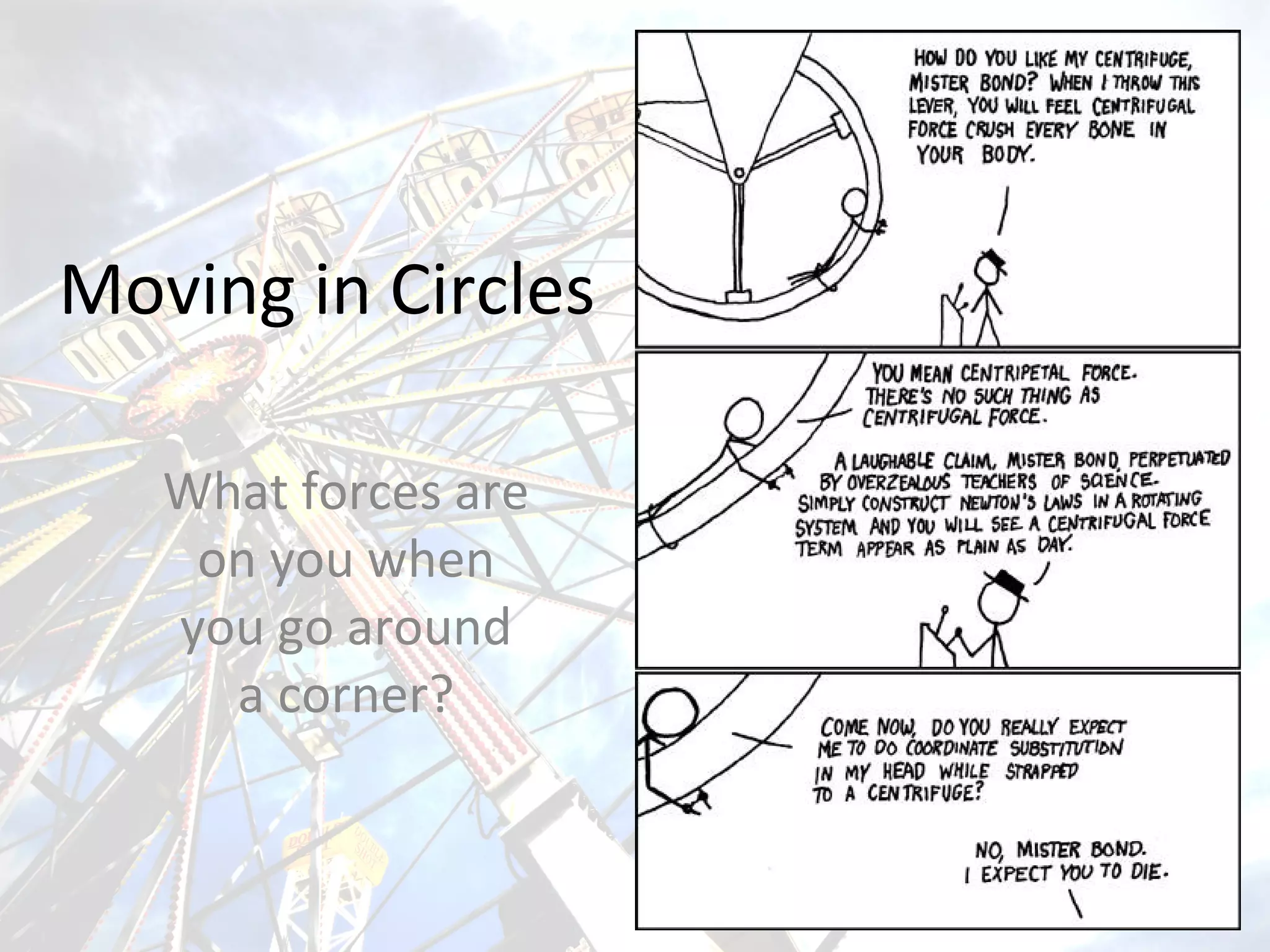
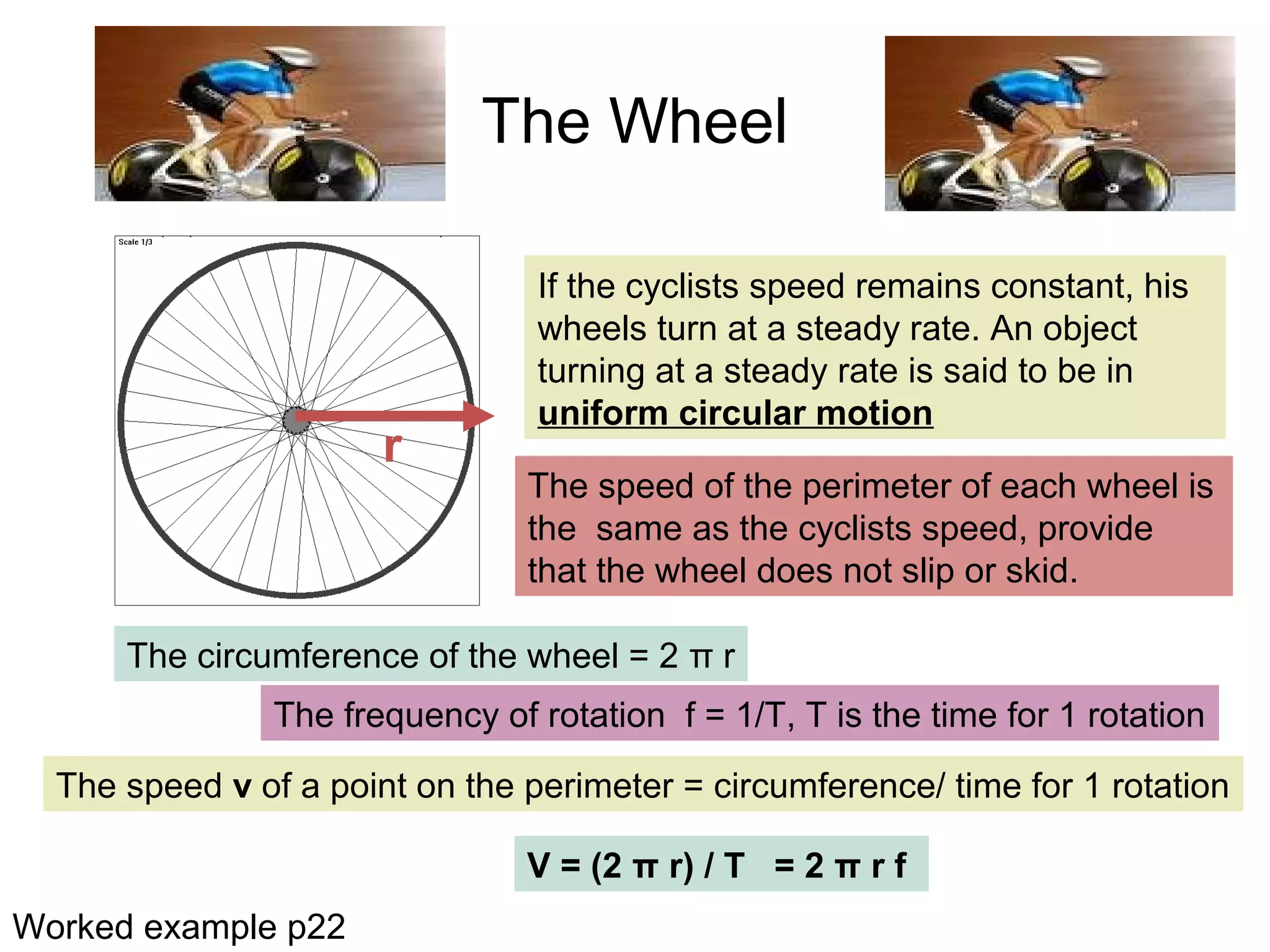
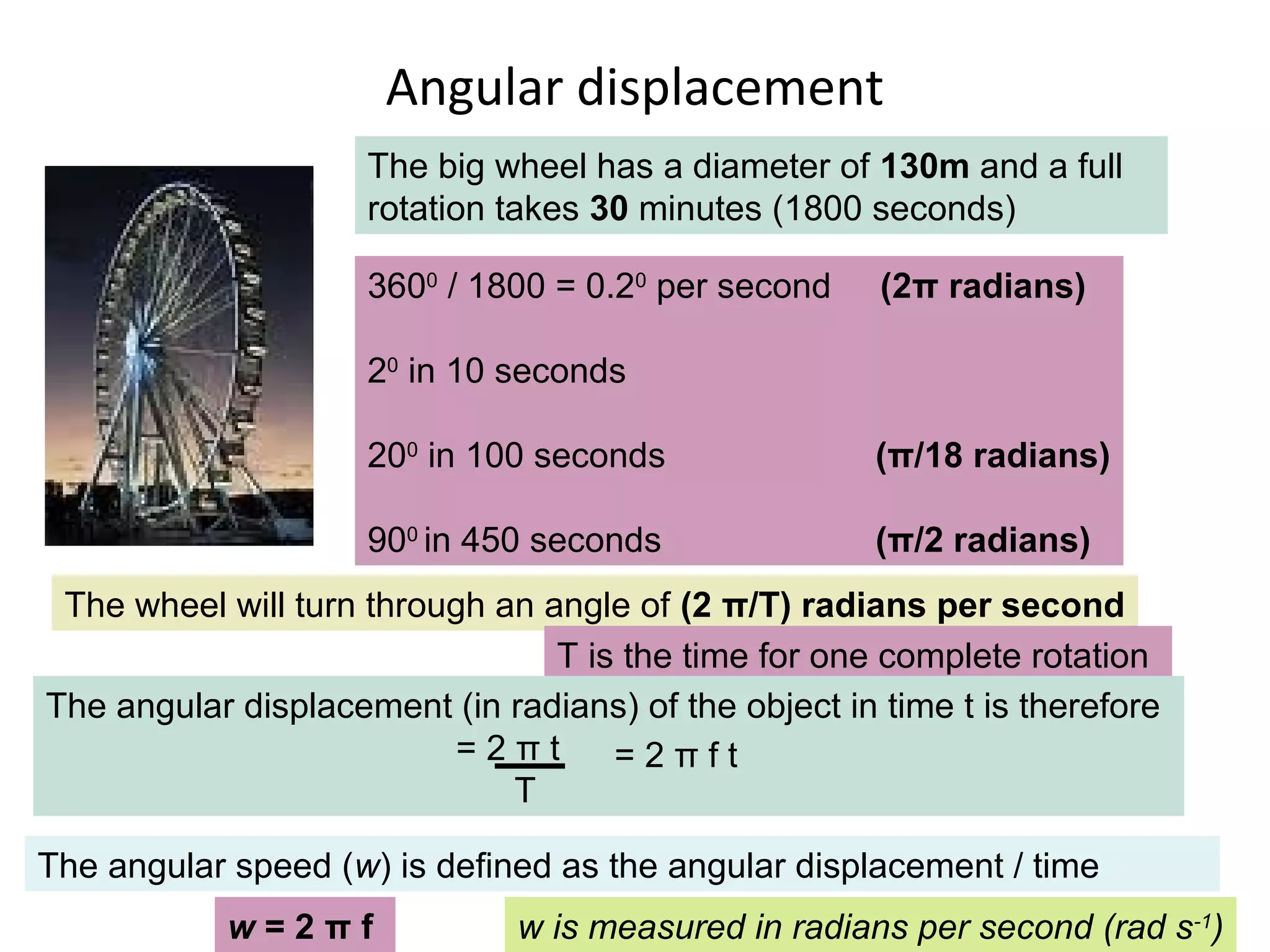
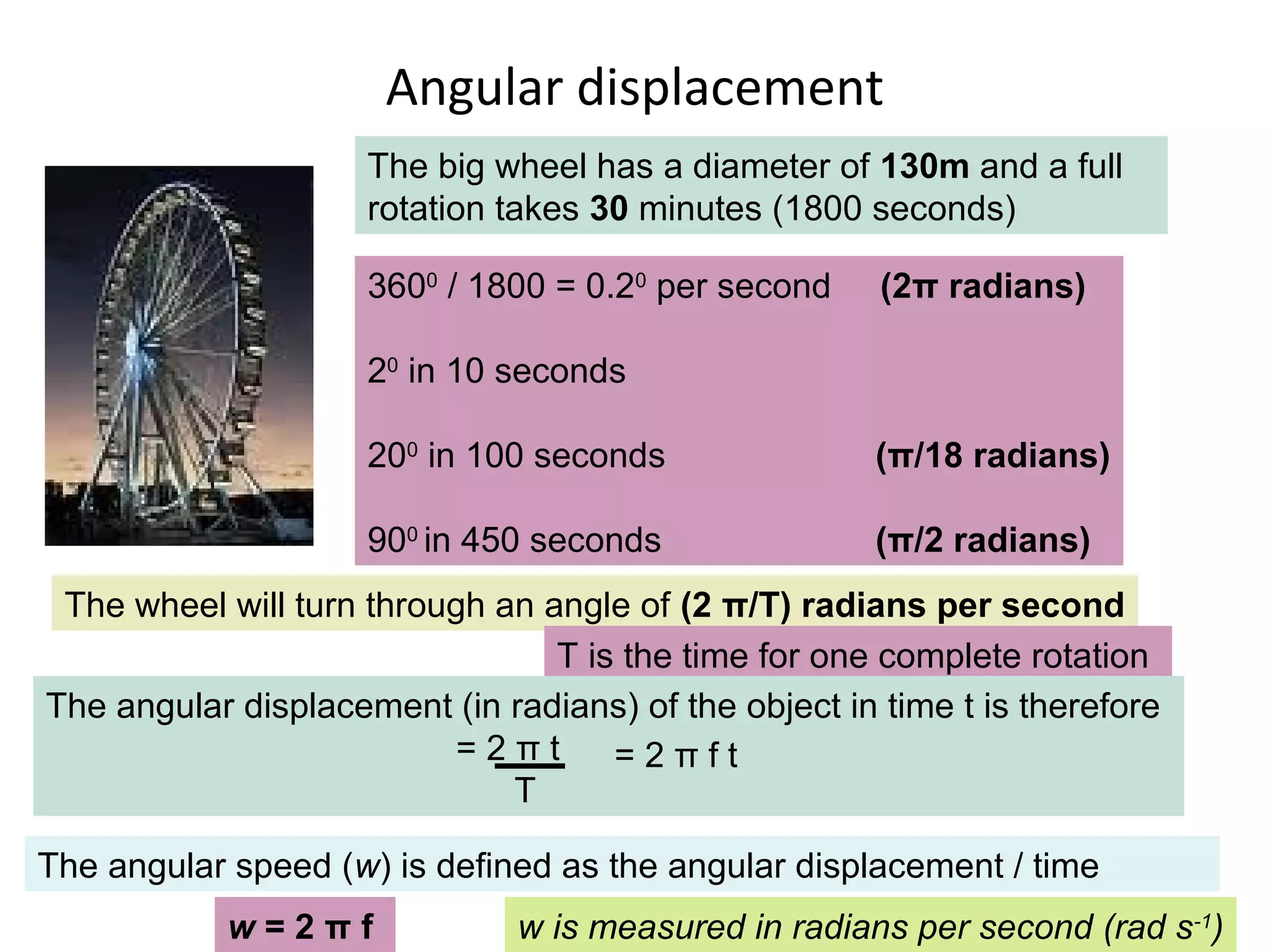
The document discusses the forces experienced when an object moves in a circular path, particularly focusing on why cars skid when cornering too quickly. It explains concepts such as uniform circular motion, angular displacement, and angular speed, providing examples like hammer throwing, spinning fairground rides, and satellites in orbit. Additionally, it includes calculations for angular speed and displacement, exemplified by a big wheel with a specific diameter and rotation time.