1. The document discusses accounting standards in India including Accounting Standards (AS), International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS), and Indian Accounting Standards (Ind AS).
2. AS are written policies issued by accounting bodies to standardize accounting methods. IFRS are international standards adopted by the IASB. Ind AS have been notified by the MCA to converge Indian standards with IFRS.
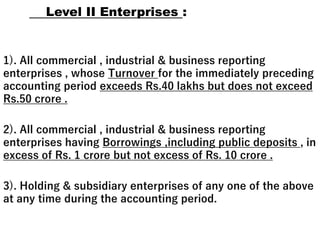
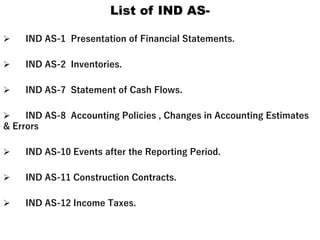
3. The document lists the objectives of AS, the levels of AS, recognition of AS under the Companies Act, and provides examples of some key AS, IFRS, and Ind AS.