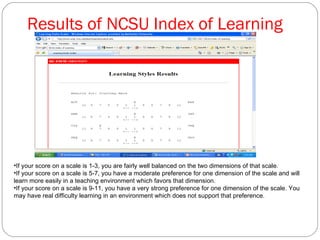
The document discusses various learning styles, including visual, auditory, and kinesthetic, and emphasizes the need for educational institutions to adapt their teaching methods to accommodate these diverse preferences. Recommendations for instructors include utilizing visual aids, audio resources, and hands-on activities to enhance learning experiences. It also references the NC State University Index of Learning Styles for assessing learning preferences and highlights the importance of active learning strategies.