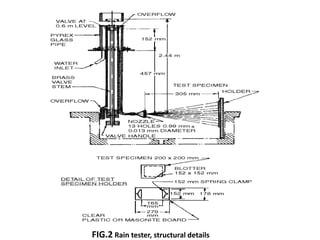
This document summarizes the AATCC Test Method 35 for measuring the water resistance of textile fabrics through a rain test. The test involves spraying fabric samples mounted on a tester with water for 5 minutes. The amount of water absorbed by a blotter paper placed behind the fabric is then measured to determine the fabric's resistance to water penetration. Testing can be done at different water pressure levels to evaluate how well a fabric withstands increasing intensities of rainfall. The test provides a way to predict how well fabrics will resist rain when used for garments or other applications.