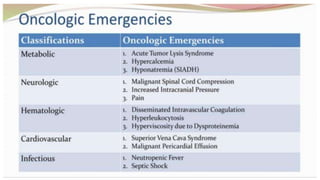
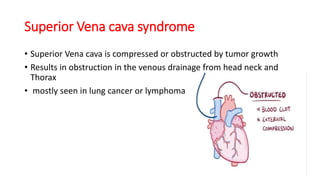
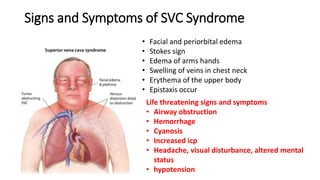
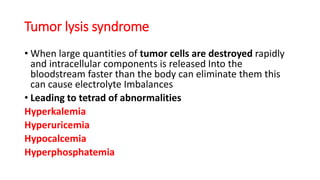
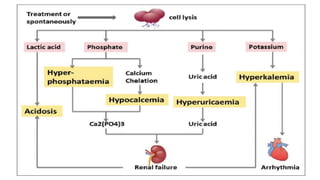
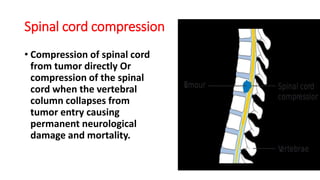
Oncological emergencies encompass life-threatening complications arising from cancer and its treatment, including conditions like superior vena cava syndrome, tumor lysis syndrome, spinal cord compression, hypercalcemia, syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (SIADH), sepsis, and disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC). Each condition has specific signs, symptoms, and interventions, emphasizing the importance of early recognition and management to prevent severe complications. Key interventions include corticosteroids, hydration, chemotherapy, and monitoring vital signs and serum levels.