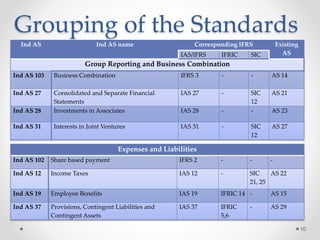
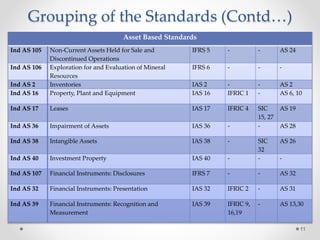
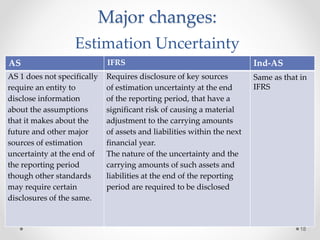
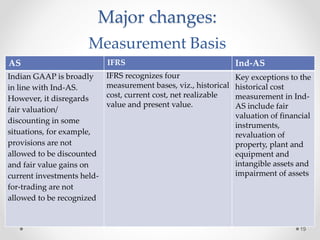
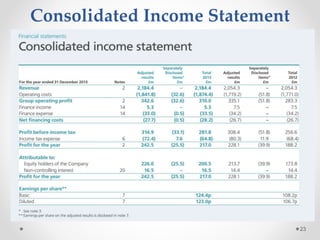
This document summarizes a research paper on the effect of adopting Ind-AS and IFRS standards on financial statement presentation in India. The paper discusses major changes such as including a statement of comprehensive income, changes in equity statement presentation, and fair value measurement. It analyzes financial statements of Intertek Group prepared under IFRS. The study finds adoption will increase transparency but some differences from IFRS remain concerns. Further research on revenue recognition, assets, and liabilities is needed as companies begin preparing statements under Ind-AS.