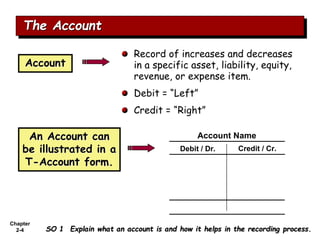
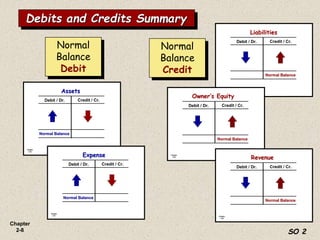
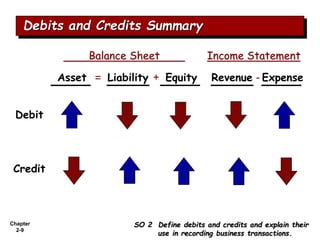
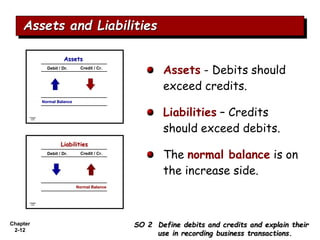
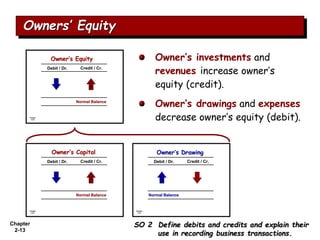
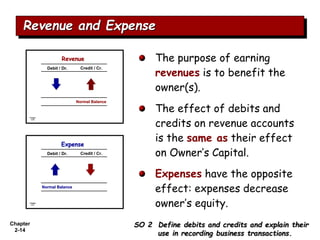
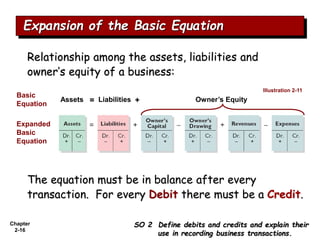
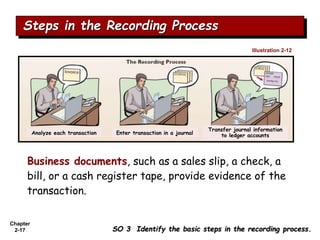
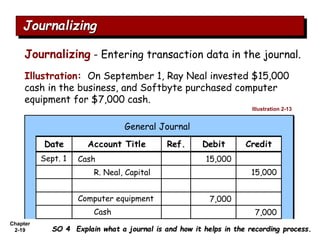
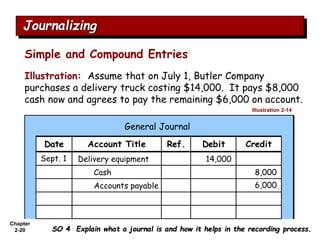
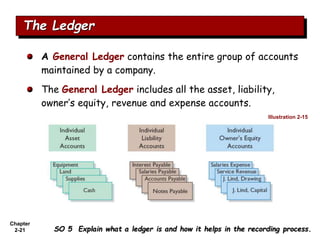
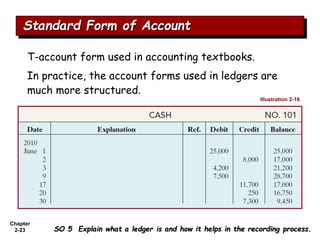
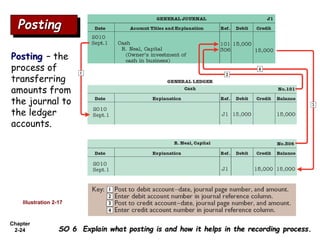
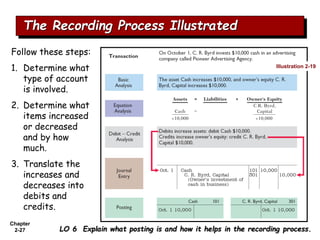
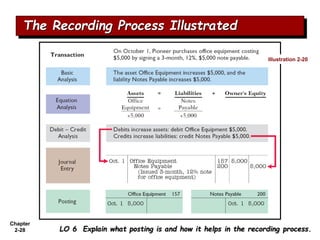
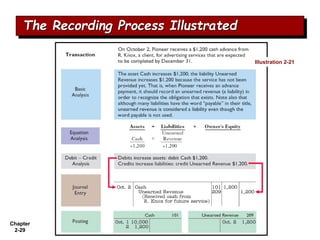
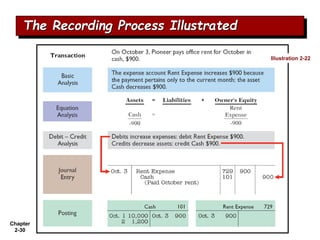
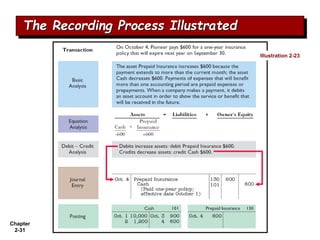
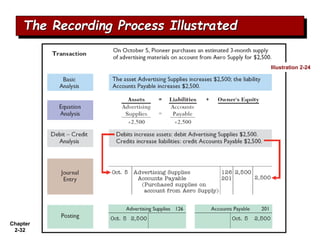
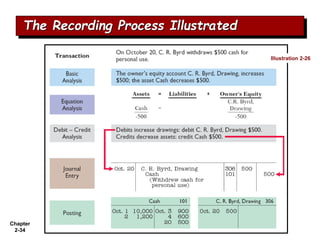
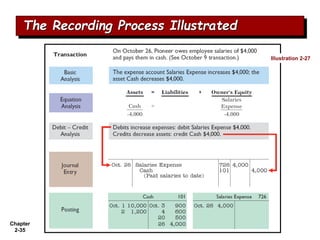
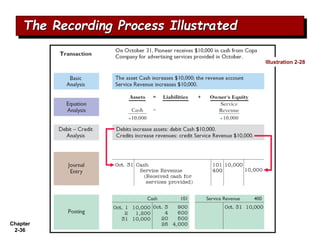
The document summarizes key aspects of the accounting recording process. It explains that the recording process involves (1) analyzing transactions, (2) journalizing transactions by recording them in a journal, and (3) posting journal entries to individual accounts in the general ledger. It also describes what a journal and general ledger are and how they are used. The chapter concludes by explaining what a trial balance is and that its purpose is to ensure total debits equal total credits.