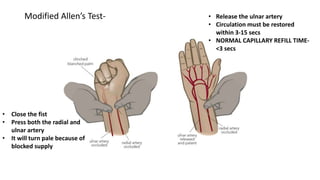
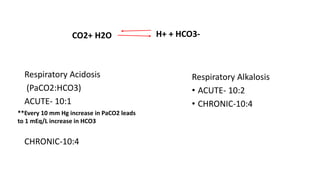
The document provides a detailed overview of arterial and venous blood gas analysis, including color, pressure, and common sampling sites for arterial blood. It outlines the modified Allen’s test for assessing collateral circulation and establishes normal blood gas values, indicating pH and concentrations for respiratory and metabolic conditions. The text explains the rules for interpreting blood gas results, distinguishing between compensated and uncompensated states in acid-base disorders.