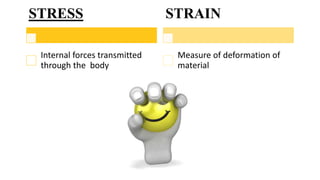
Engineering mechanics is a branch of applied science that deals with the laws and principles of mechanics and their application to engineering problems. It is concerned with the motion and rest of bodies under the action of forces. Some key terms in engineering mechanics include mass, time, space, length, displacement, velocity, acceleration, momentum, force, stress, and strain. Mass is a measure of the amount of matter in a body, while time is a measure of successive events like the Earth's rotation. Space and length help define the region and dimensions over which a body exists.