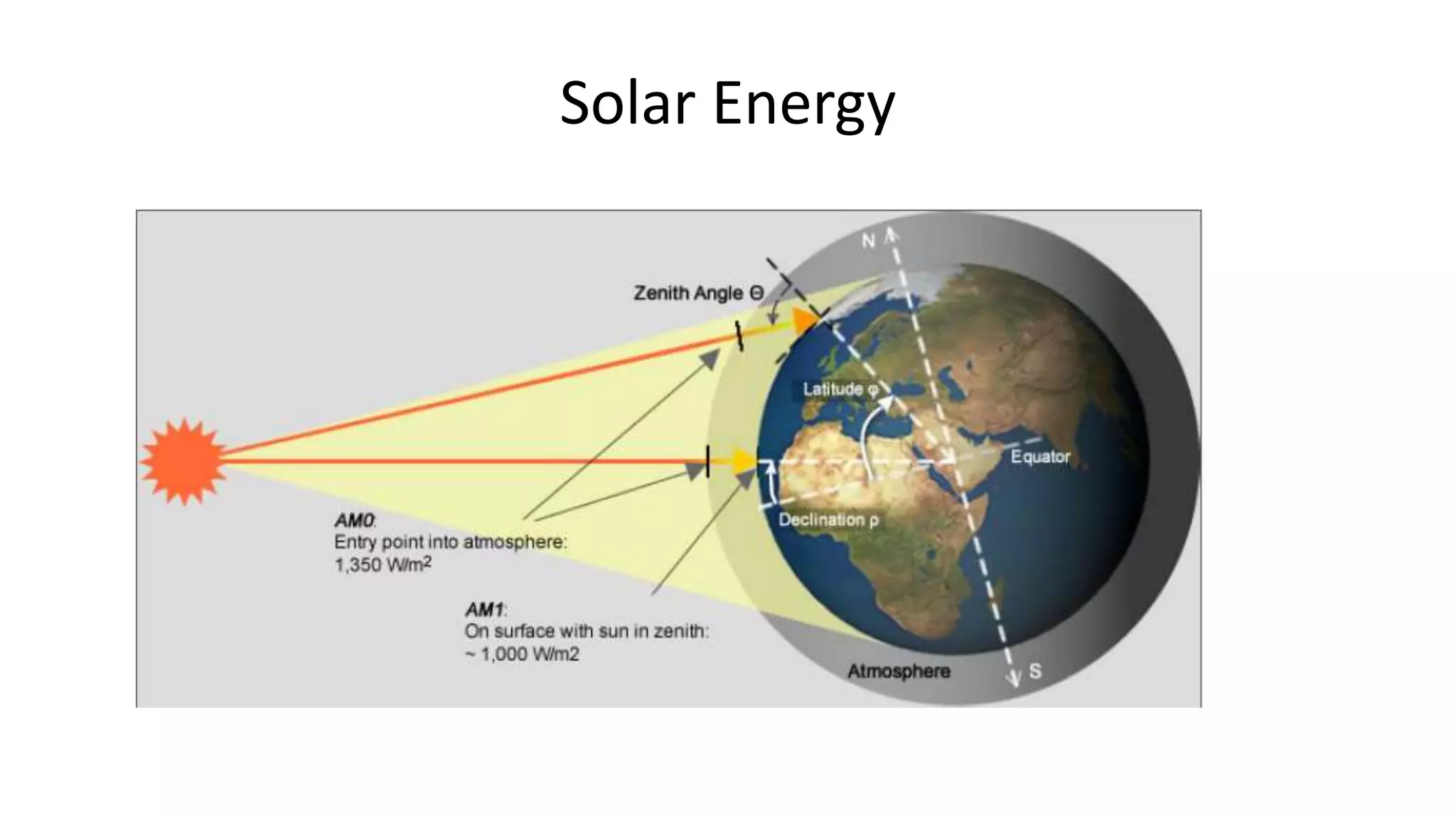
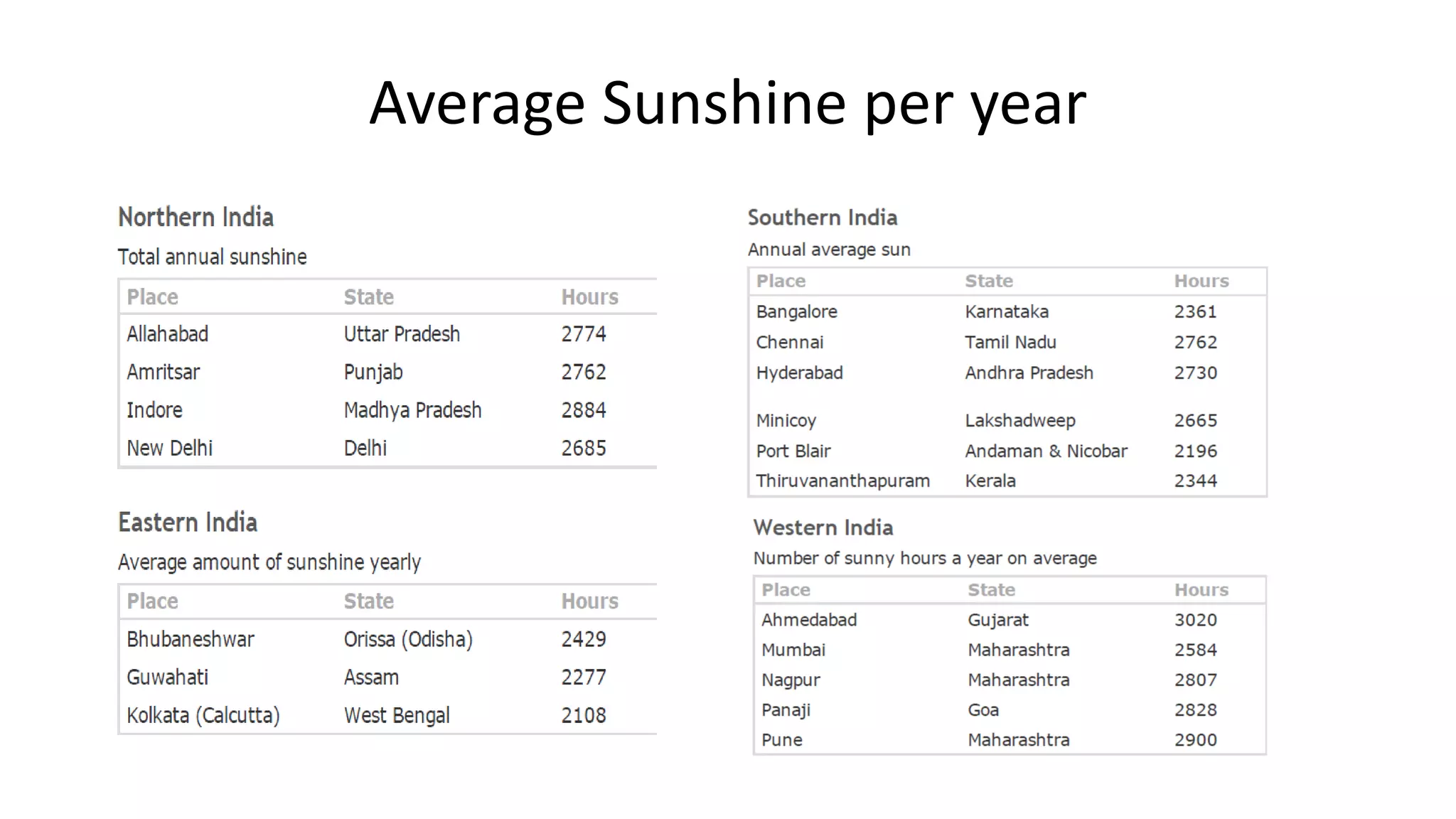
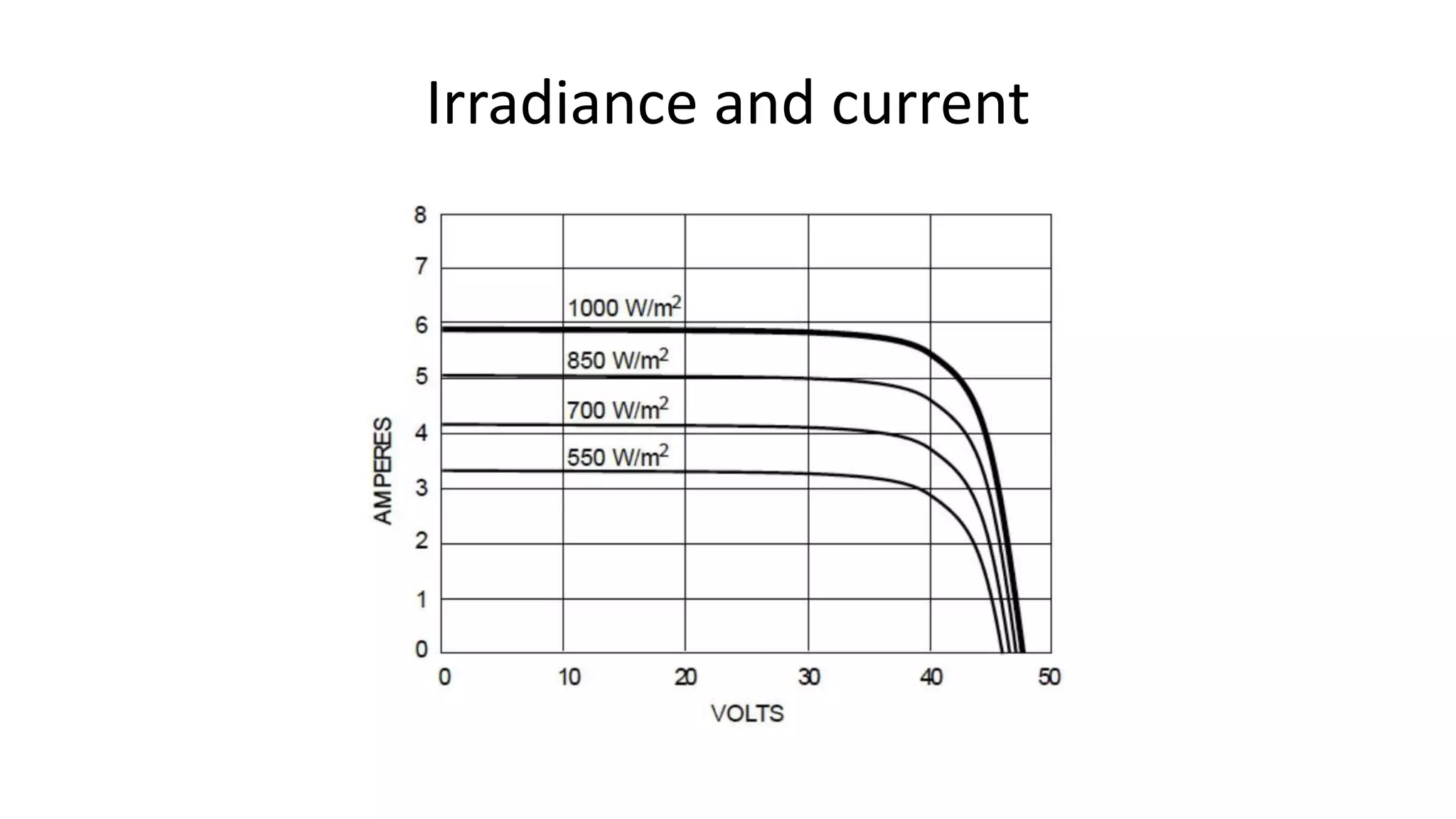
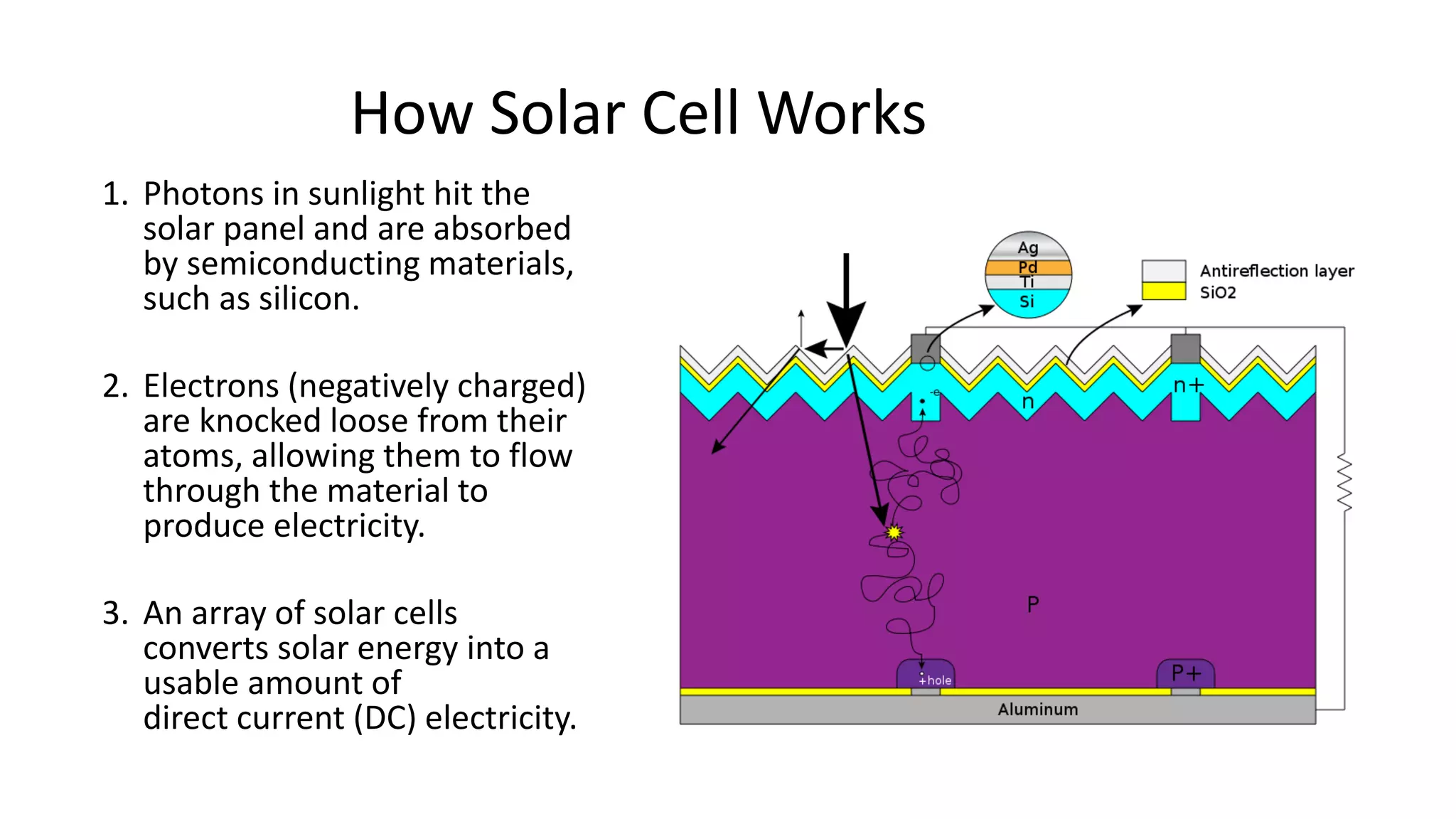
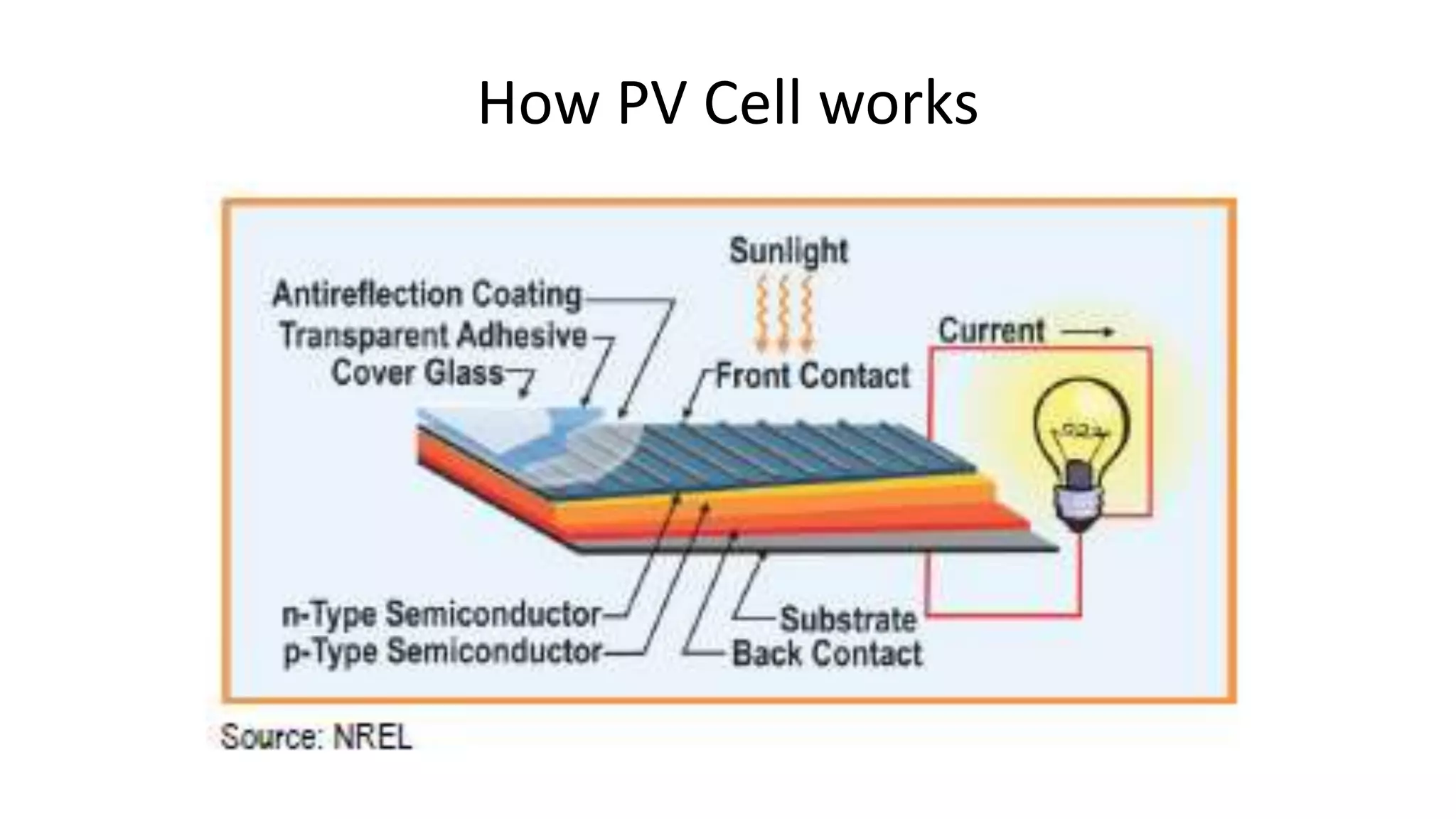
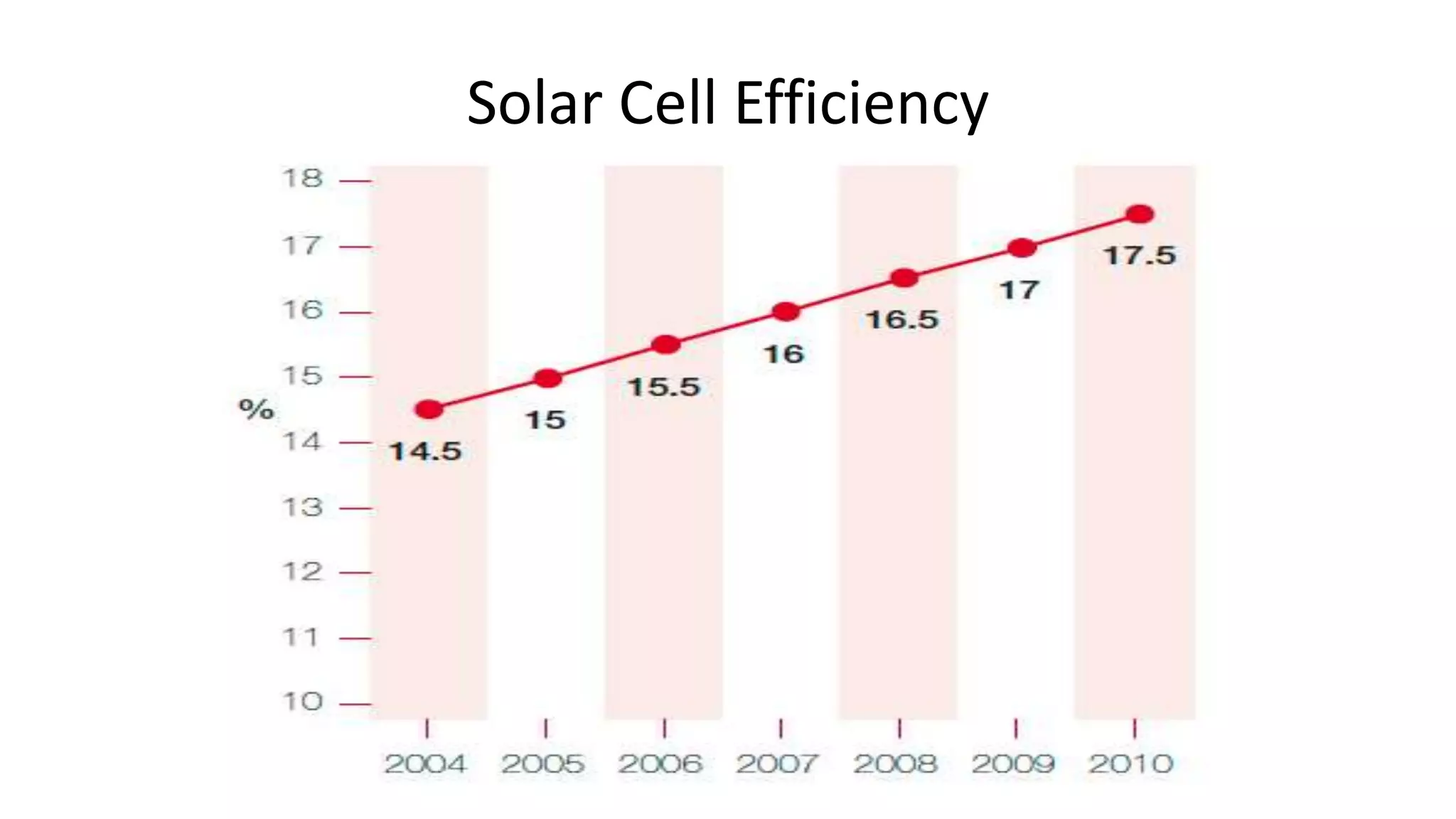
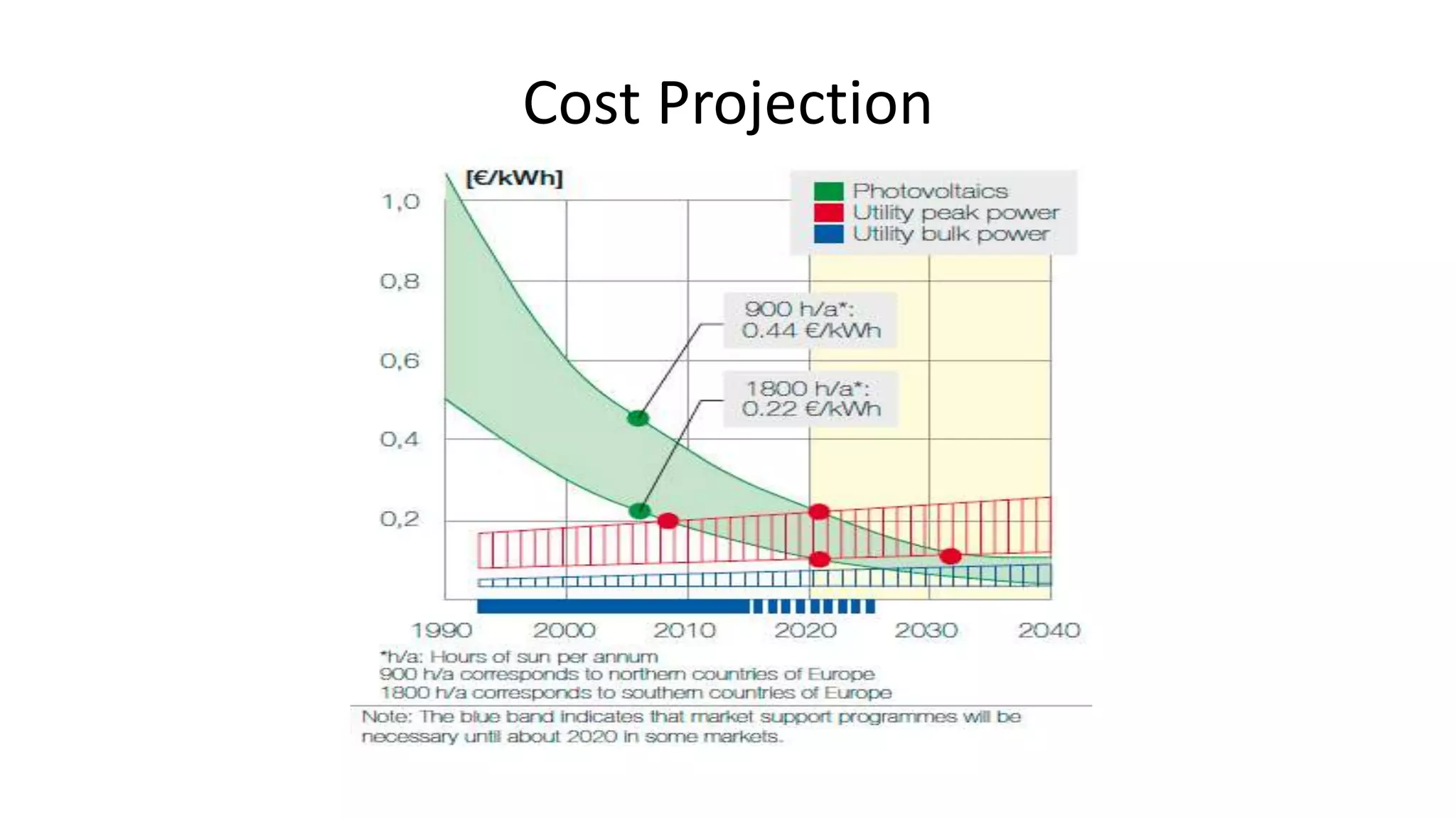
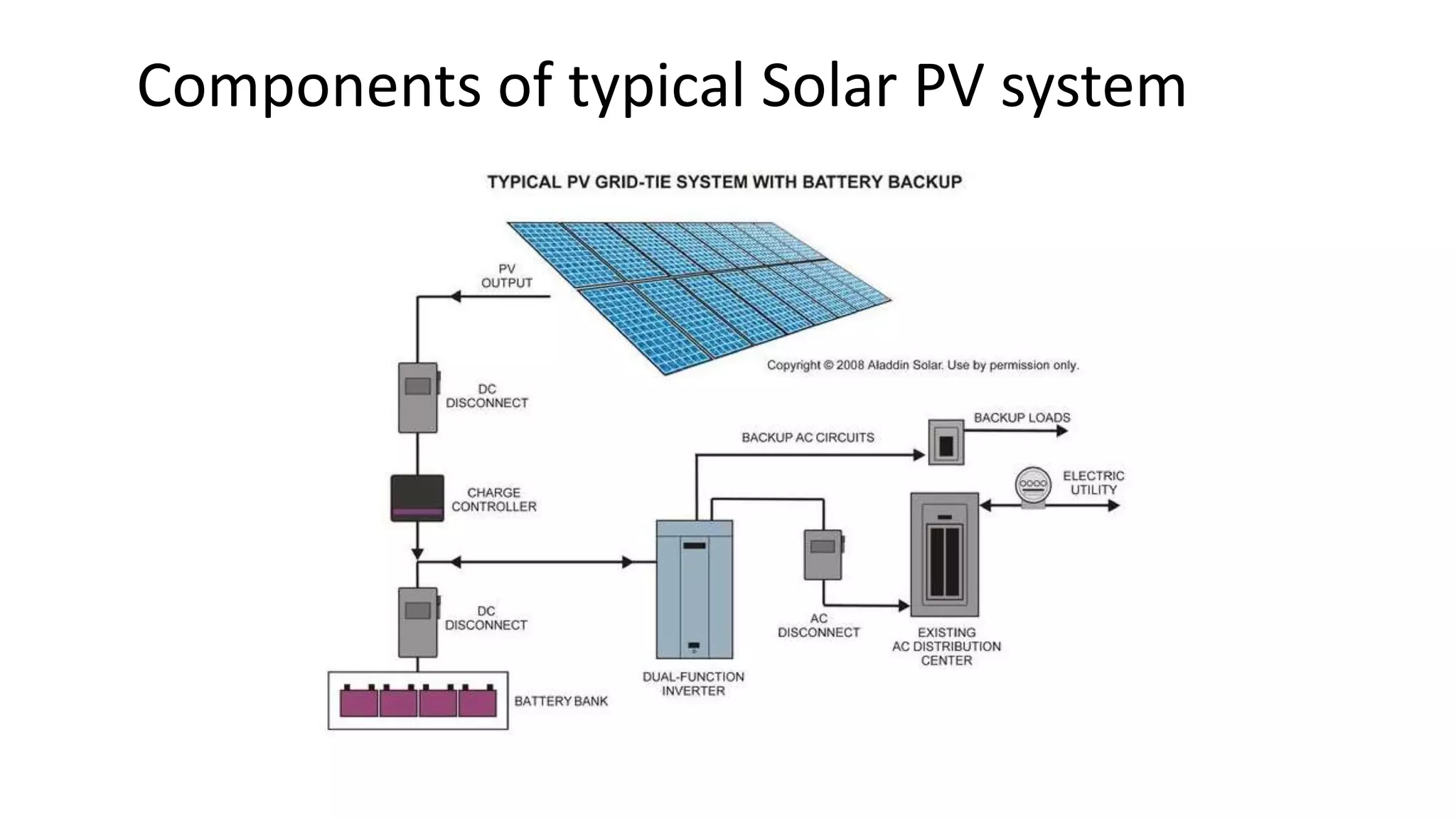
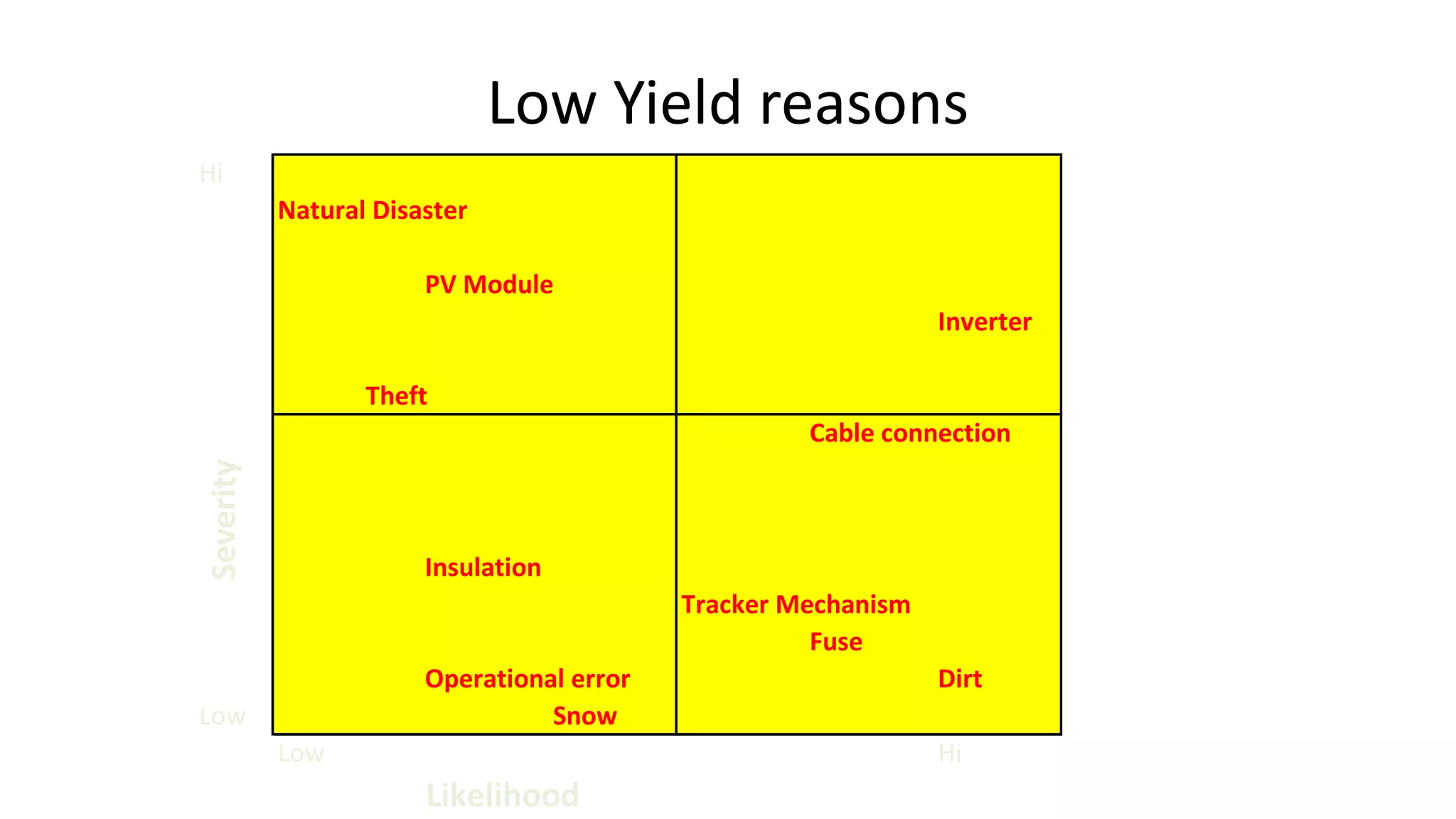
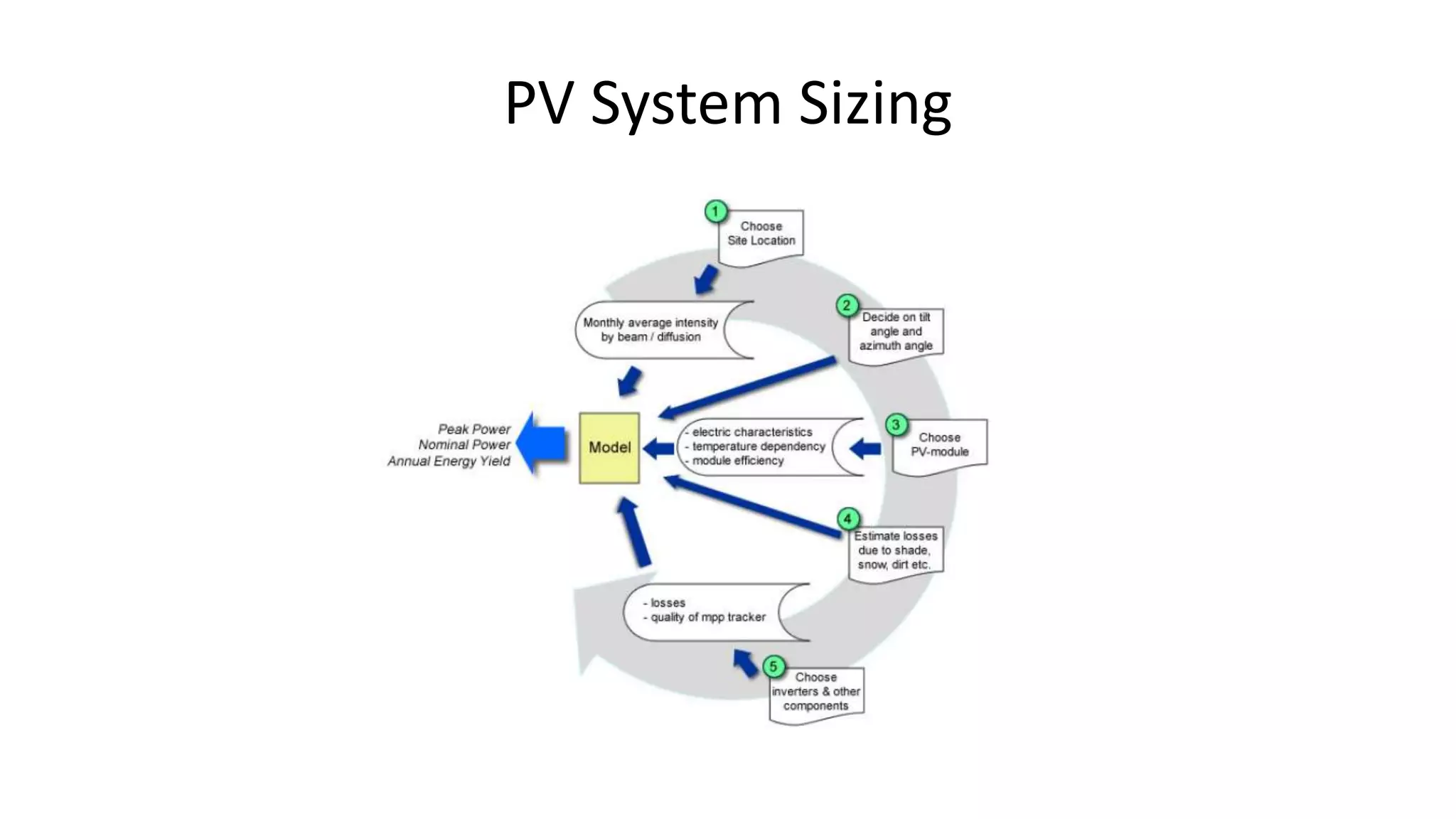
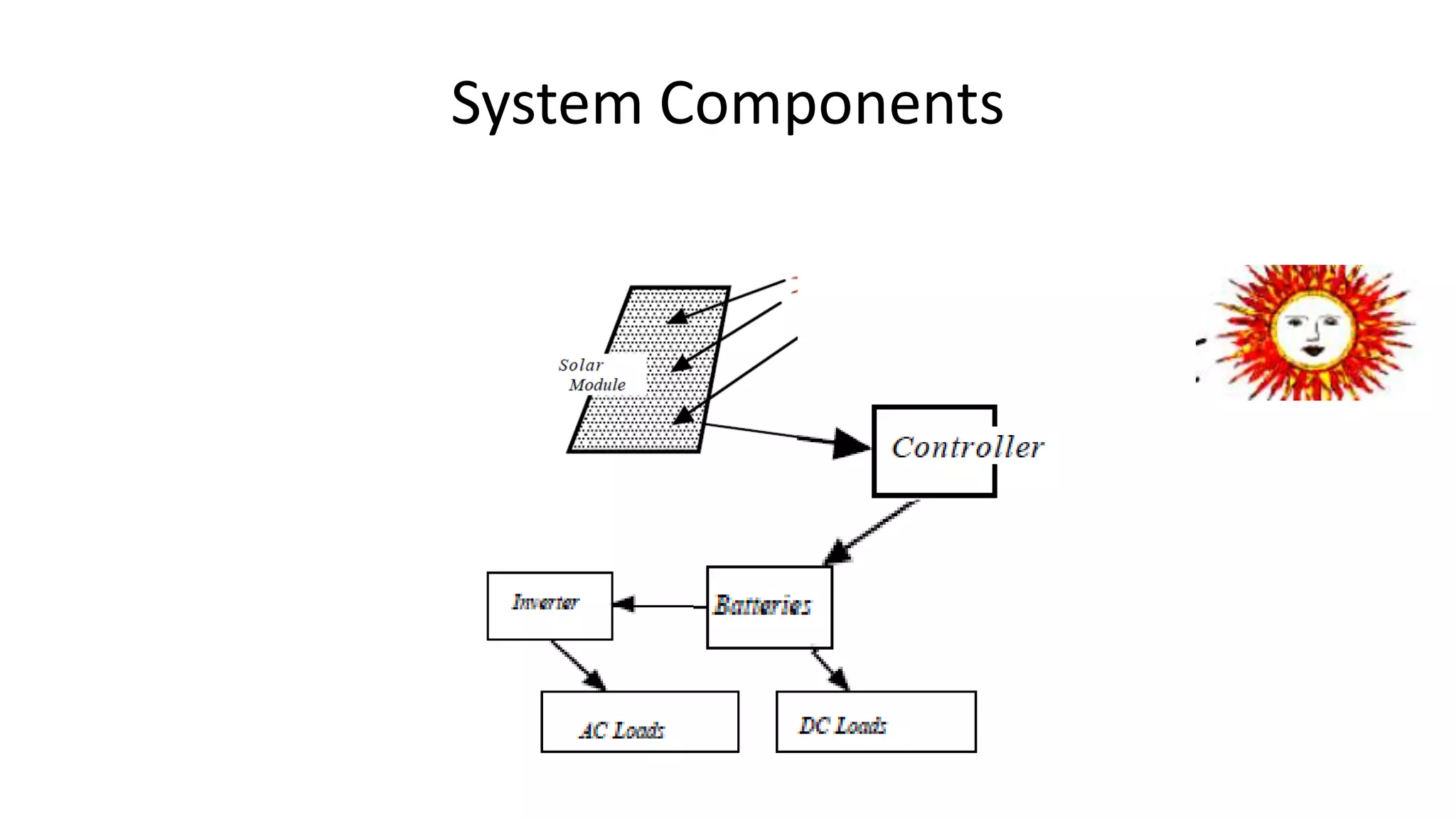
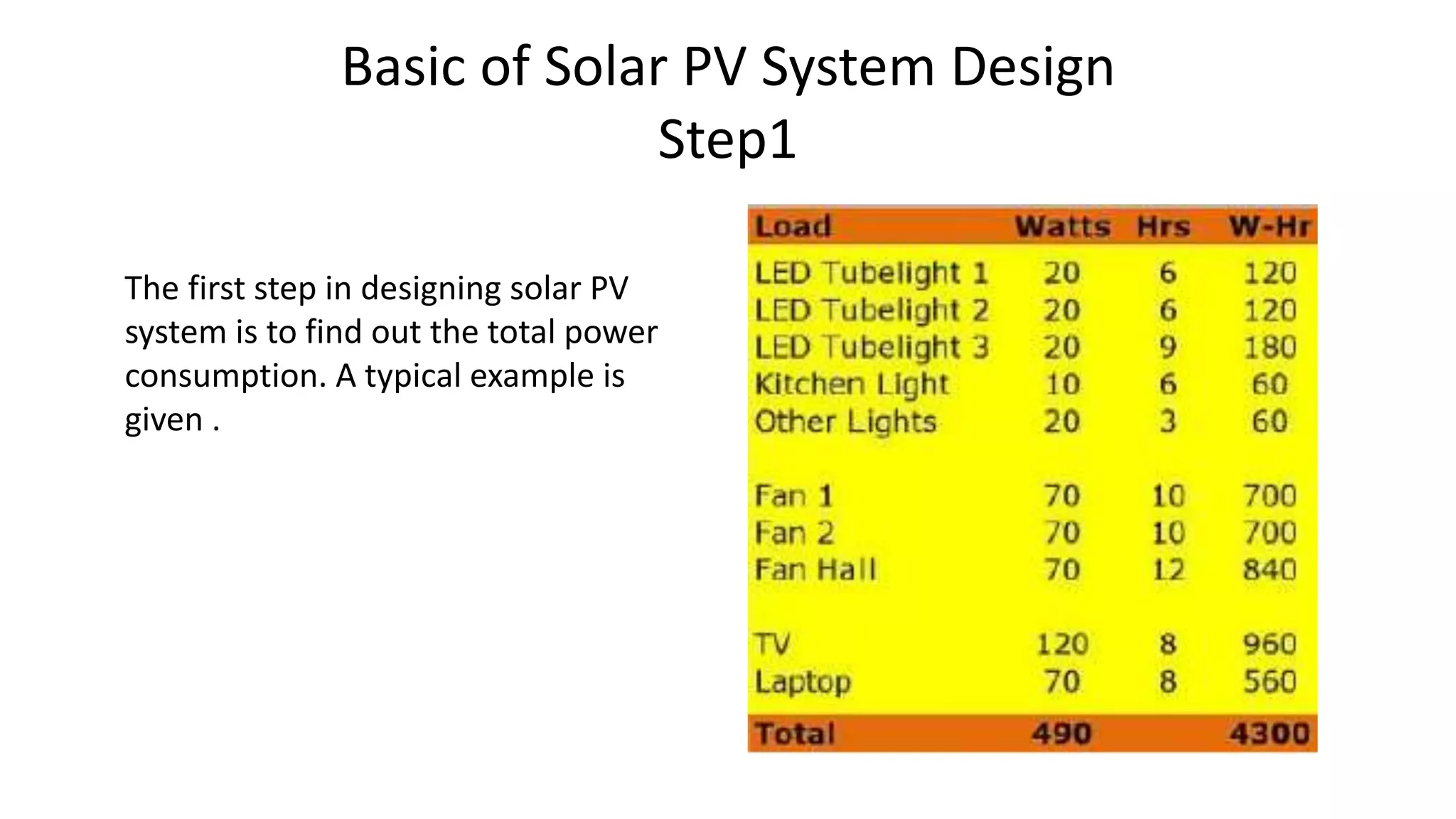
Acorn Solar provides a comprehensive overview of solar energy, detailing its origins from the sun's fusion reactions, its environmental benefits, and historical developments in solar technology. The document highlights the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of solar panels, particularly for underserved communities lacking electricity. It concludes with information about Acorn Solar's customer-focused approach and transparent practices in promoting solar energy solutions.