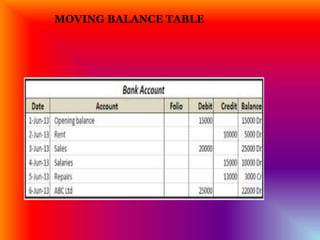
The document presents an overview of accounting principles, emphasizing the importance of recording financial transactions systematically to assess a business's financial position. It details Mr. Shagor's financial activities, demonstrating cash inflow and outflow calculations, and introduces key accounting concepts like accounts, debits, and credits. The document also explains the structure of a company's chart of accounts and the utility of t-accounts and moving balance tables in tracking financial data.

![ACCOUNTS
5
This presentation is owned by
ABUL KALAM AZAD PATWARY
“for class 9-10[accounting]”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/accounting-chapter-5-150209045728-conversion-gate02/85/Accounting-chapter-5-2-320.jpg)