This document discusses paralyzed diaphragm. It begins by describing how diaphragmatic paralysis can occur and the symptoms patients may experience depending on whether it is unilateral or bilateral. Common causes of paralysis include iatrogenic injury, malignancy, and certain medical conditions. Diagnosis involves imaging and tests of diaphragm movement. Treatment depends on a patient's symptoms, with conservative care used for mild cases and diaphragmatic plication surgery considered for more severe symptoms. Bilateral paralysis has a poorer prognosis than unilateral paralysis.
![© 2005 WebMD, Inc. All rights reserved. ACS Surgery: Principles and Practice
4 THORAX 6 PARALYZED DIAPHRAGM — 1
6 PARALYZED DIAPHRAGM
Bryan F Meyers, M.D., F.A.C.S., and Benjamin D. Kozower, M.D.
.
Evaluation of Elevated Hemidiaphragm
Paralysis of the diaphragm is an unusual and challenging clinical compromise. Patients may sleep in a semirecumbent position or in
problem that may occur either in isolation or as part of a systemic the lateral decubitus position with the affected hemidiaphragm
disease. It can be caused by a number of disorders and should be down. Most patients have few respiratory symptoms at rest, but
considered in the differential diagnosis whenever a chest radi- some complain of dyspnea, cough, or chest pain with exertion [see
ograph shows an elevated hemidiaphragm. At one time, diaphrag- Figure 1]. Patients with left-side paralysis may experience GI com-
matic paralysis was generally considered to be a benign condition, plaints resulting from compression of the stomach [see Figure 2].
but it is now clear that many patients experience various pul- In addition, patients may suffer from recurrent pneumonia, bron-
monary, cardiac, and gastrointestinal symptoms. The symptoms chitis, or cardiac arrhythmias.
reported are typically nonspecific, and the correct diagnosis is Bilateral diaphragmatic paralysis, on the other hand, is poorly
often difficult to make. tolerated. Patients with this condition depend more on their acces-
It is helpful to remember that the clinical manifestations of sory muscles of respiration, avoid the supine position, and are
diaphragmatic paralysis are usually explained by the pathophysiol- more prone to chronic respiratory failure.5
ogy. Interruption of the phrenic nerve anywhere between the neck In children, diaphragmatic paralysis may cause severe respirato-
and the diaphragm results in paralysis of the ipsilateral hemidi- ry distress. Compared with adults, children have weaker inter-
aphragm [see Discussion, Diaphragmatic Anatomy, below]. costal muscles, a more compliant chest wall, and a more mobile
Because the diaphragm is a continuous muscular sheet, one might mediastinum. Accordingly, children must depend on their
suppose that paralysis of one side would adversely affect the other. diaphragms to achieve adequate tidal volumes. Unilateral
Actually, the two sides of the diaphragm function independently: diaphragmatic paralysis in a child usually necessitates mechanical
tension from one side is not distributed to the other across the ventilation; bilateral paralysis is often fatal without prompt venti-
central tendon.1 Bilateral diaphragmatic paralysis is rarely encoun- latory support.
tered by the thoracic surgeon. When it does occur, it is usually a
manifestation of neuromuscular or systemic disease. Common Causes of Diaphragmatic Paralysis
The functional effects of hemidiaphragmatic paralysis are simi- As noted (see above), bilateral diaphragmatic paralysis is usual-
lar to but less striking than those of bilateral paralysis [see ly a manifestation of a systemic disease, such as a neuromuscular
Discussion, Normal Diaphragmatic Function, below].2 An elevat- junction disorder, an immunologic phenomenon, or a myopathy.
ed hemidiaphragm compresses the hemithorax and results in a Because thoracic surgeons rarely treat these conditions, the ensu-
restrictive pattern of lung disease. In the seated position, the
patient’s vital capacity and total lung capacity decrease by approx-
imately 20%; in the supine position, vital capacity decreases by
nearly 40%.3 Ventilation and perfusion of the lower lobe are also
reduced on the affected side. Mismatching may widen the alveo-
lar-arterial oxygen difference and produce mild hypoxemia.4
Generally, adults with healthy lungs tolerate these changes well;
however, patients who are obese or have underlying lung disease
are more likely to be symptomatic.
Diaphragmatic paralysis is frequently described in the literature
in conjunction with eventration of the diaphragm. Eventration is a
condition in which all or a portion of one hemidiaphragm is per-
manently elevated while retaining its continuity and its normal
attachments to the costal margins. Although eventration and uni-
lateral paralysis are technically different, they often give rise to the
same physiologic disturbances and radiographic findings.
Clinical Evaluation
HISTORY
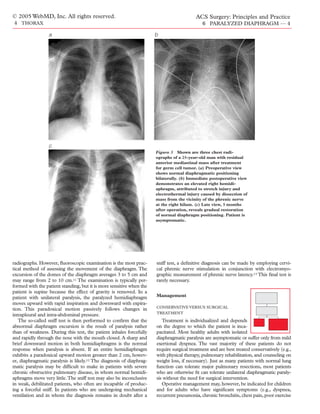
Figure 1 Shown is a postoperative radiograph from a 55-year-
In adults, the clinical presentation of uni- old woman who underwent left upper lobectomy. Because the
lateral paralysis of the diaphragm is highly tumor was directly adherent to the phrenic nerve, a 2 cm portion
variable. Right and left hemidiaphragmatic of the left phrenic nerve was resected along with the tumor.
paralysis seem to occur with equal frequency Recovery was uneventful, and the only late symptom was mild
and usually cause little or no respiratory dyspnea with exertion.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acs0406-paralyzeddiaphragm-100726063213-phpapp02/85/Acs0406-Paralyzed-Diaphragm-1-320.jpg)
![© 2005 WebMD, Inc. All rights reserved. ACS Surgery: Principles and Practice
4 THORAX 6 PARALYZED DIAPHRAGM — 3
inite connection between the two has not been established.
The outcome of phrenic nerve injury incurred during cardiac
surgery has been well studied. In many cases, the injured phrenic
nerves recover; typical recovery times for diaphragmatic function
range from 6 months to 2 years.6,8 In 20% of cases, however, the
injury is permanent [see Figure 3]. Although morbidity is usually
minimal, bilateral diaphragmatic paralysis after cardiac surgery
has occasionally resulted in death. It should be kept in mind that
diaphragmatic paralysis after cardiac surgery is a more serious
problem in children than in adults. In pediatric patients, phrenic
nerve injury usually results in respiratory distress, which may pre-
vent weaning from mechanical ventilation.9
In current usage, the term iatrogenic phrenic nerve injury refers
to either (1) unintentional injury to the nerve during an operation
or (2) intentional resection of the nerve to permit complete exci-
sion of a chest neoplasm. In the past, however, phrenic nerve
injury was sometimes deliberately induced to elevate or disable a
hemidiaphragm for therapeutic purposes, either permanently or
temporarily. Therapeutic phrenic nerve paralysis was originally
achieved by crushing the nerve at the level of the diaphragm with
Figure 2 Shown is a postoperative radiograph of a 70-year-old a surgical clamp; subsequently, temporary paralysis was achieved
man who underwent left upper lobectomy for removal of a periph- by exposing the phrenic nerve in the neck and infiltrating the area
eral 3 cm lesion. The phrenic nerve was injured with the electro- around it with local anesthetics. This technique was employed in
cautery during mediastinal lymph node dissection. The radi- the treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis and was occasionally
ograph shows permanent elevation of the left hemidiaphragm
performed to elevate a hemidiaphragm and help obliterate a diffi-
with gastric bloating 3 years after operation. The patient is neither
dyspneic nor dyspeptic and does not require surgical intervention.
cult pleural space problem. It must be emphasized that in current
practice, therapeutic phrenic nerve paralysis is of historic interest
only. It is never necessary, and it is no longer considered appro-
ing discussion focuses on conditions associated with isolated priate or beneficial.
diaphragmatic paralysis [see Table 1].The two most common caus-
es of unilateral diaphragmatic paralysis are (1) iatrogenic injury Malignancy involving phrenic nerve Neoplastic involve-
after a cardiothoracic or cervical procedure and (2) malignancy. ment of the phrenic nerve accounts for one third of cases of
diaphragmatic paralysis.10 Bronchogenic carcinomas are the
Injury to phrenic nerve Common mechanisms of phrenic lesions that most commonly affect the phrenic nerve, and paraly-
nerve injury during cardiac procedures include stretching, crush- sis is usually secondary to mediastinal lymph node involvement or
ing, transection, and hypothermia. During the mid-1980s, topical direct mediastinal invasion by central tumors. Other mediastinal
ice slush was frequently employed in cardiopulmonary bypass pro- tumors that may affect the phrenic nerve include thymomas, lym-
cedures, and this practice dramatically increased the incidence of phomas, and germ cell tumors. It is reassuring to note that in
phrenic nerve injury. After cooling jackets replaced topical ice slush patients with unilateral diaphragmatic paralysis of no clear origin,
in this setting, the incidence of elevated hemidiaphragms fell from malignancy turns out to be the cause in fewer than 5% of cases.
23% to 2%.6,7 It has been suggested that harvesting the internal Although patients with unexplained diaphragmatic paralysis are
mammary artery may contribute to phrenic nerve injury, but a def- unlikely to have an occult malignancy, they are also unlikely to
recover their diaphragmatic function.10
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
Table 1—Causes of Isolated Diaphragmatic Patients with diaphragmatic paralysis may be asymptomatic or
Paralysis may present with some of the nonspecific clinical findings men-
tioned (see above). Physical examination usually reveals decreased
Idiopathic paralysis
Phrenic neuropathy
breath sounds on the affected side, a mediastinal shift during inspi-
Phrenic nerve injury ration, or a scaphoid abdomen. Percussion may demonstrate an
Iatrogenic elevated hemidiaphragm with decreased excursion on inspiration.
Malignancy (invasion or compression)
Trauma
Therapeutic (tuberculosis) Investigative Studies
Mononeuritis In the majority of cases, an asympto-
Viral infection (Guillain-Barré syndrome) matic person is referred to the surgeon
Vasculitis
because a chest radiograph demonstrates
Diabetes
an elevated hemidiaphragm. It is impor-
Connective tissue disease
Anterior horn cell lesions
tant to remember that there is a broad dif-
Herpes zoster ferential diagnosis for an elevated hemidi-
Poliomyelitis aphragm and that diaphragmatic paralysis
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is relatively rare [see Table 2].
Workup usually begins with inspiratory and expiratory chest](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acs0406-paralyzeddiaphragm-100726063213-phpapp02/85/Acs0406-Paralyzed-Diaphragm-3-320.jpg)