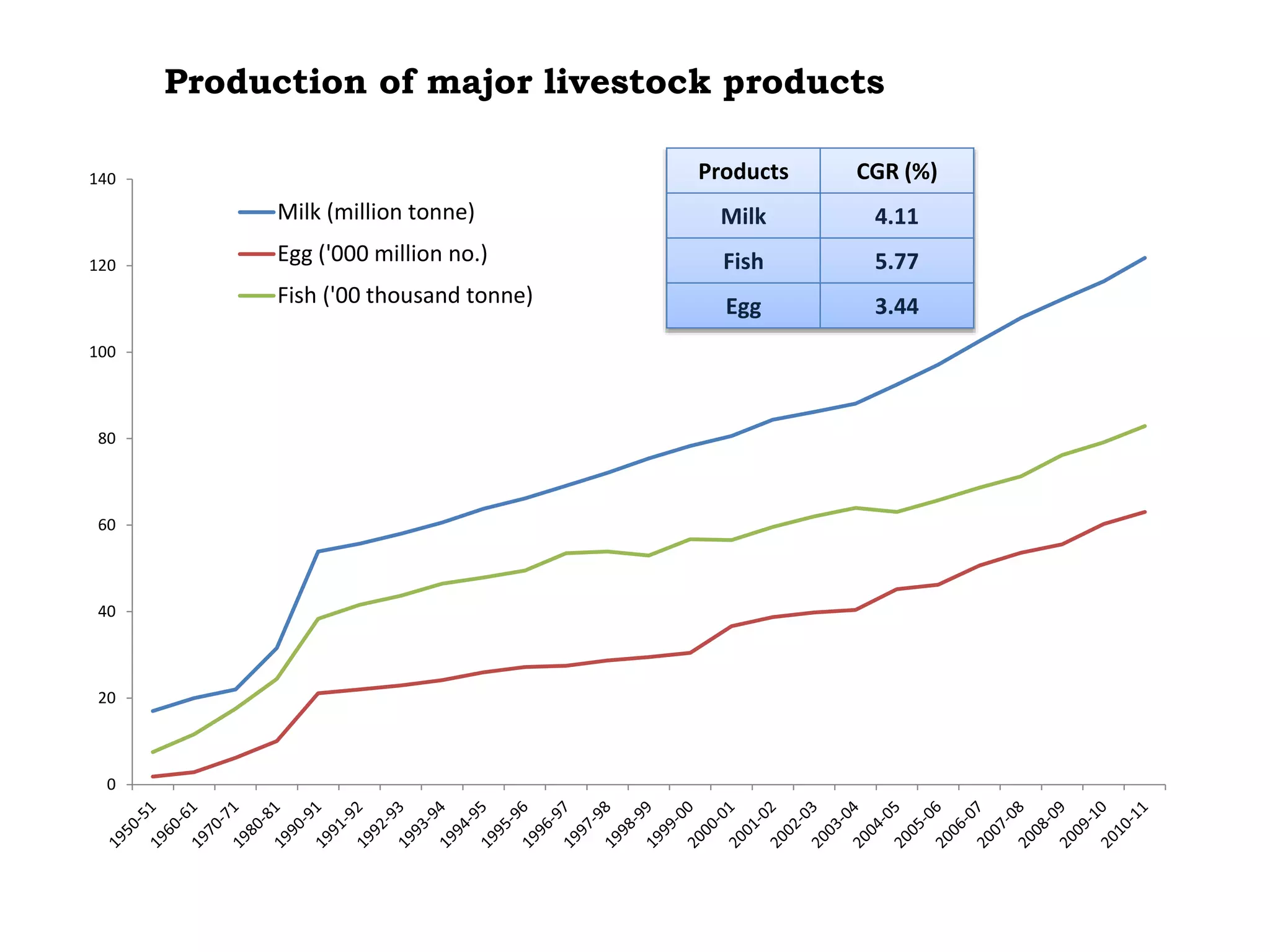
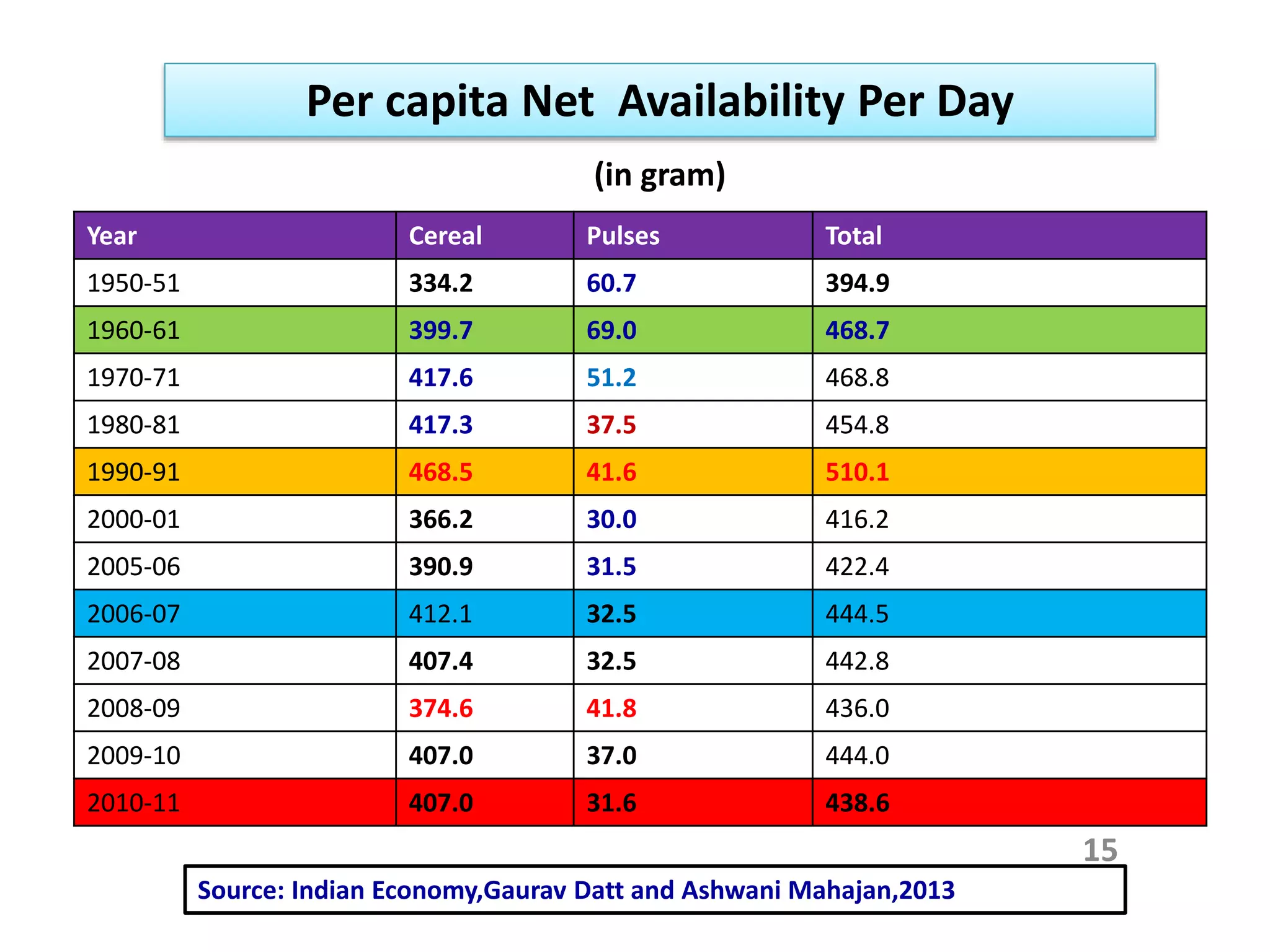
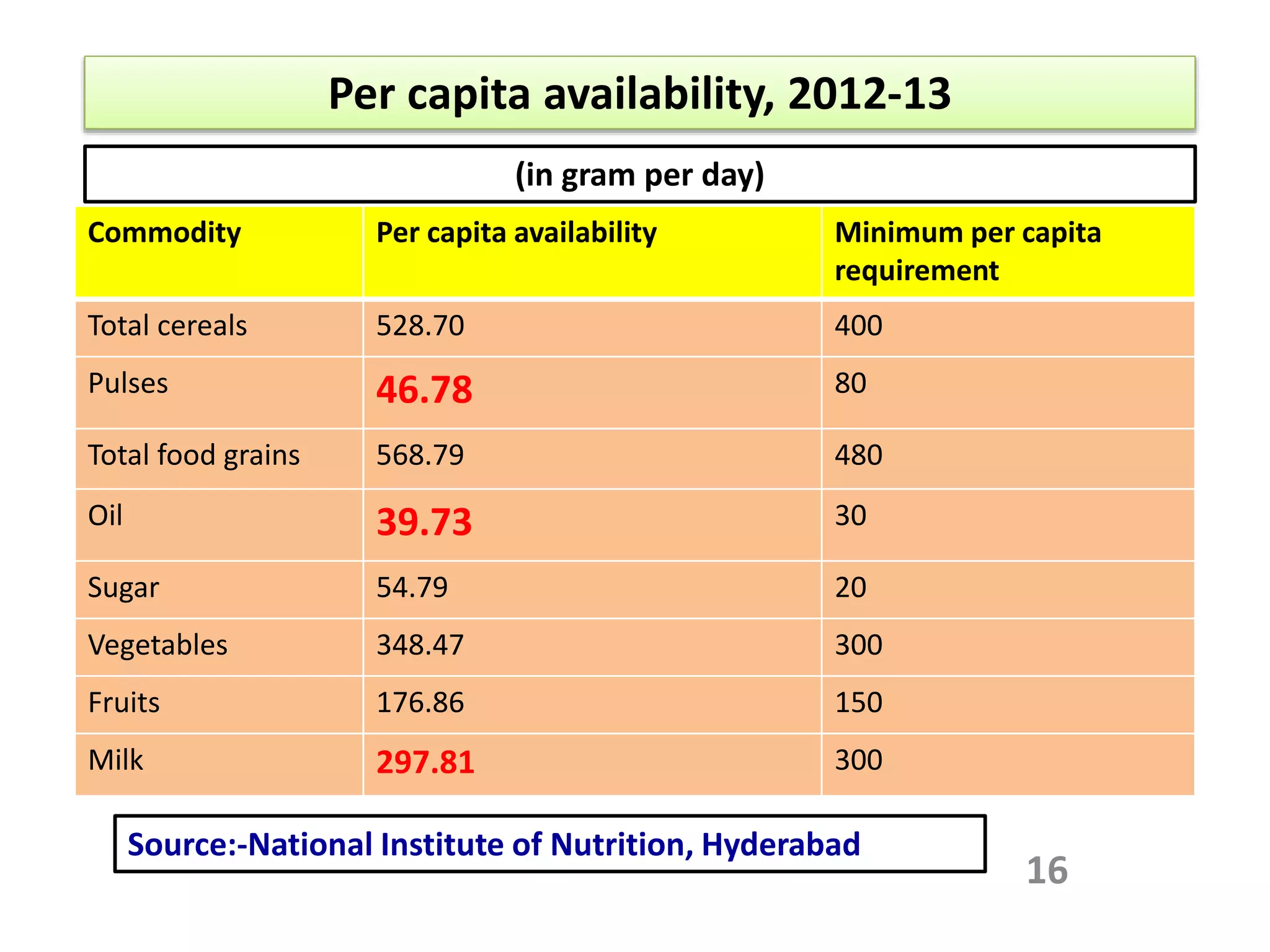
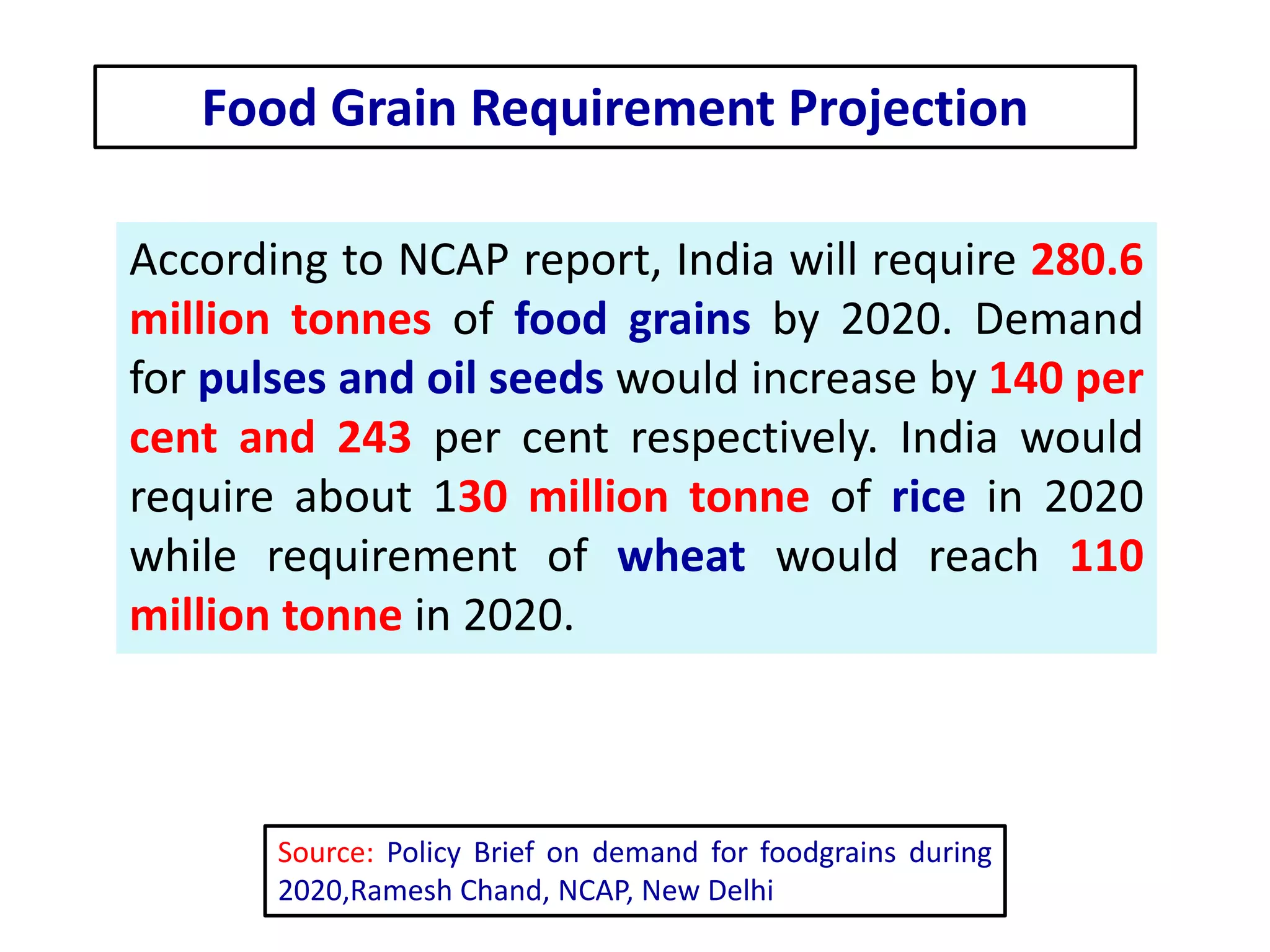
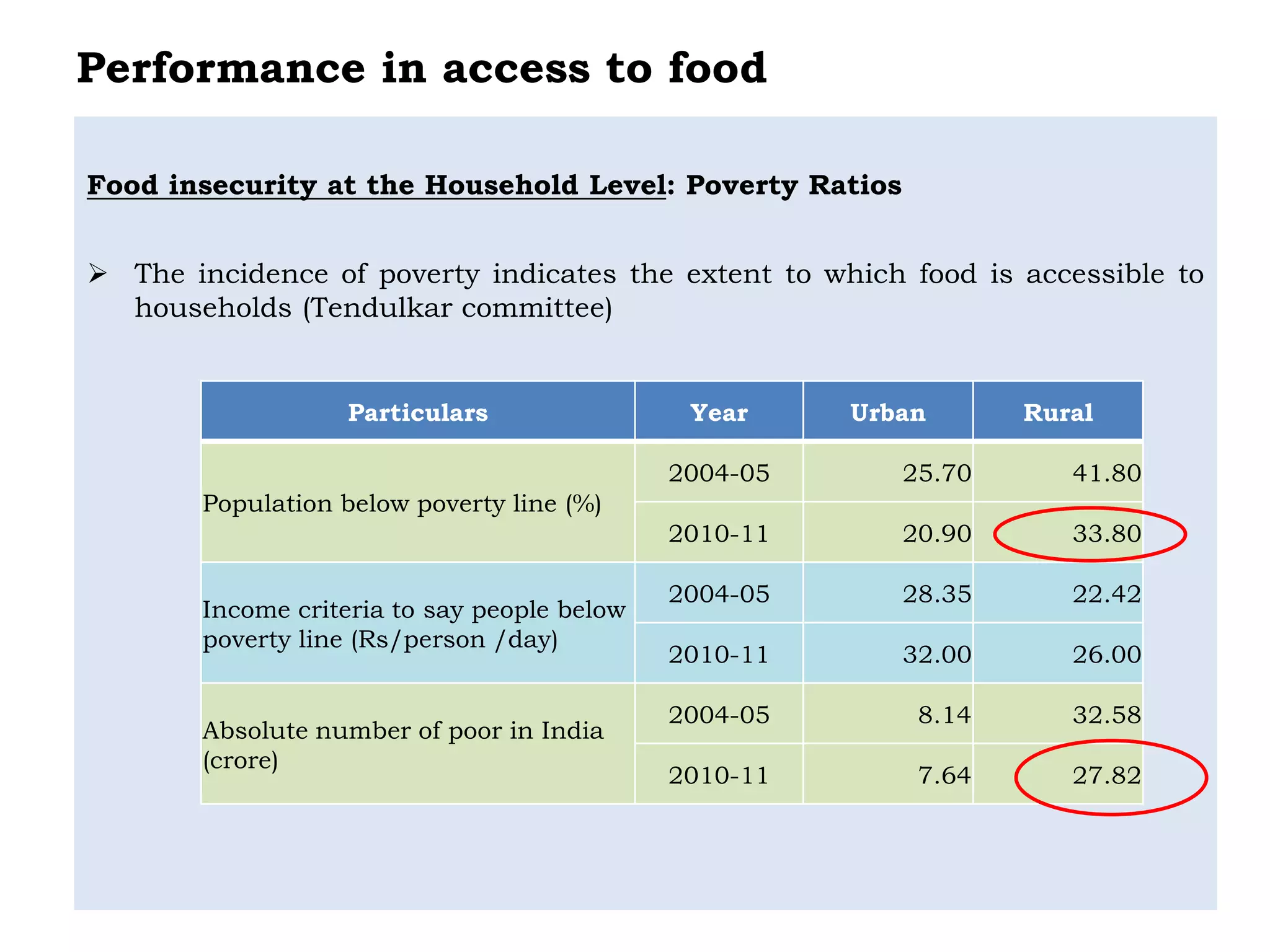
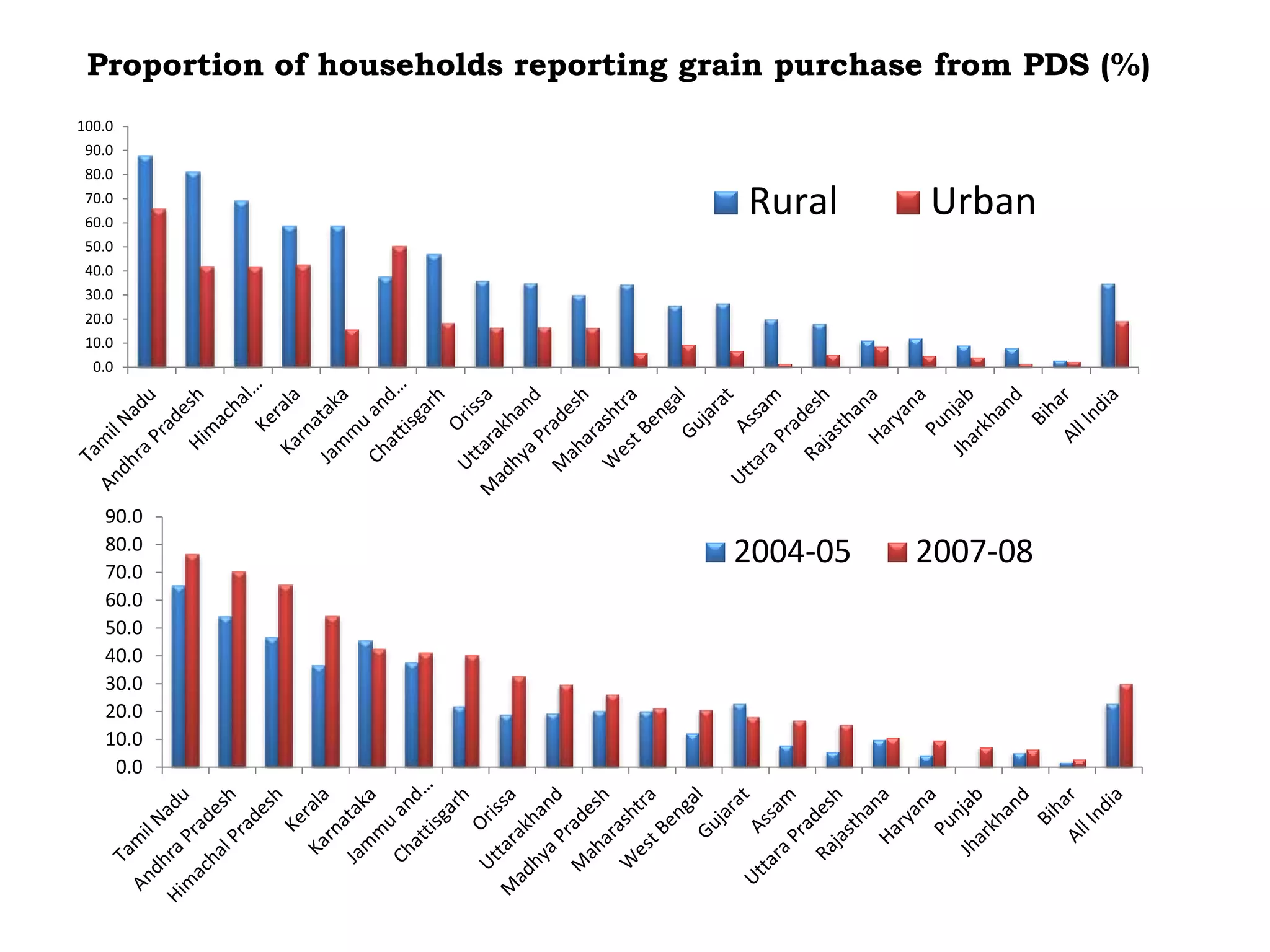
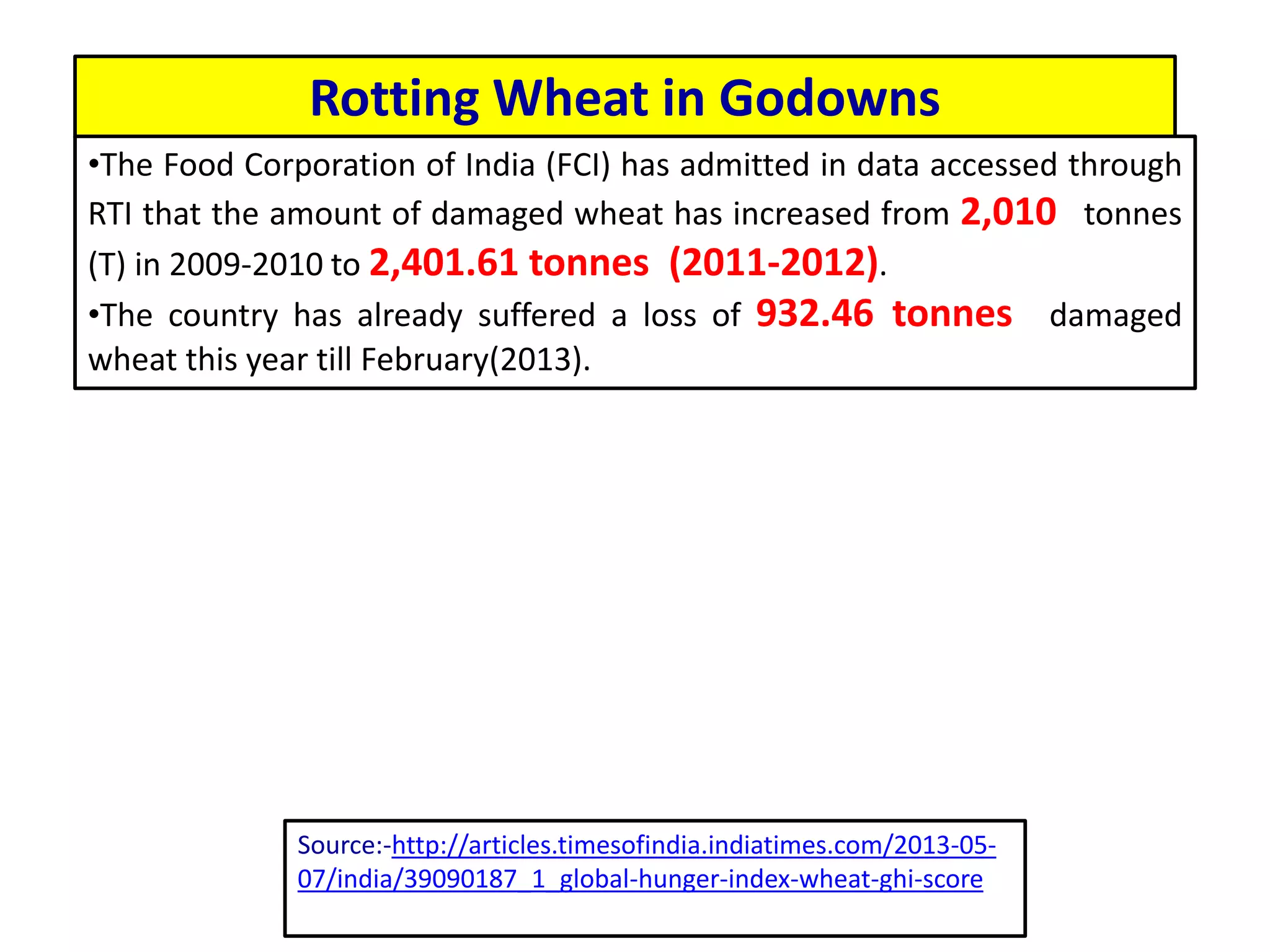
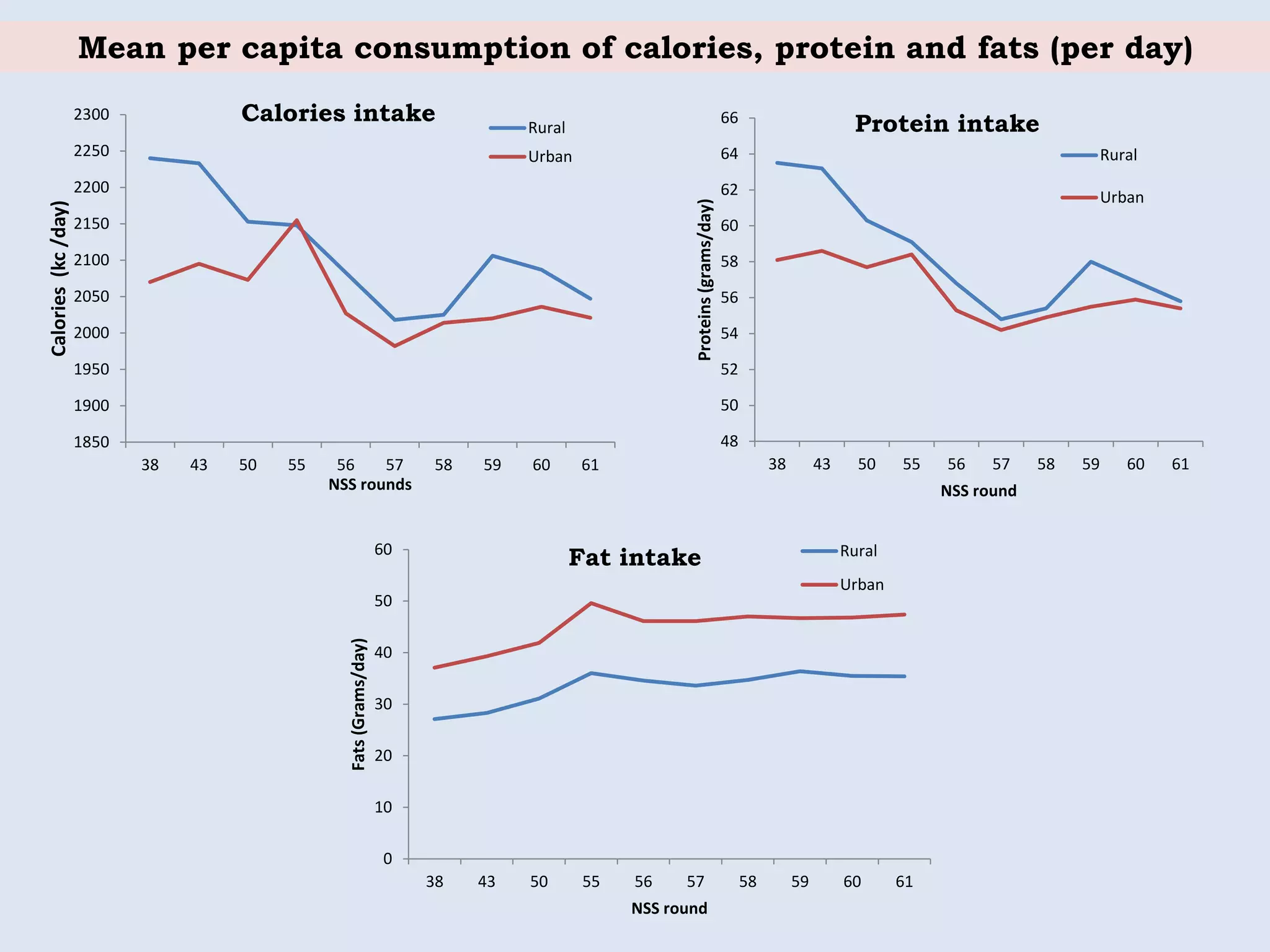
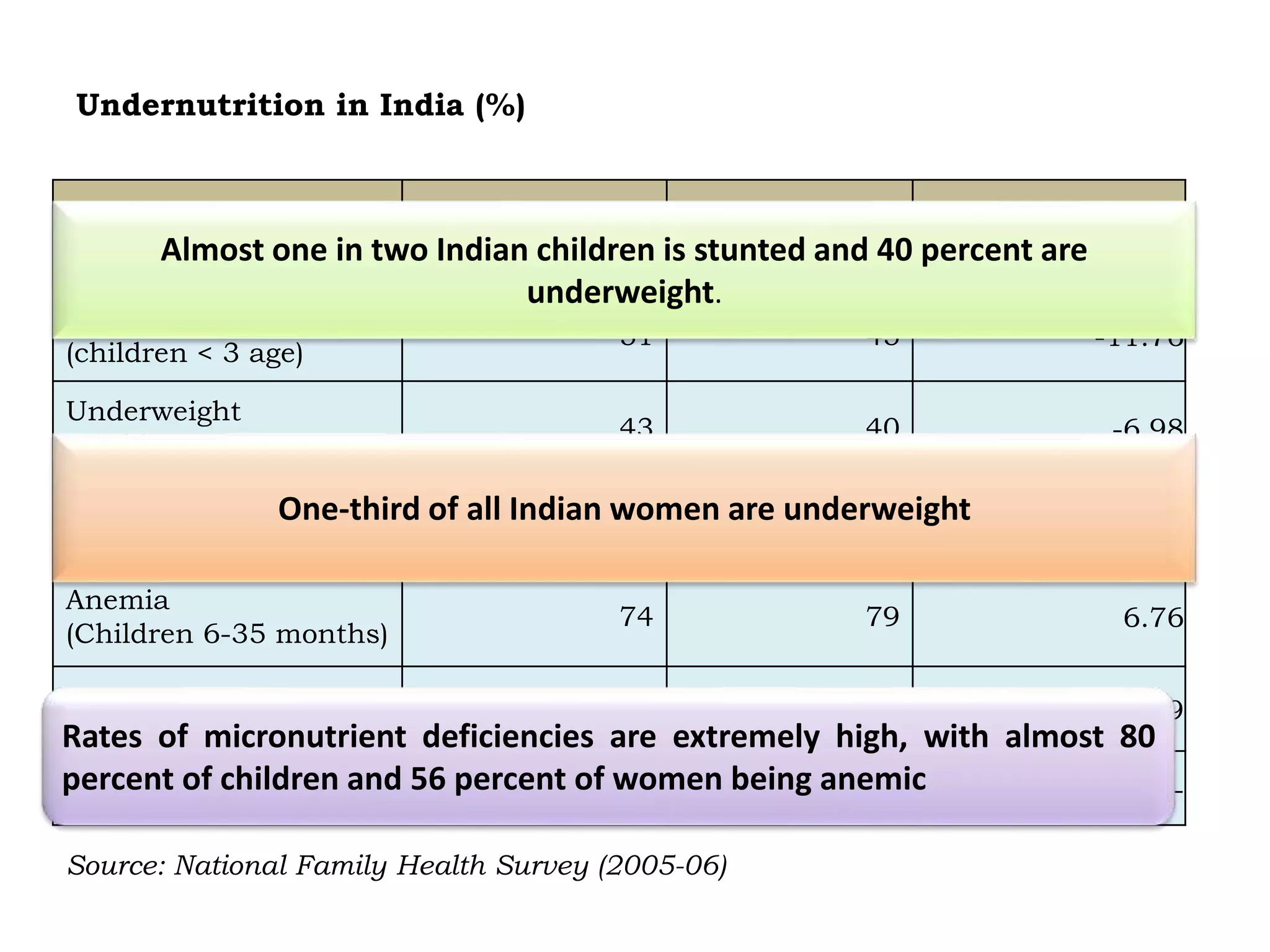
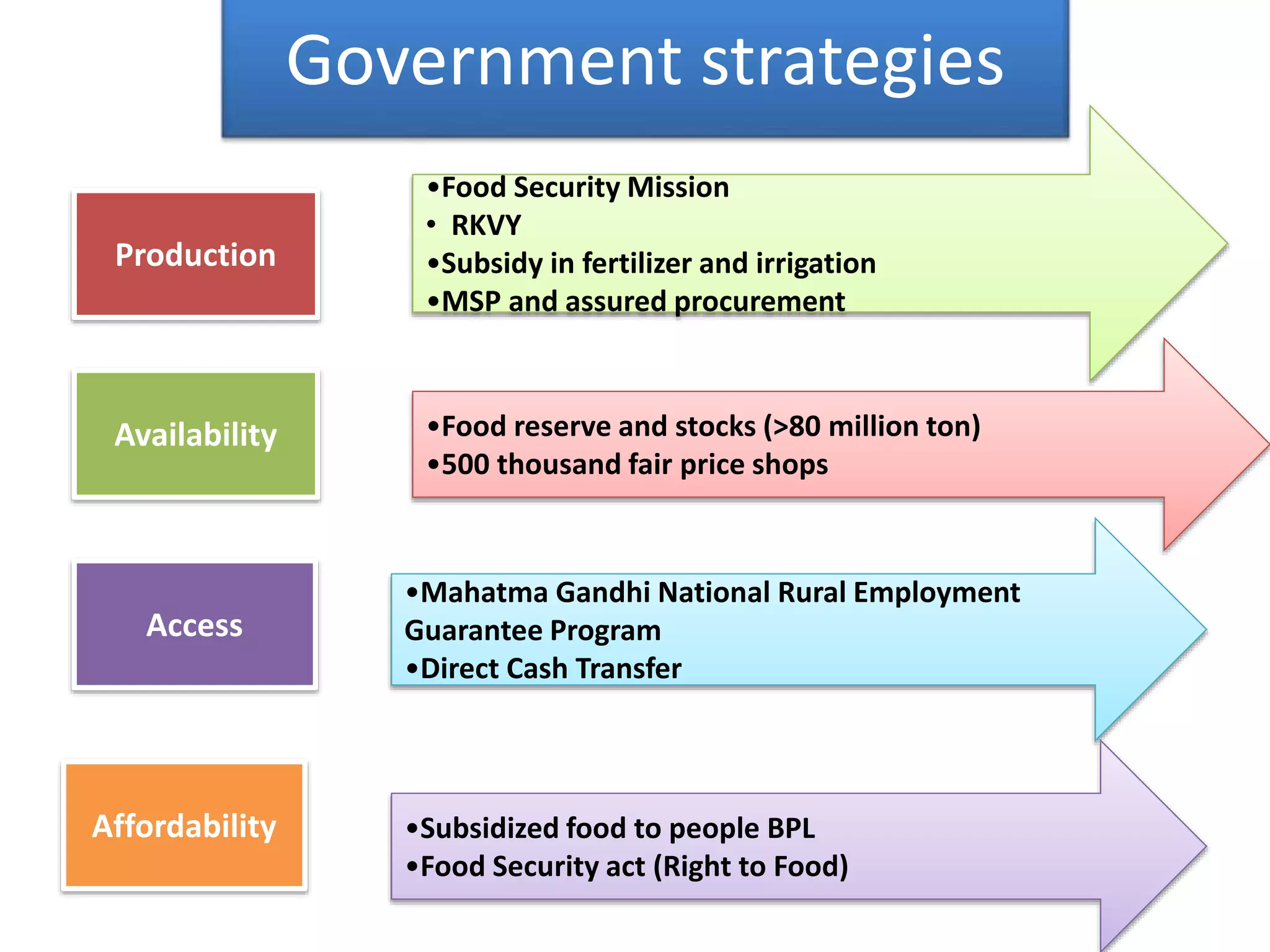
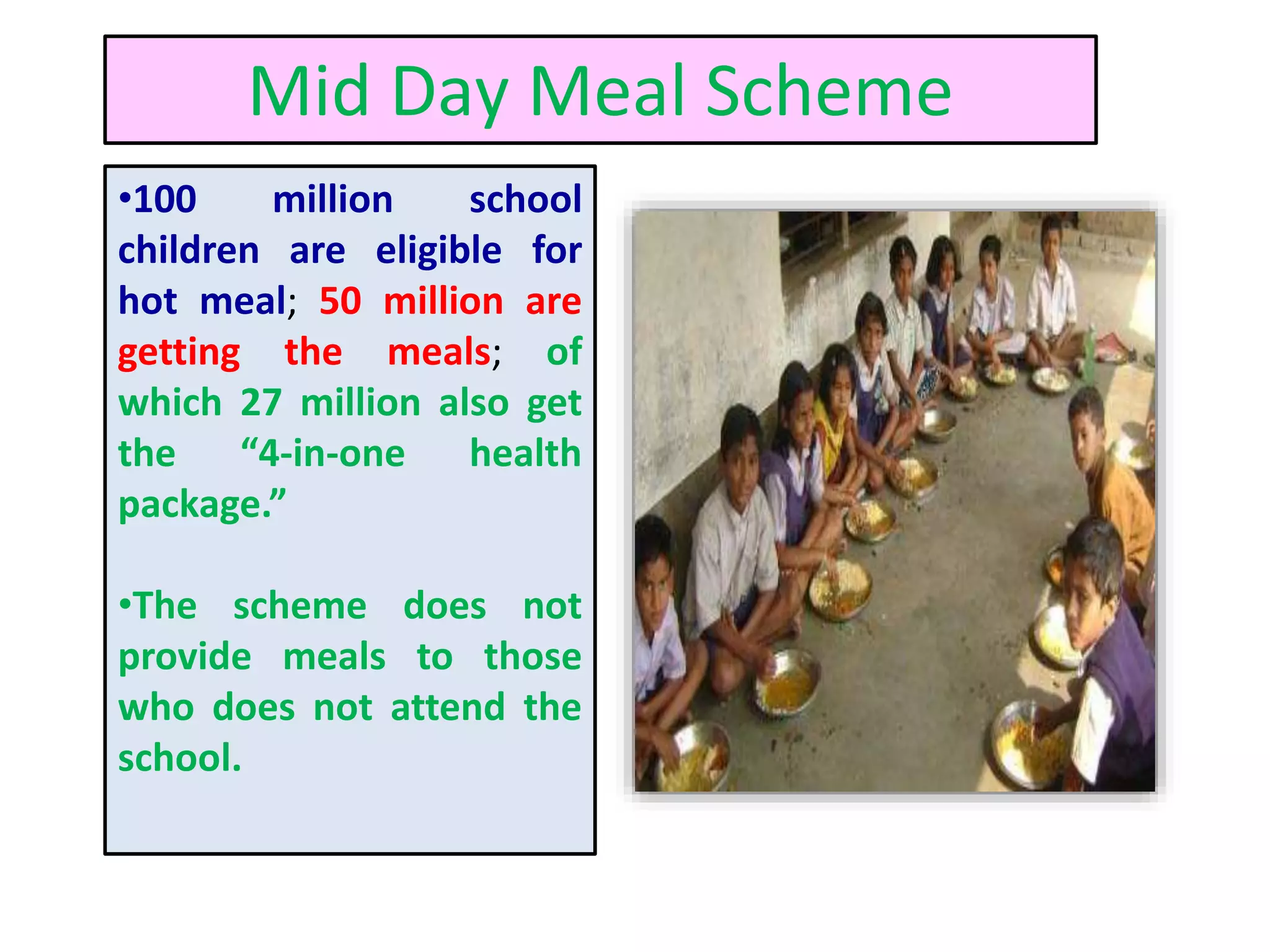
The document discusses food and nutritional security challenges in India, highlighting that a significant portion of the population lives below the poverty line and faces hunger. It outlines the importance of improving food production, access, and nutritional quality, indicating the need for strategies such as community farming and social protection programs to enhance food availability and purchasing power. Additionally, it notes projections for food grain requirements by 2020 and emphasizes the importance of addressing food insecurity and malnutrition.