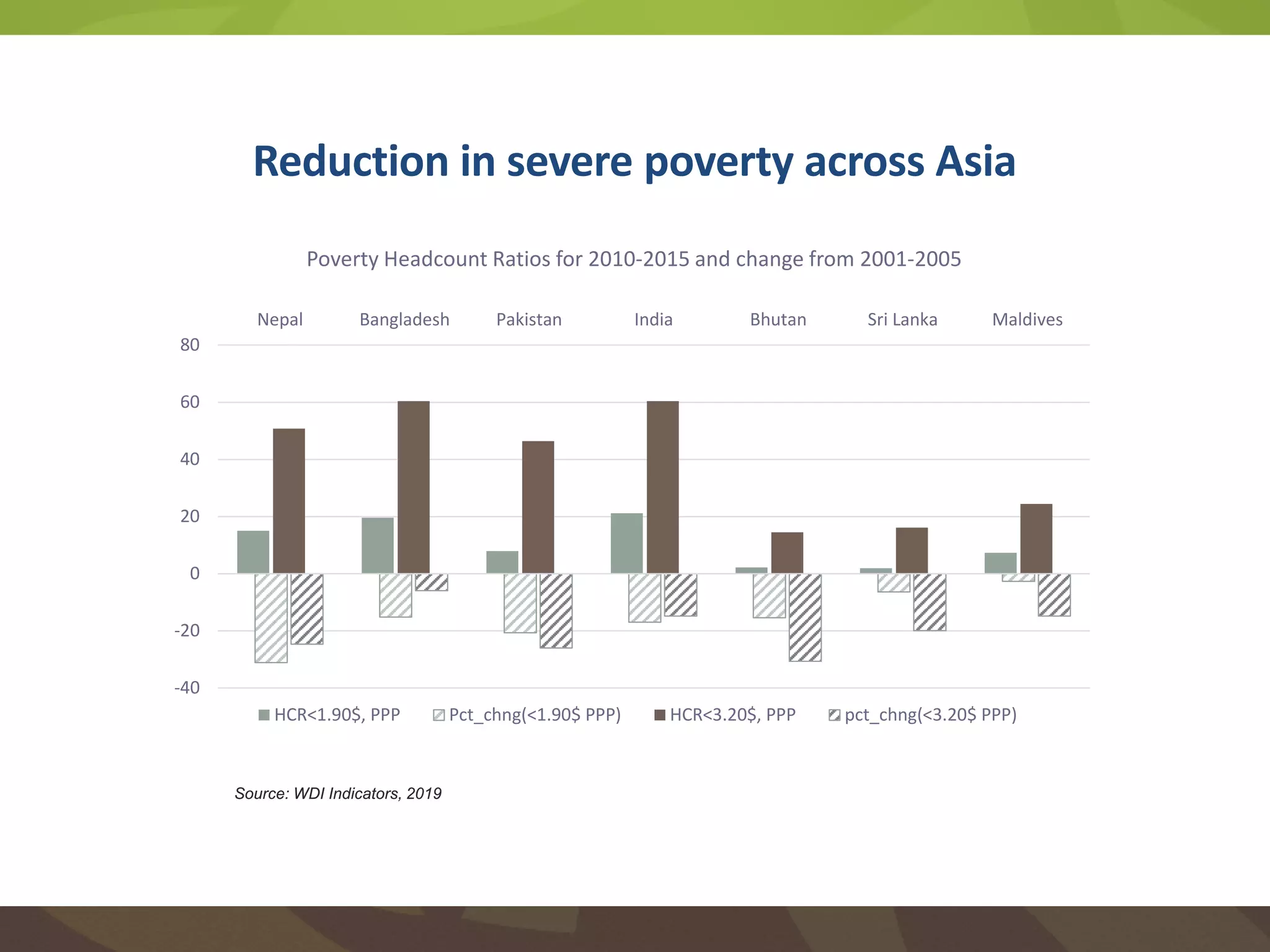
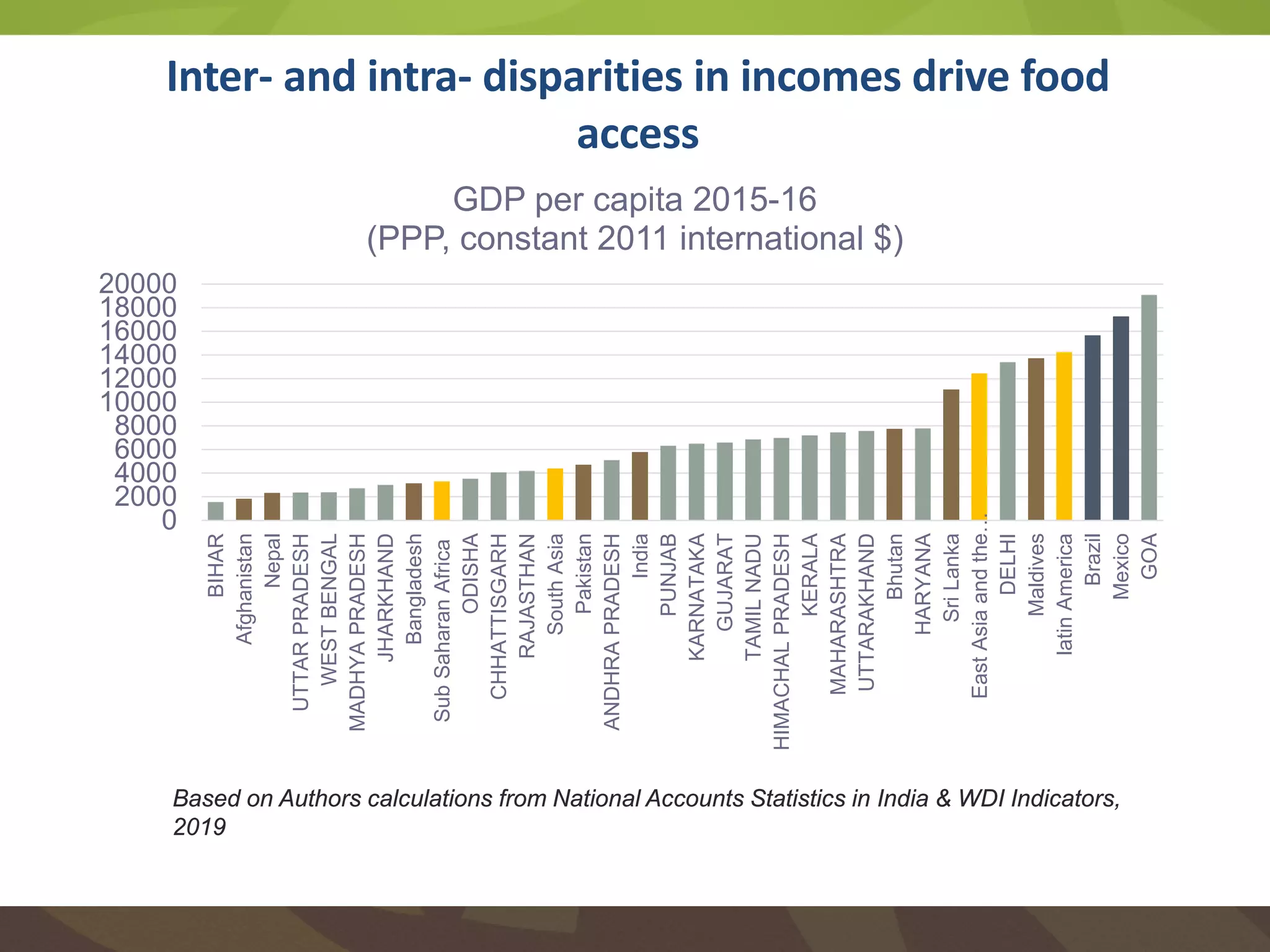
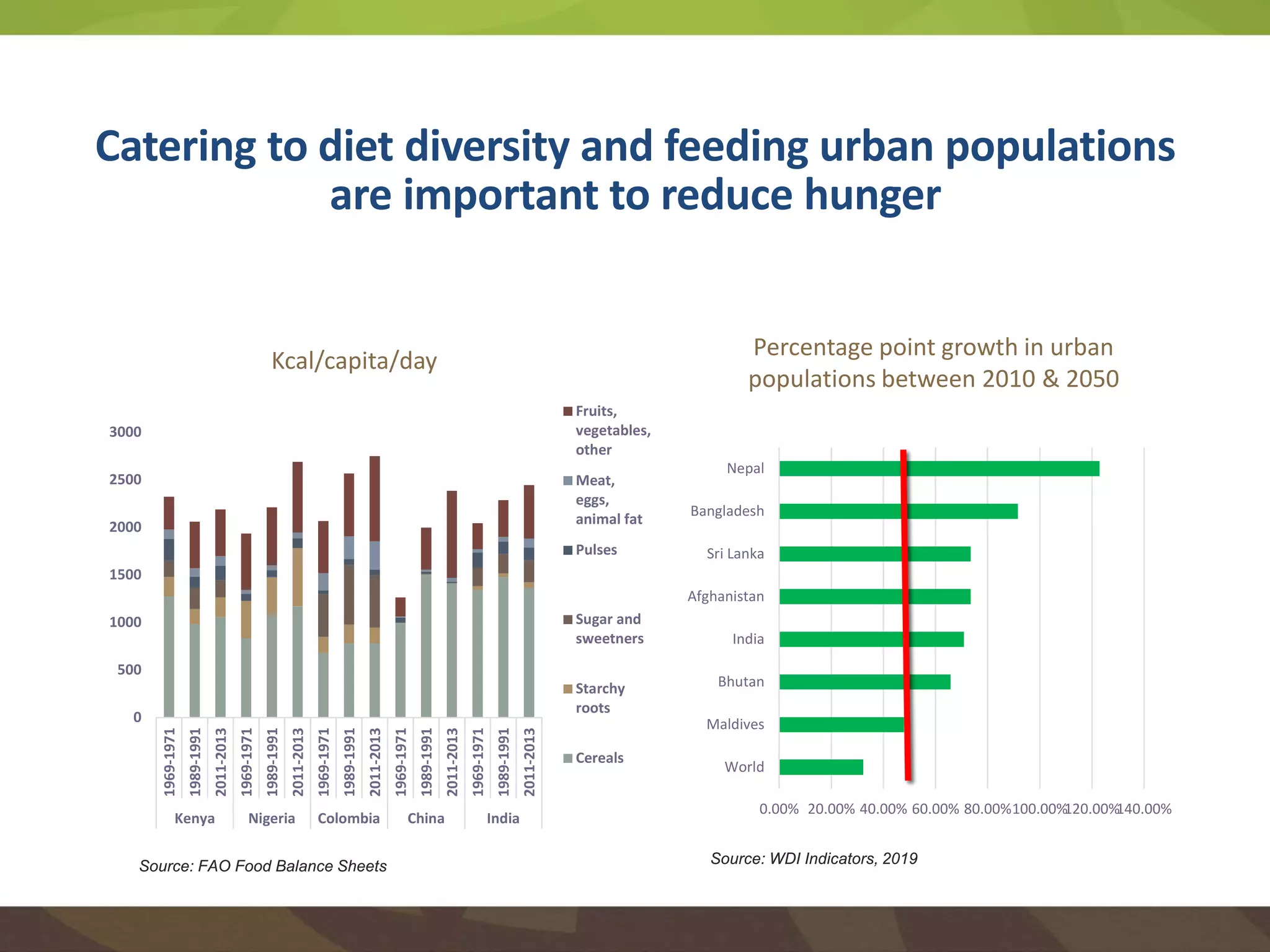
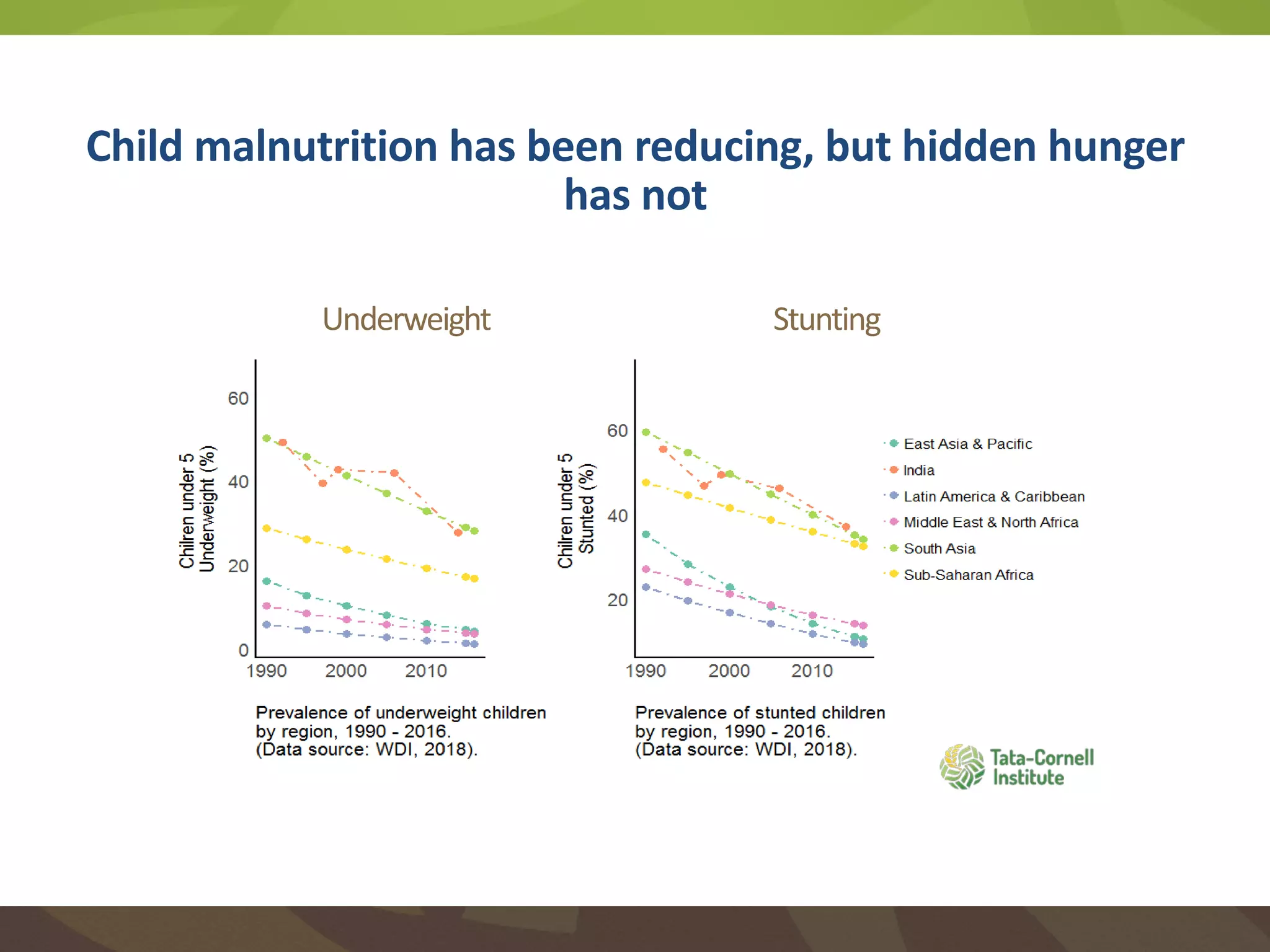
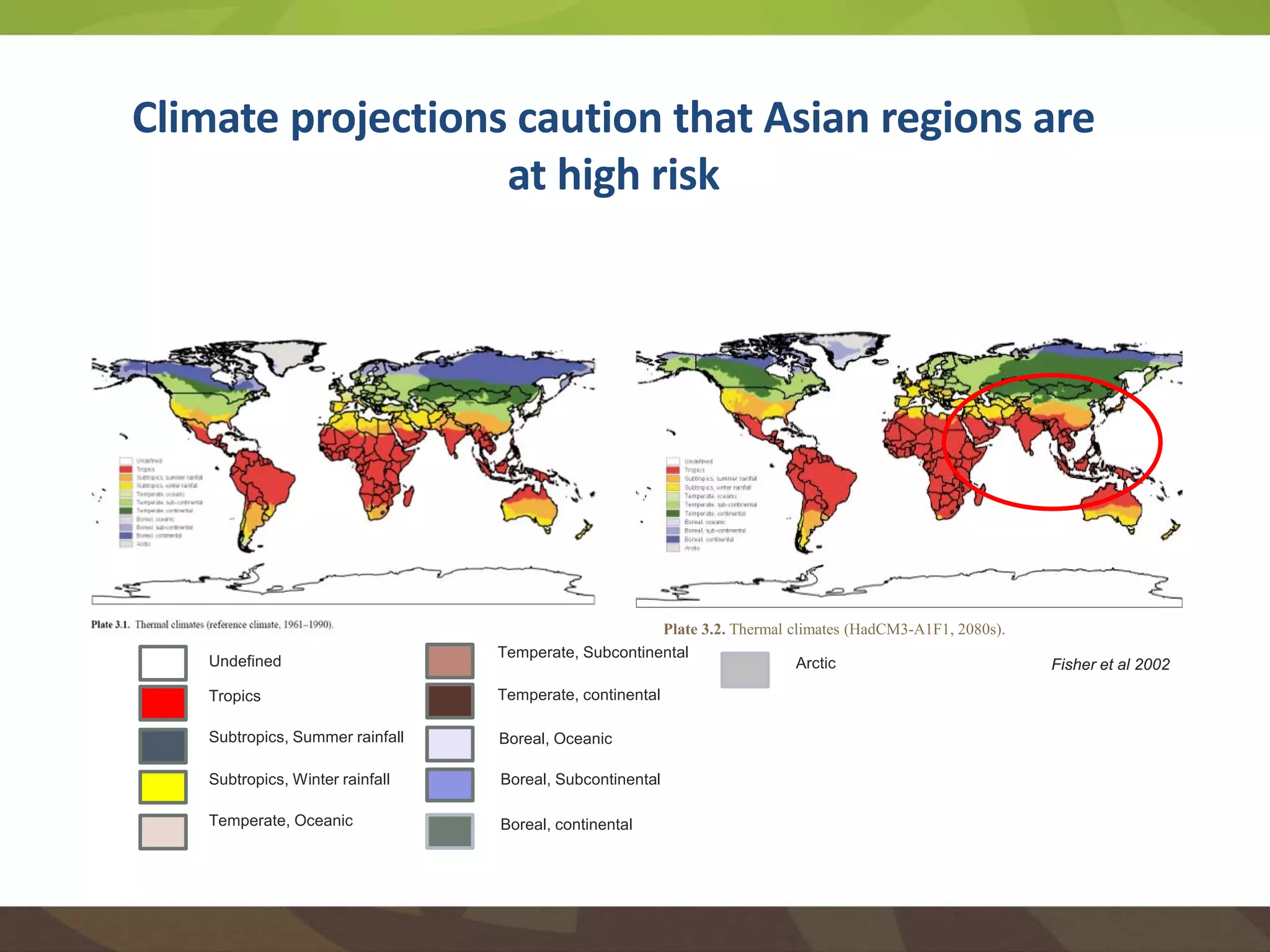
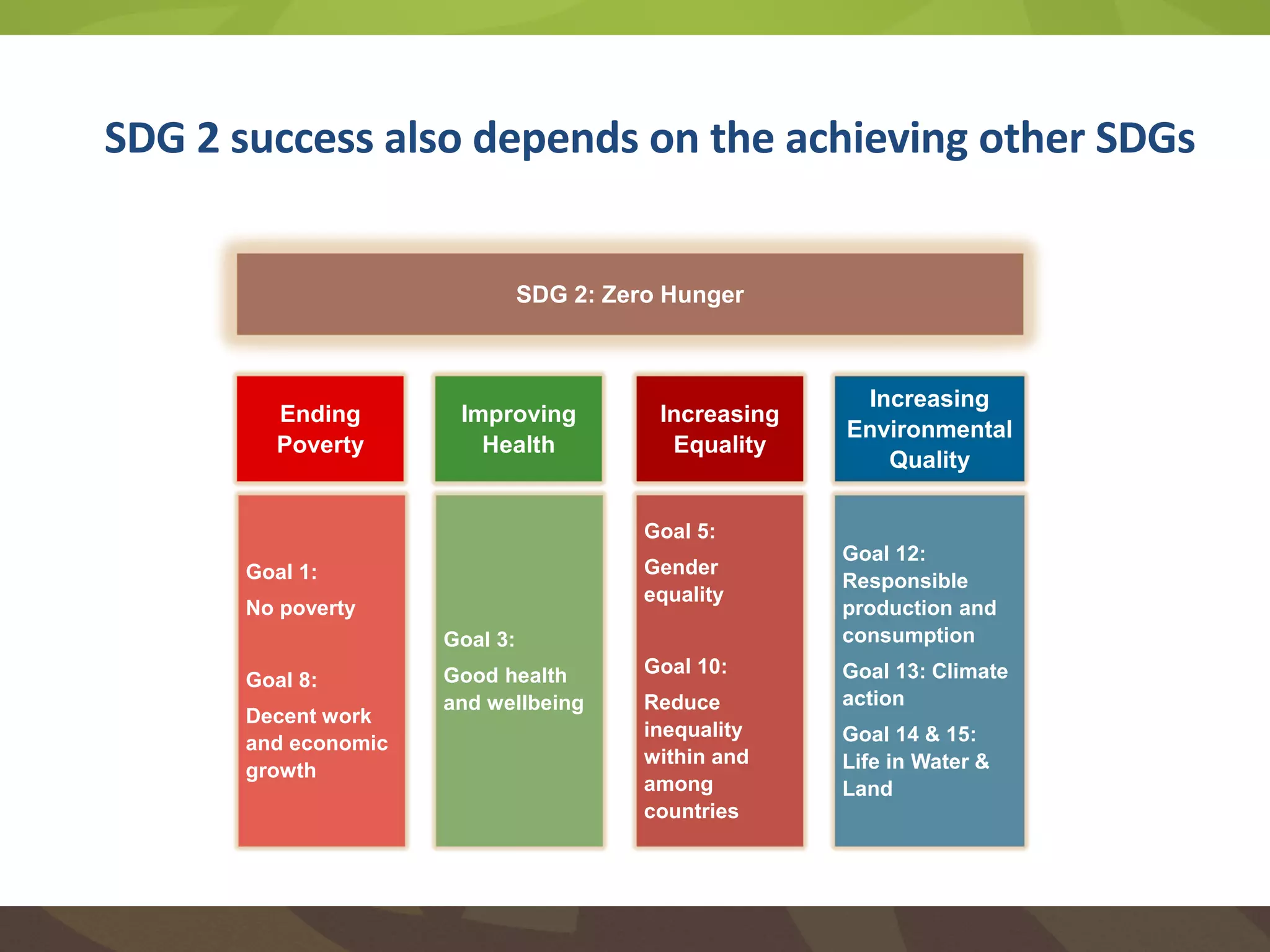
The document discusses the implications of transforming food systems in Asia to achieve Sustainable Development Goal 2 (SDG 2): Zero Hunger by 2030. It highlights the need for increased agricultural productivity, improved nutrition, and sustainable practices while addressing inter- and intra-regional disparities in access to food. Furthermore, it emphasizes the role of technology in enhancing food production and the necessity for coordinated efforts to adapt to climate change challenges.