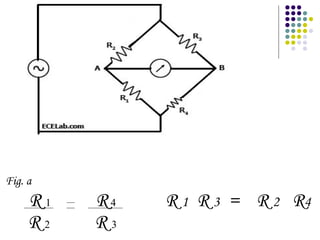
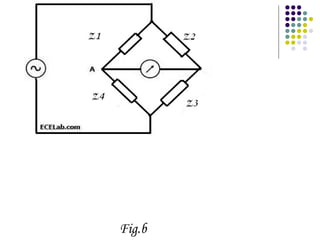
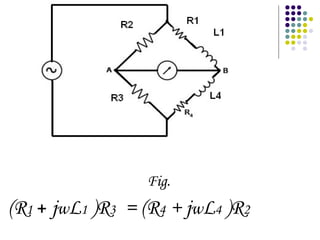
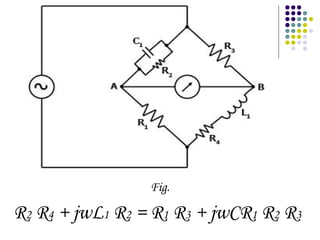
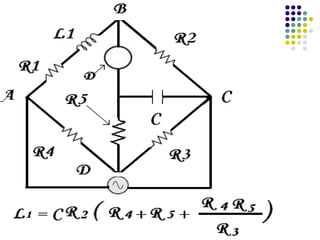
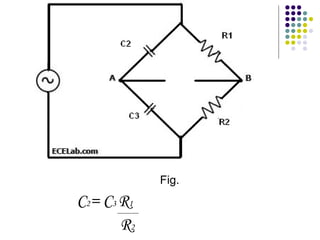
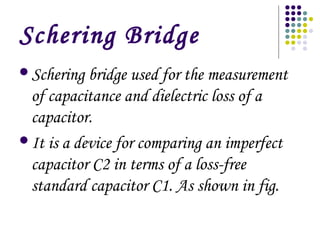
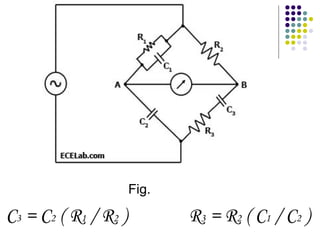
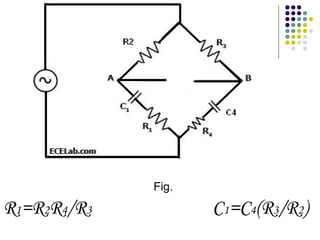
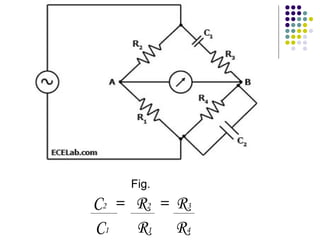
A.C. bridges are circuits used to measure unknown resistances, capacitances, inductances, frequencies, and mutual inductances. Some common bridges include the Wheatstone bridge for measuring resistance using direct current, Maxwell's bridges for measuring inductance using alternating current, and the De Sauty, Schering, Wien series, and Wien parallel bridges for measuring capacitance using various balanced circuit configurations. Each bridge uses a balanced circuit equation to relate known components to unknown values.