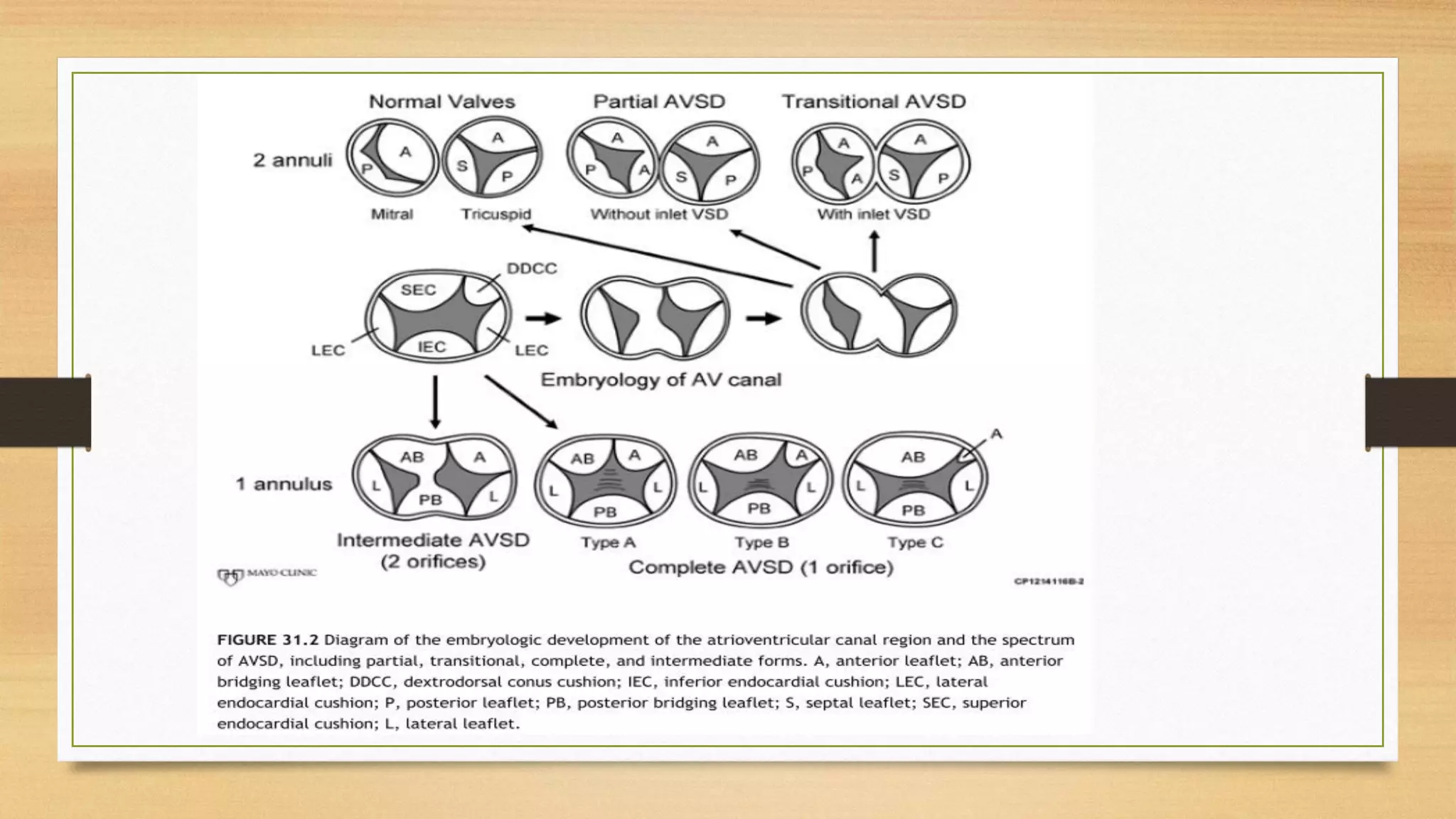
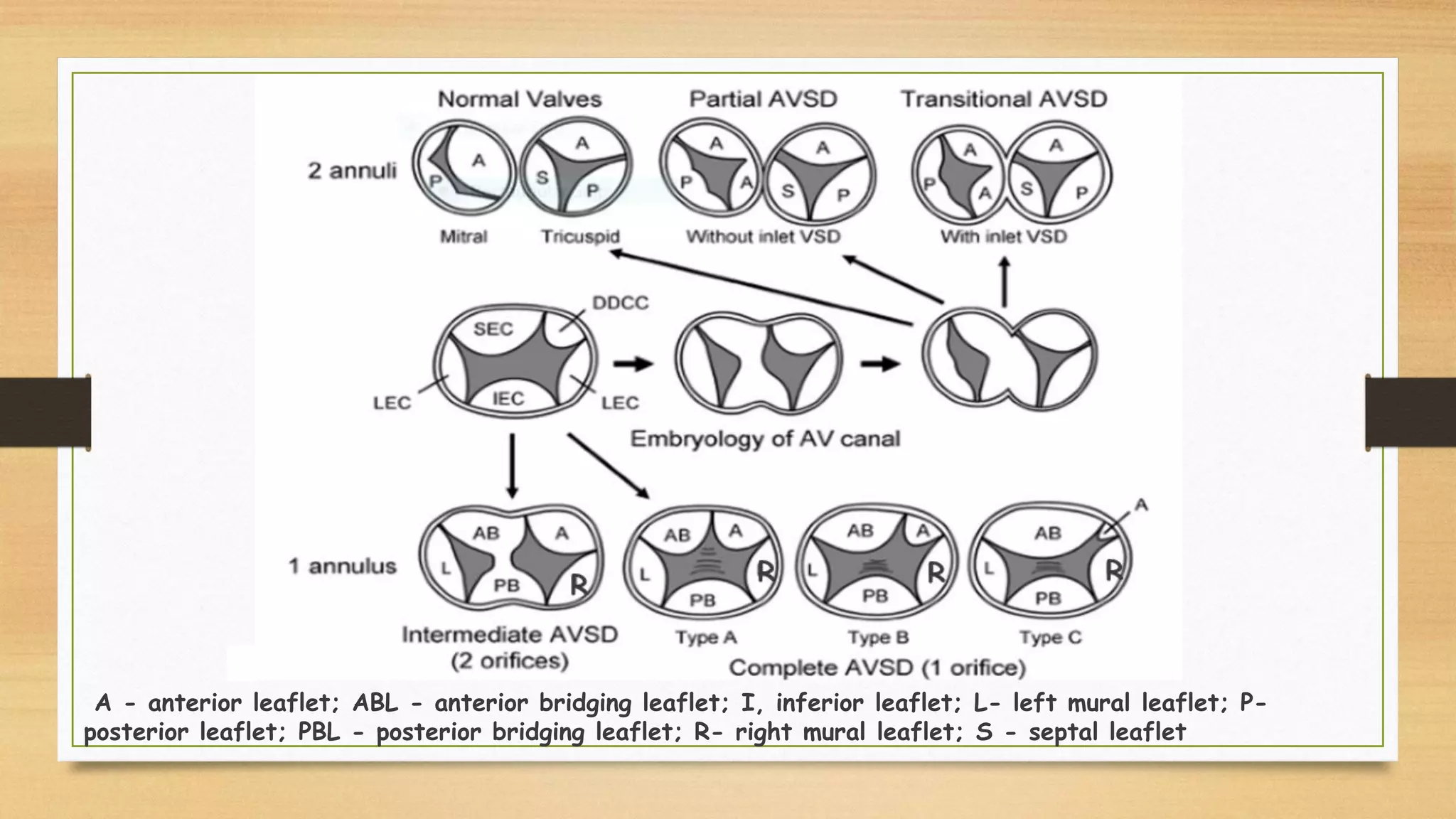
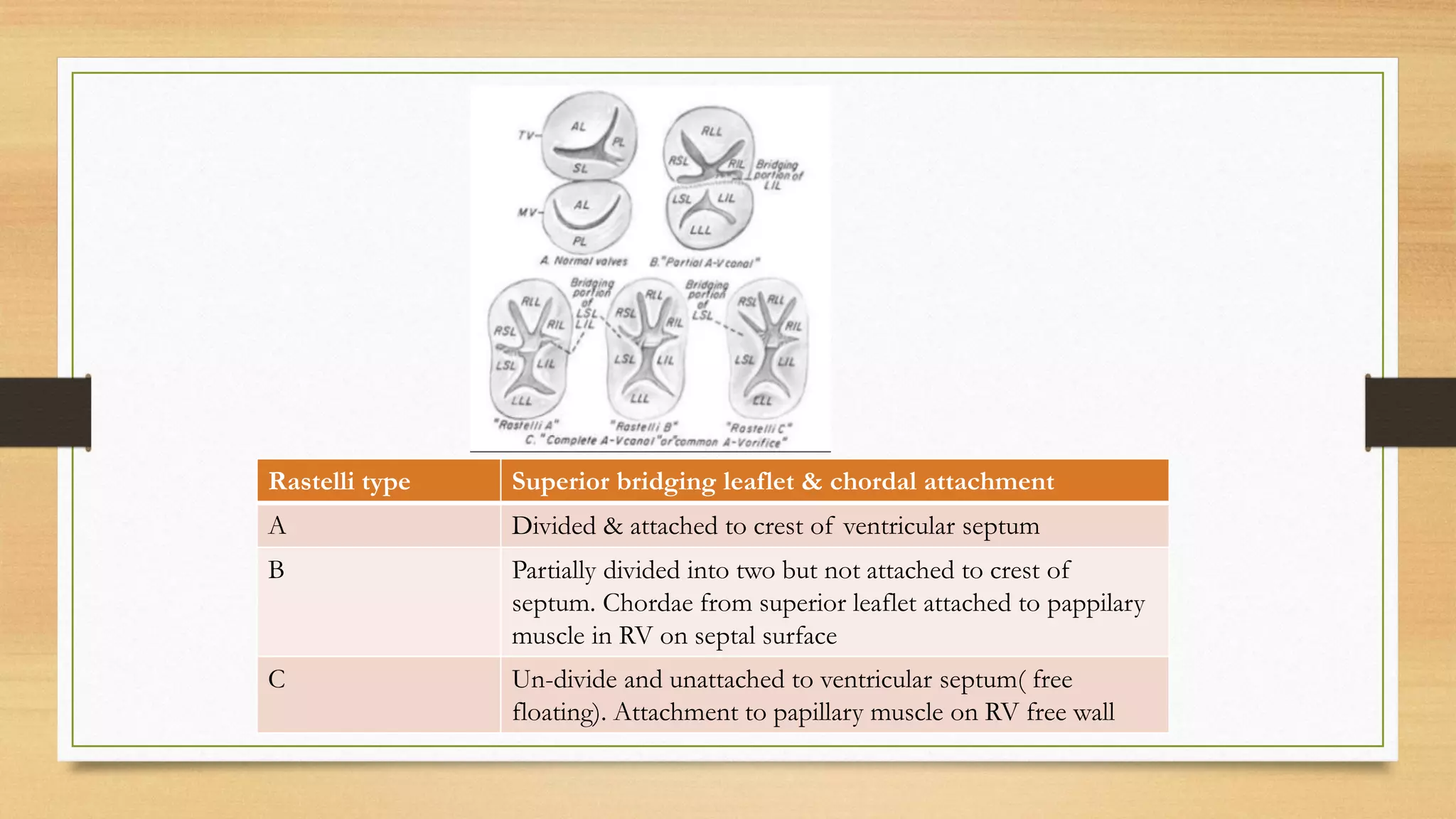
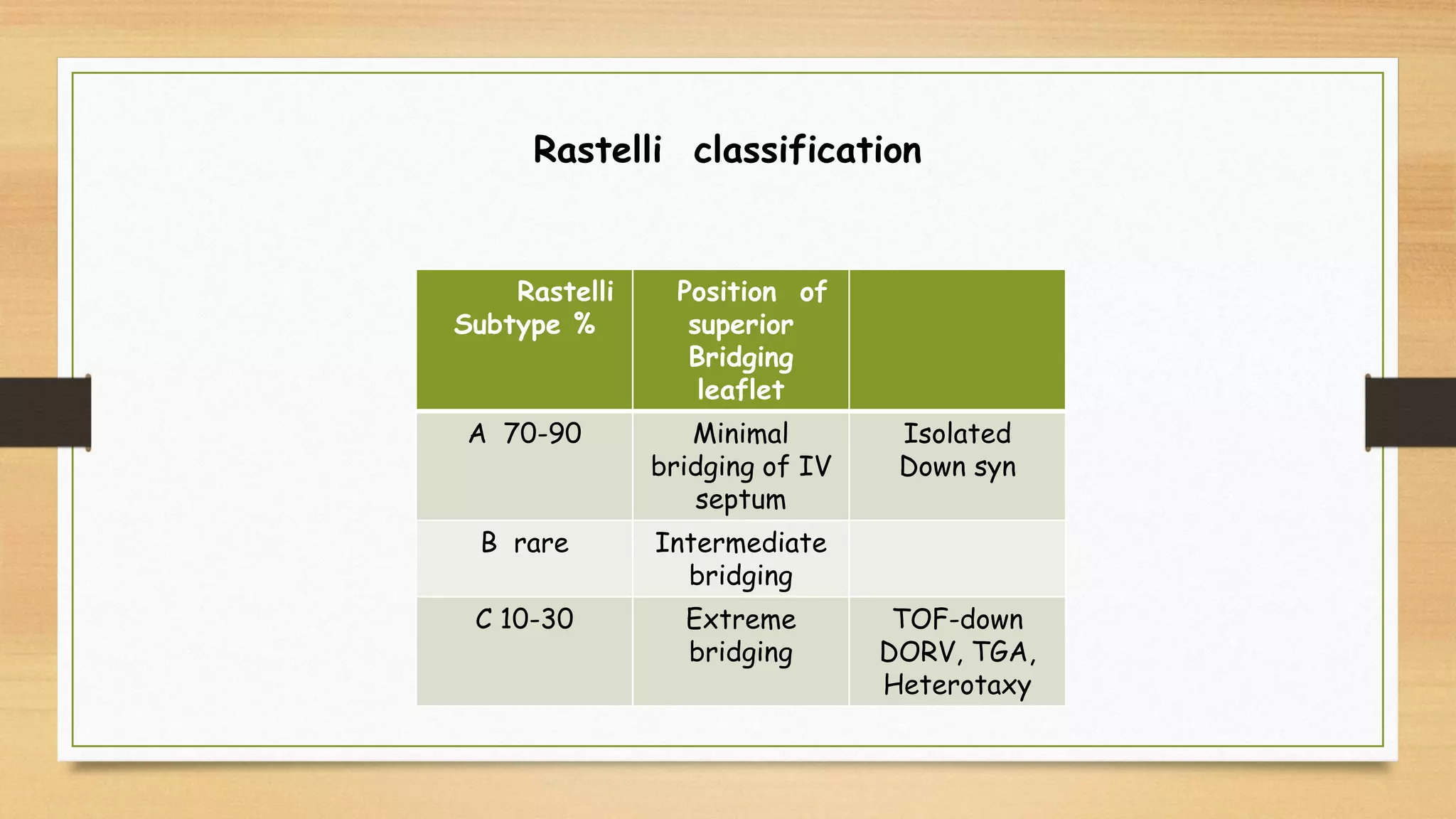
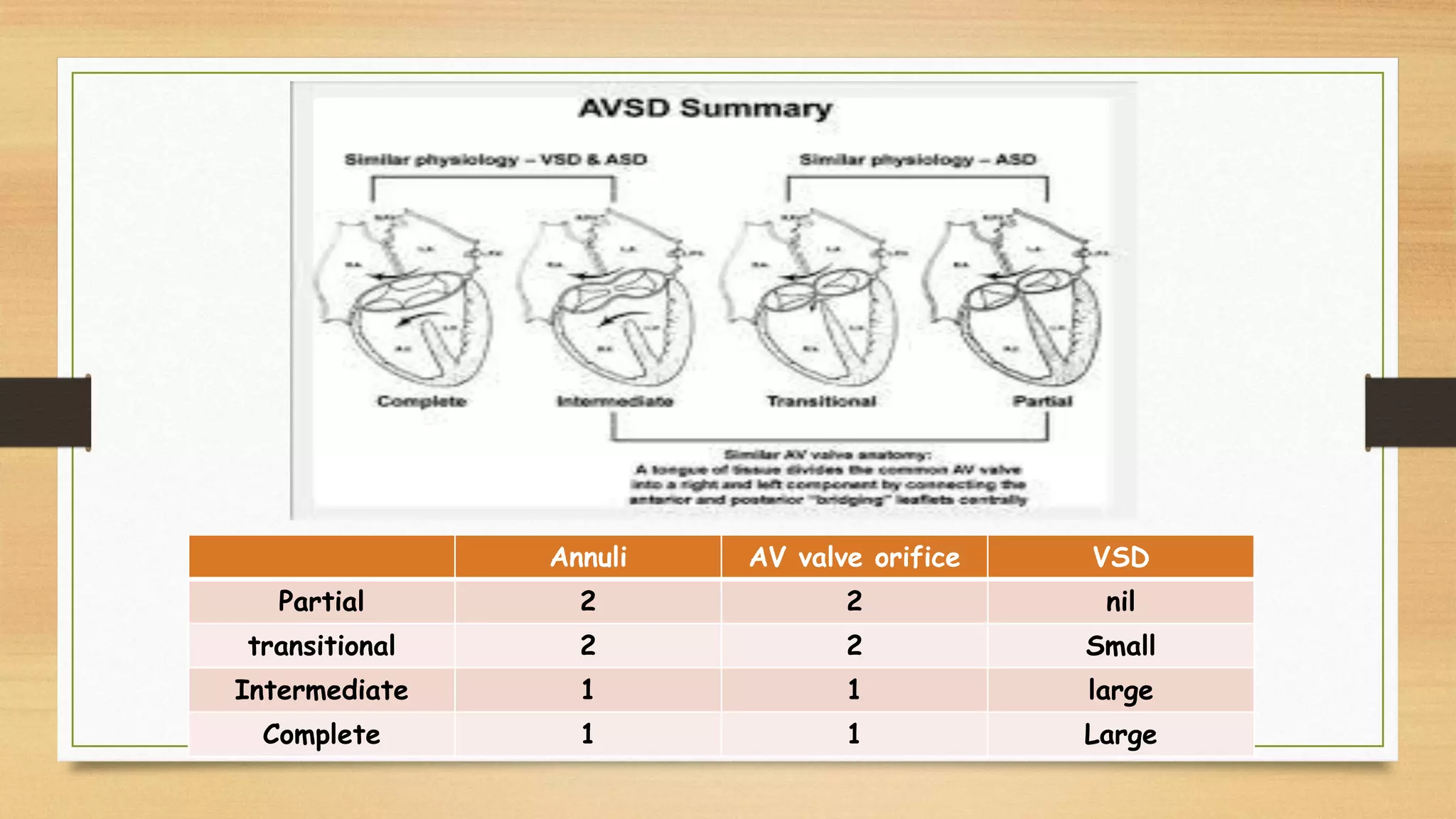
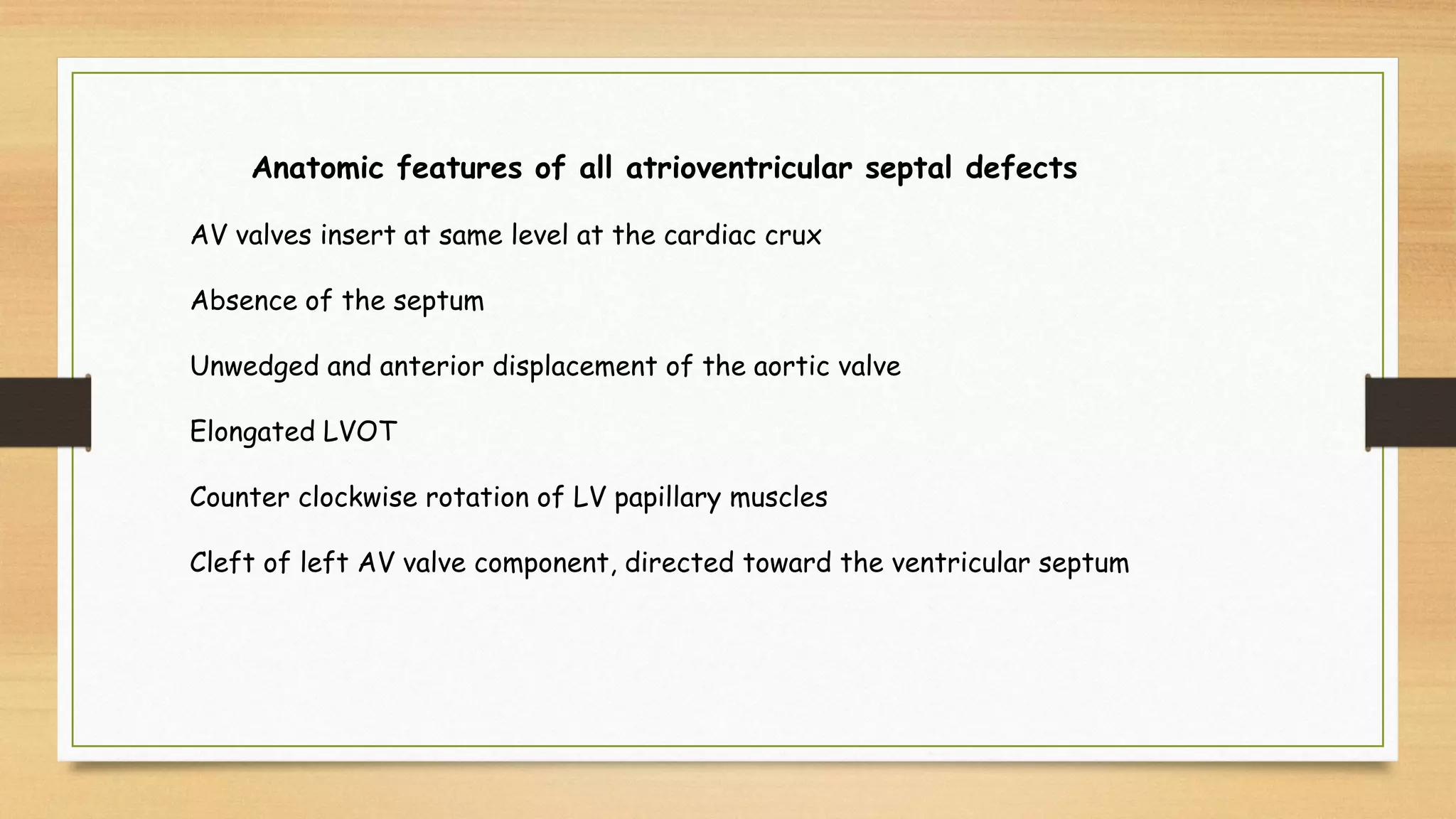
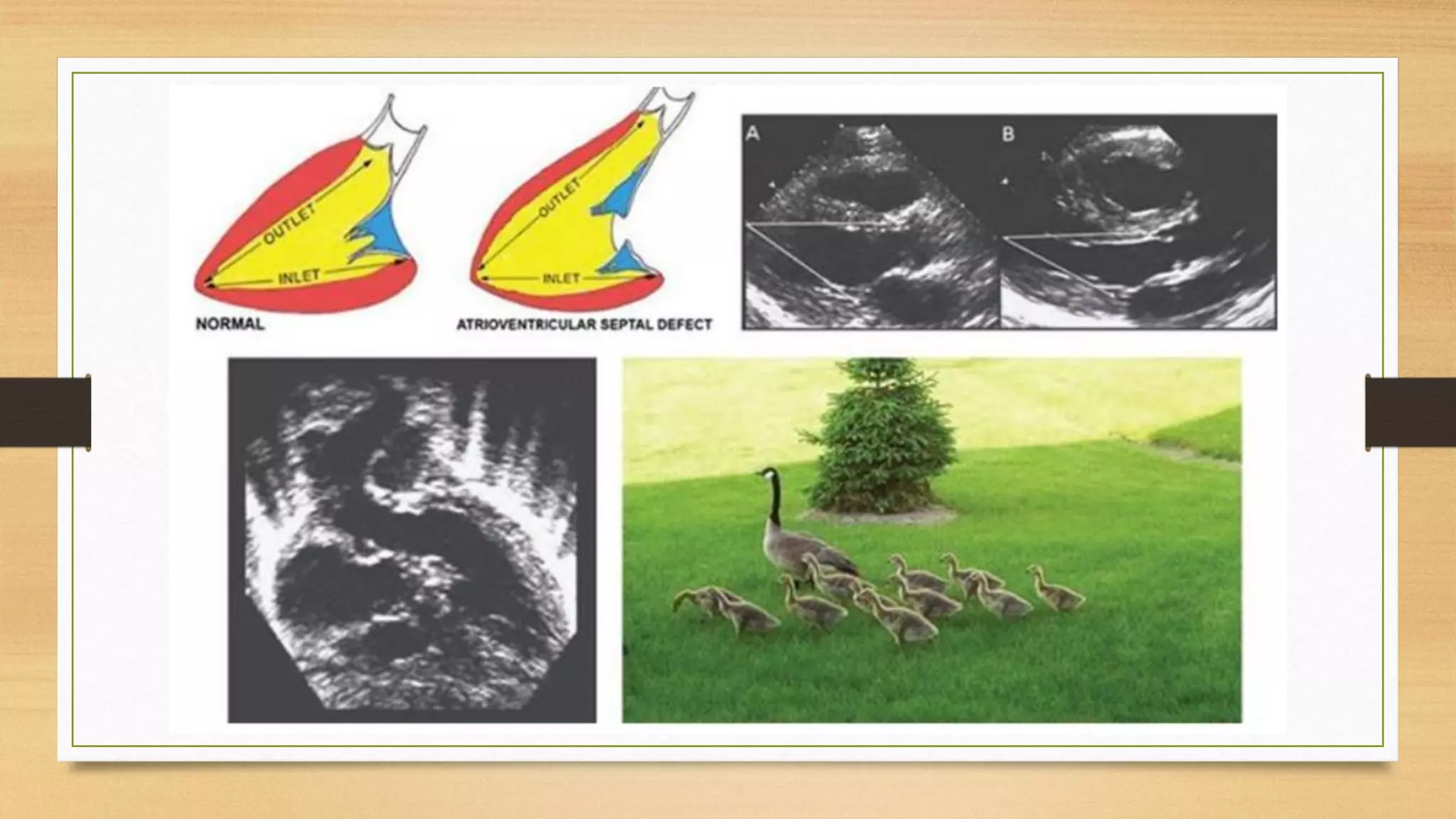
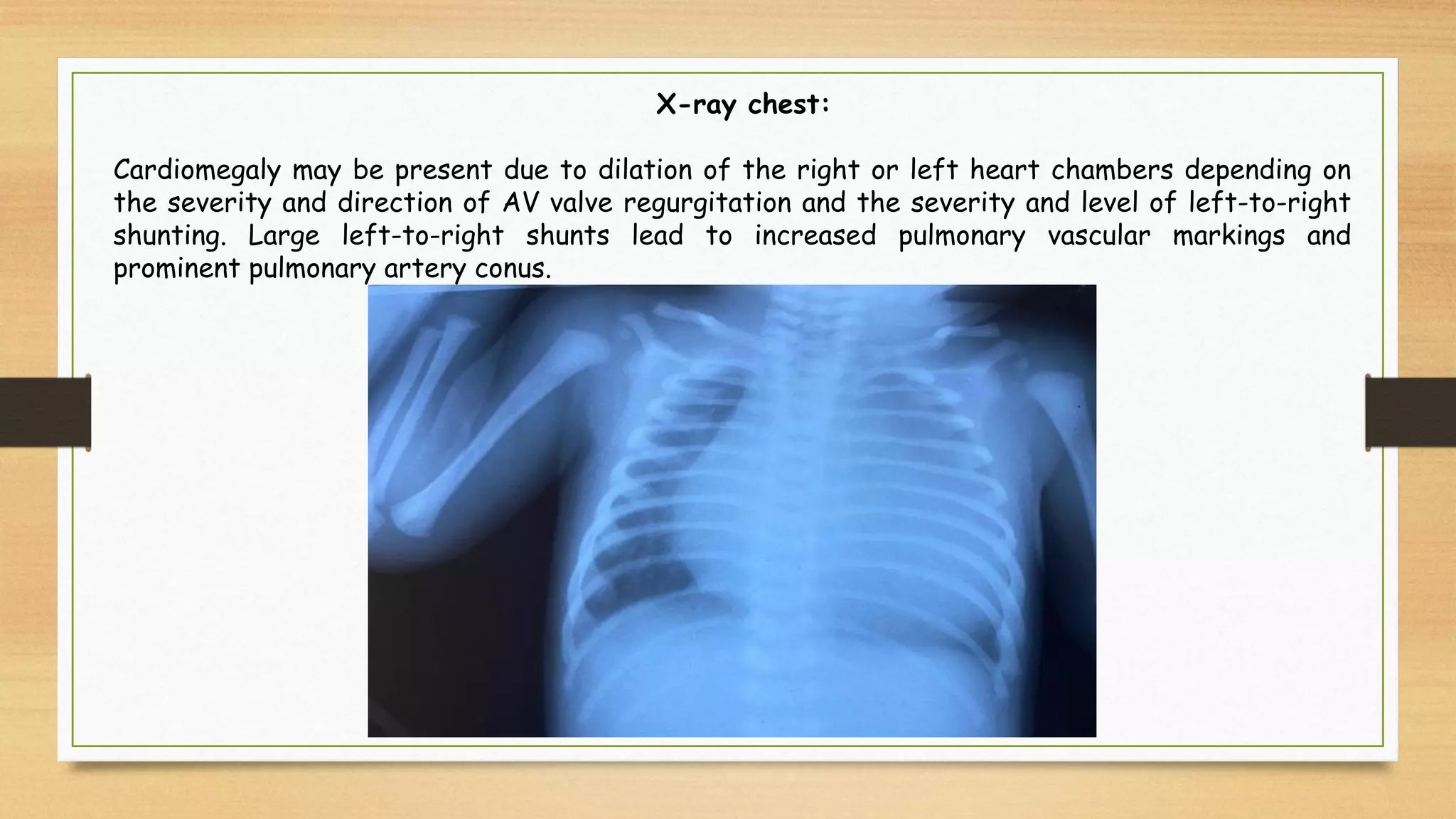
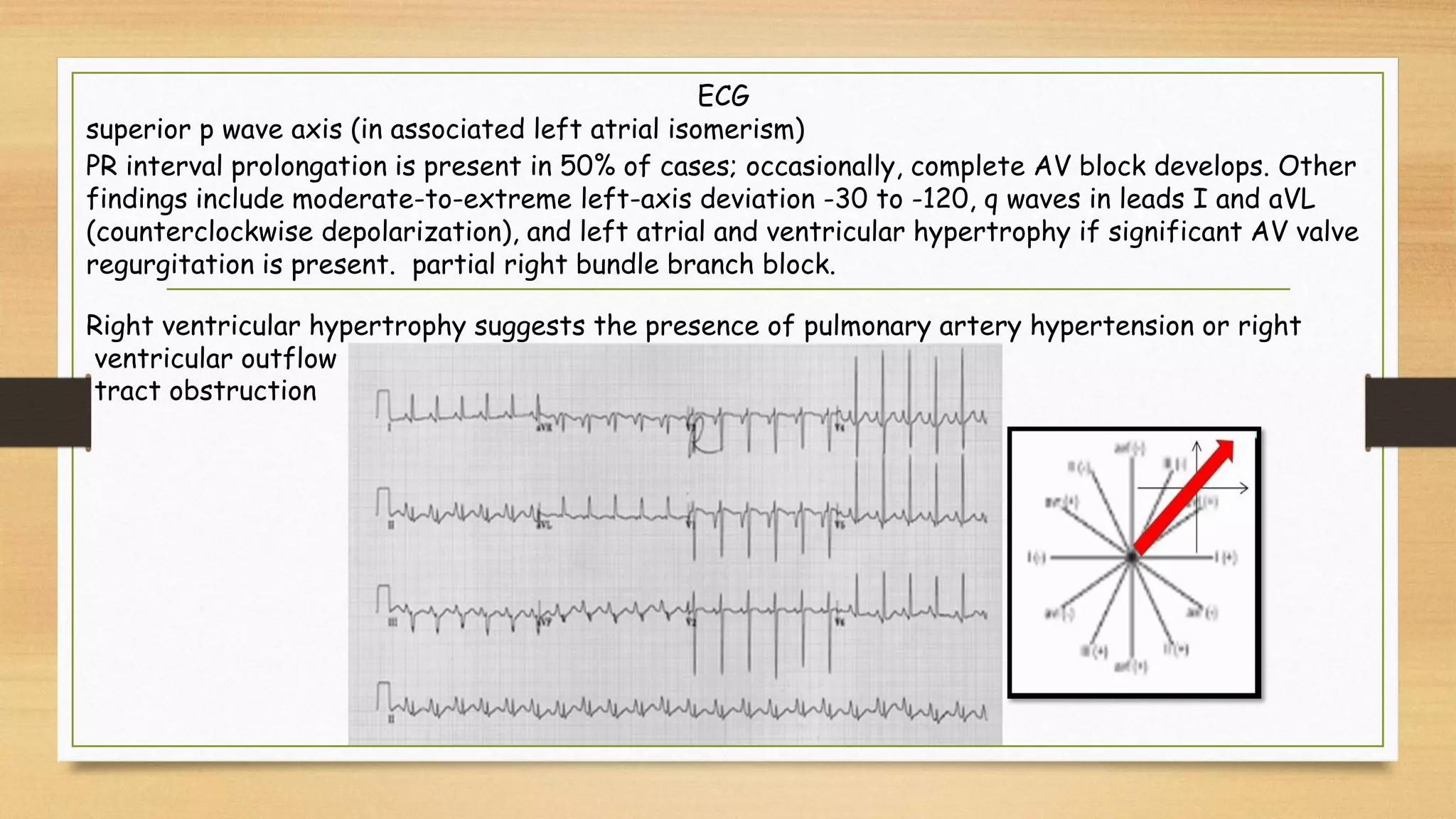
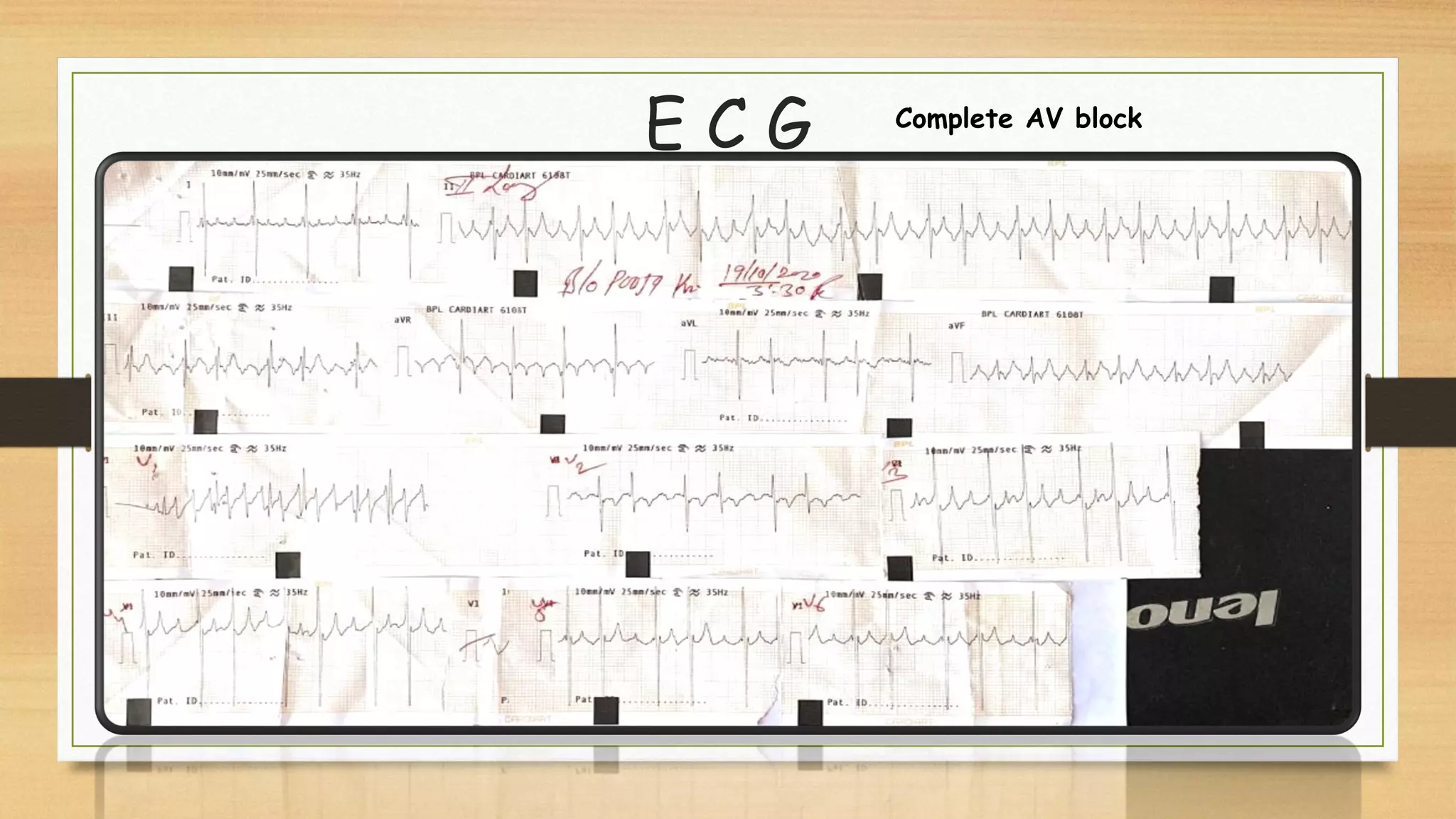
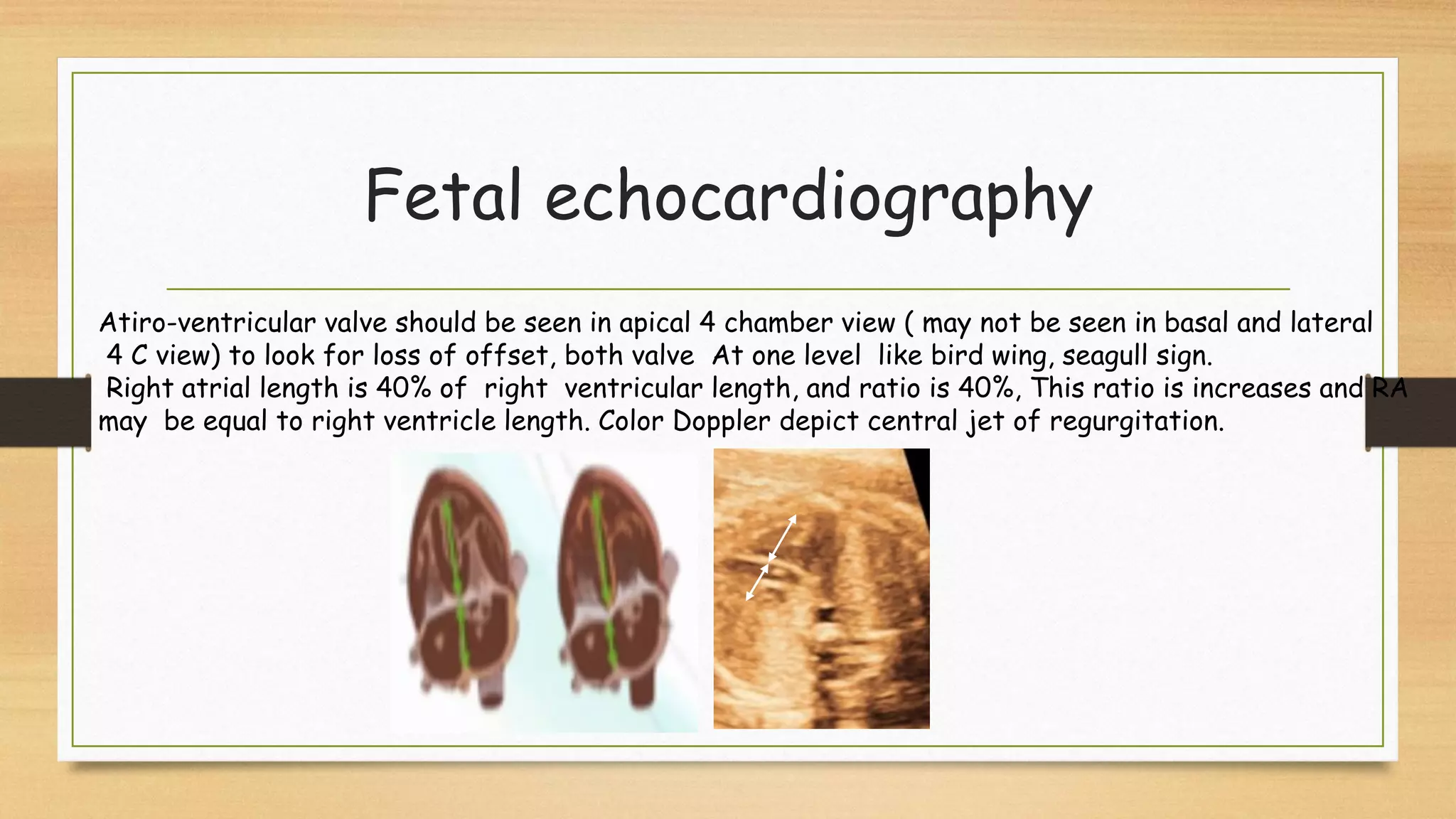
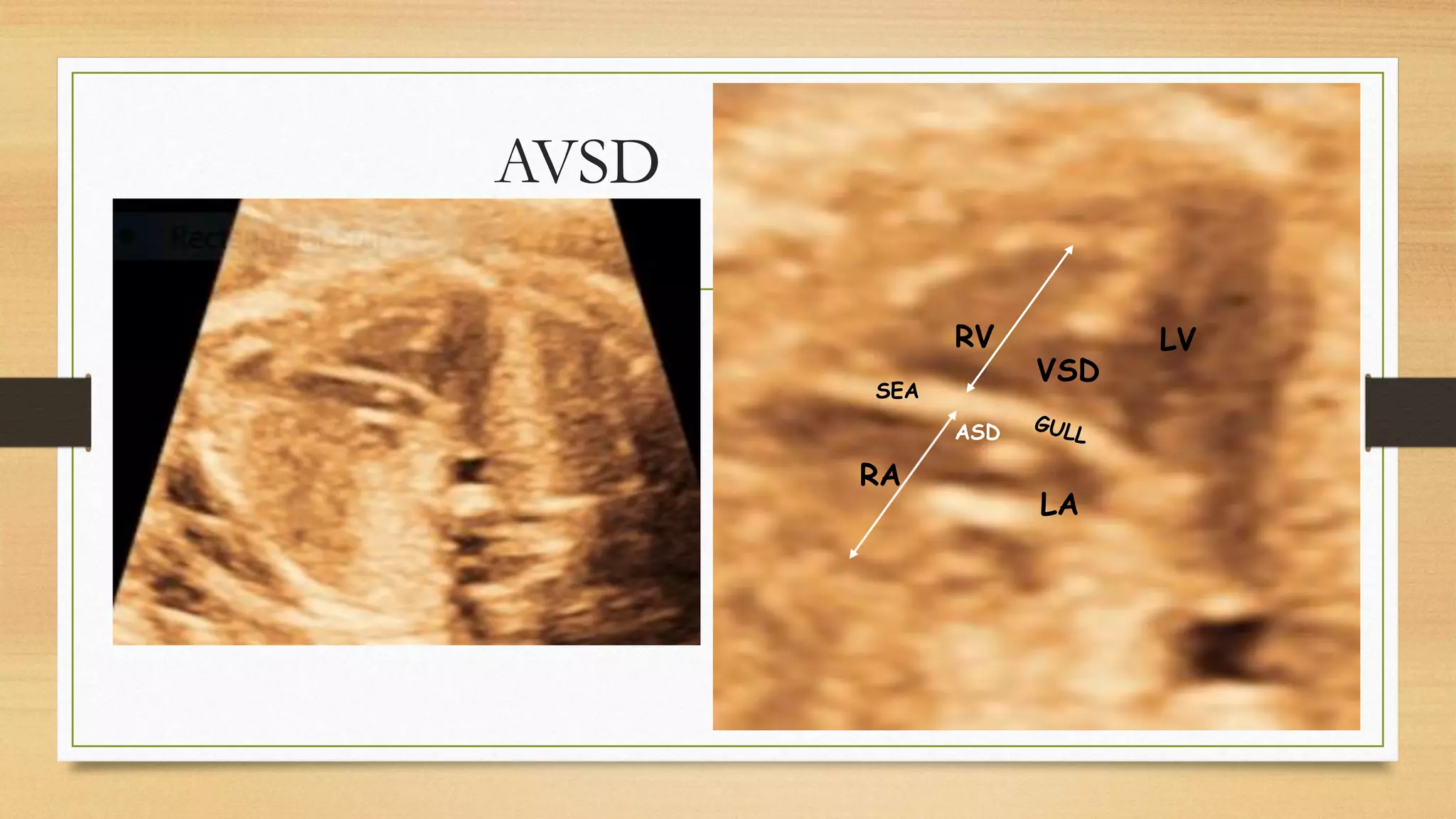
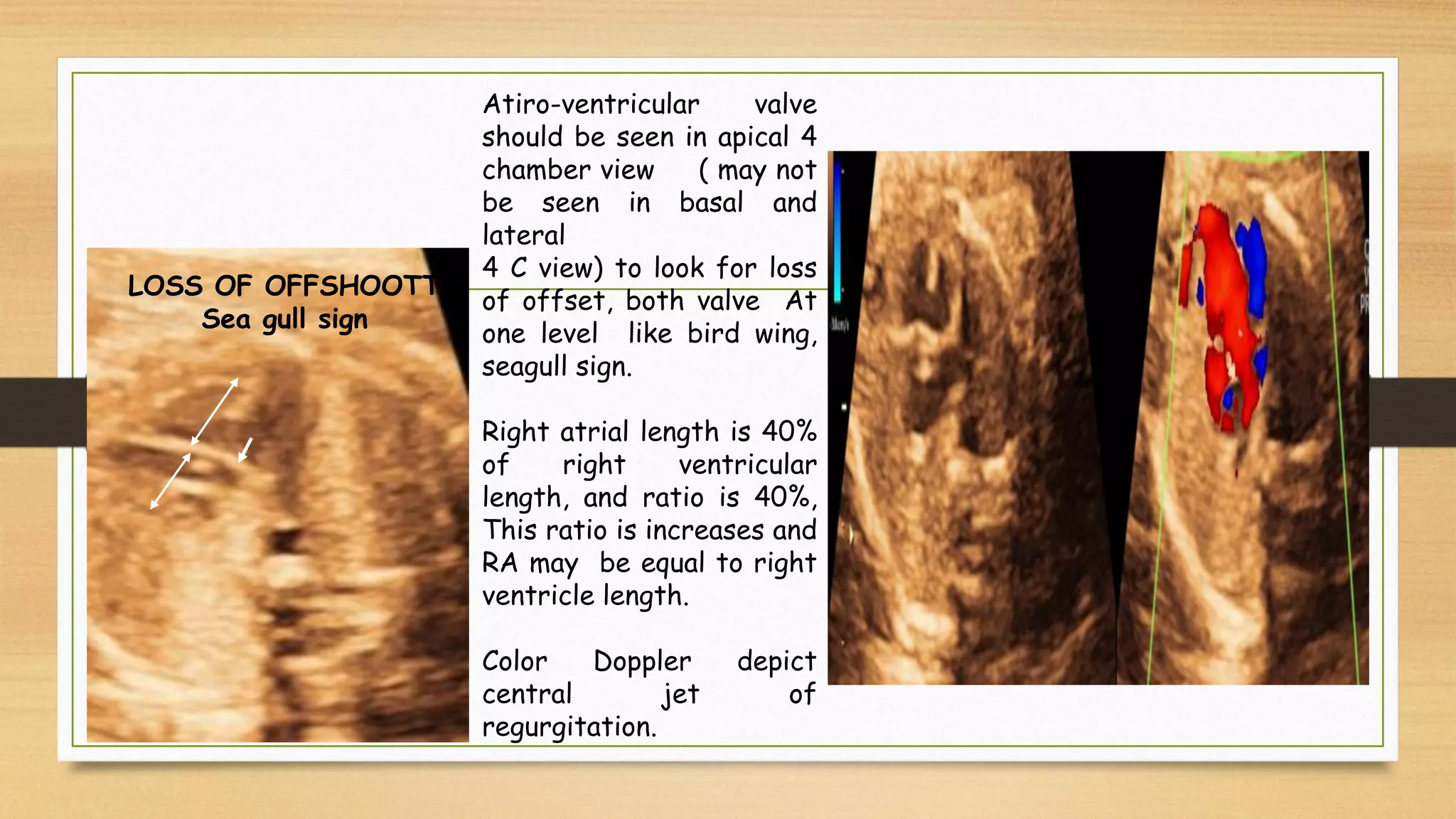
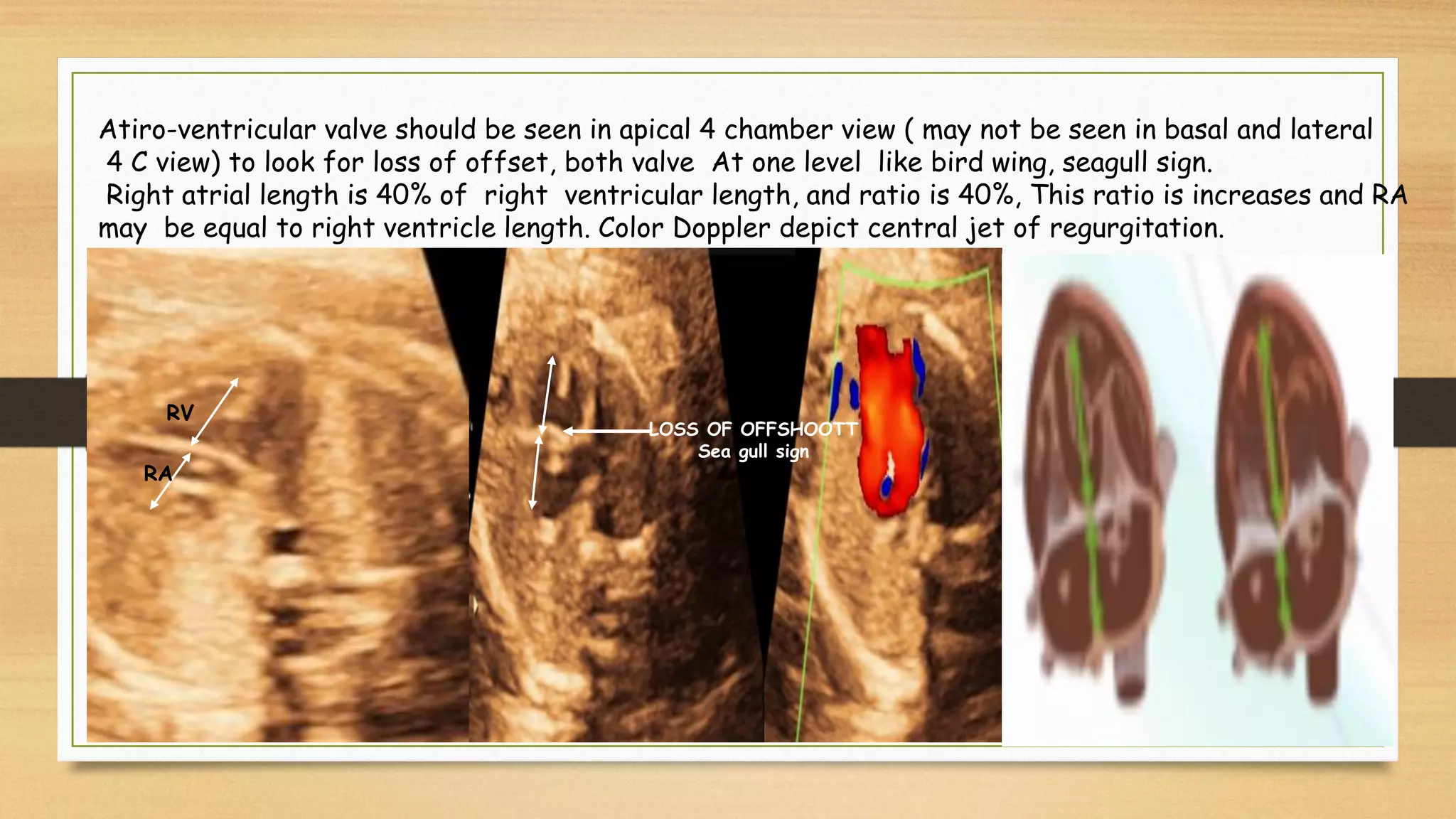
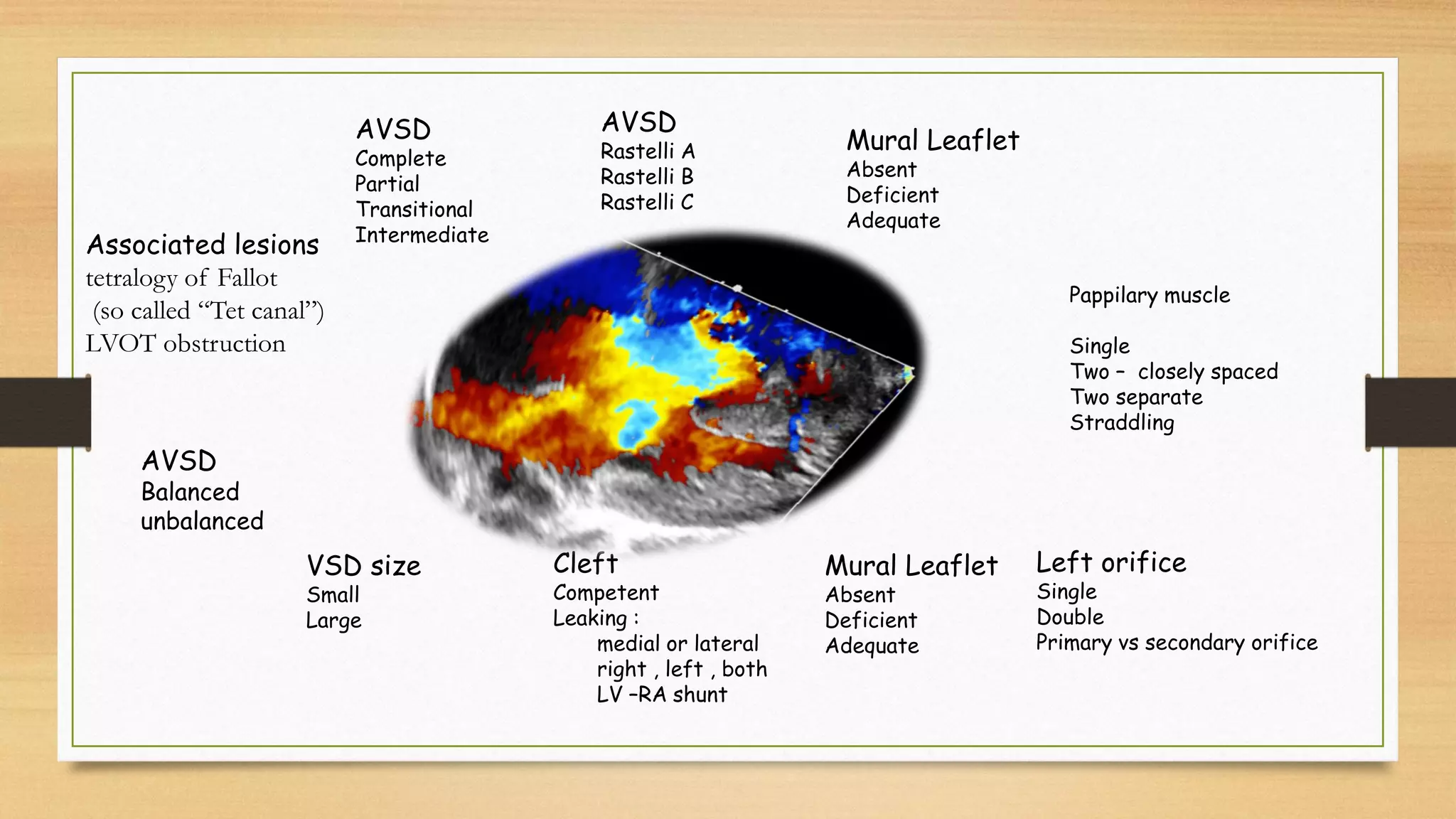
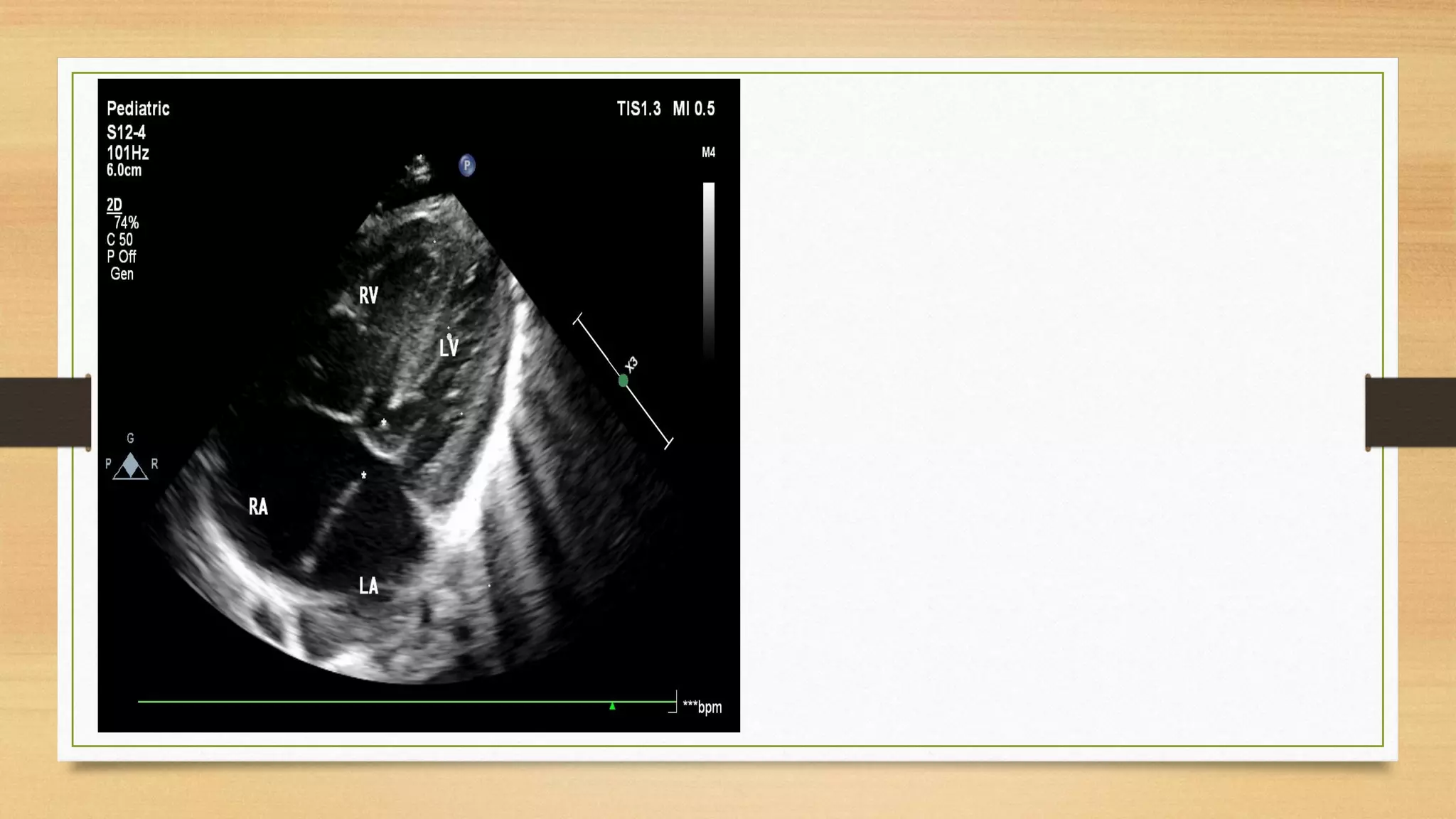
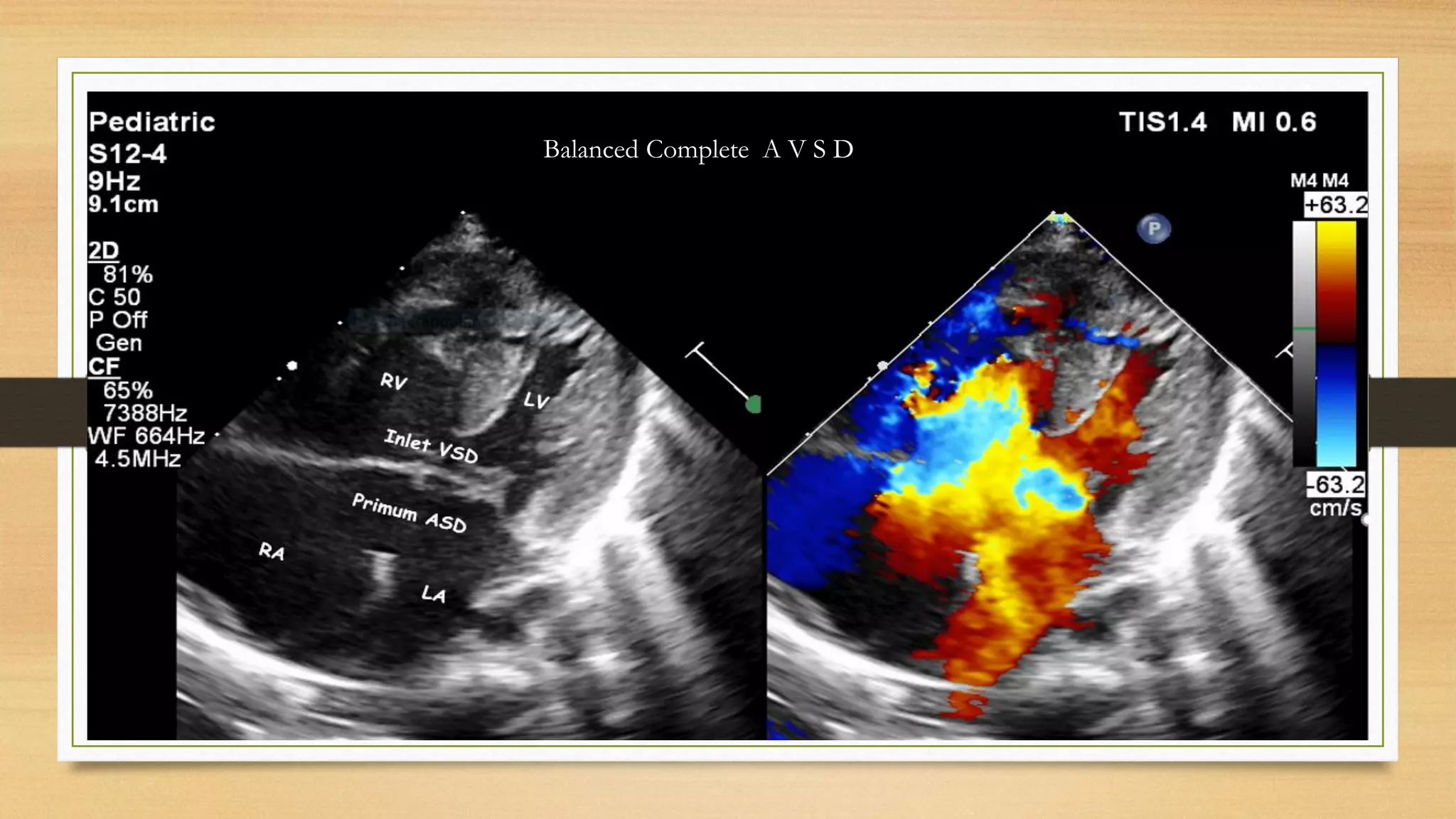
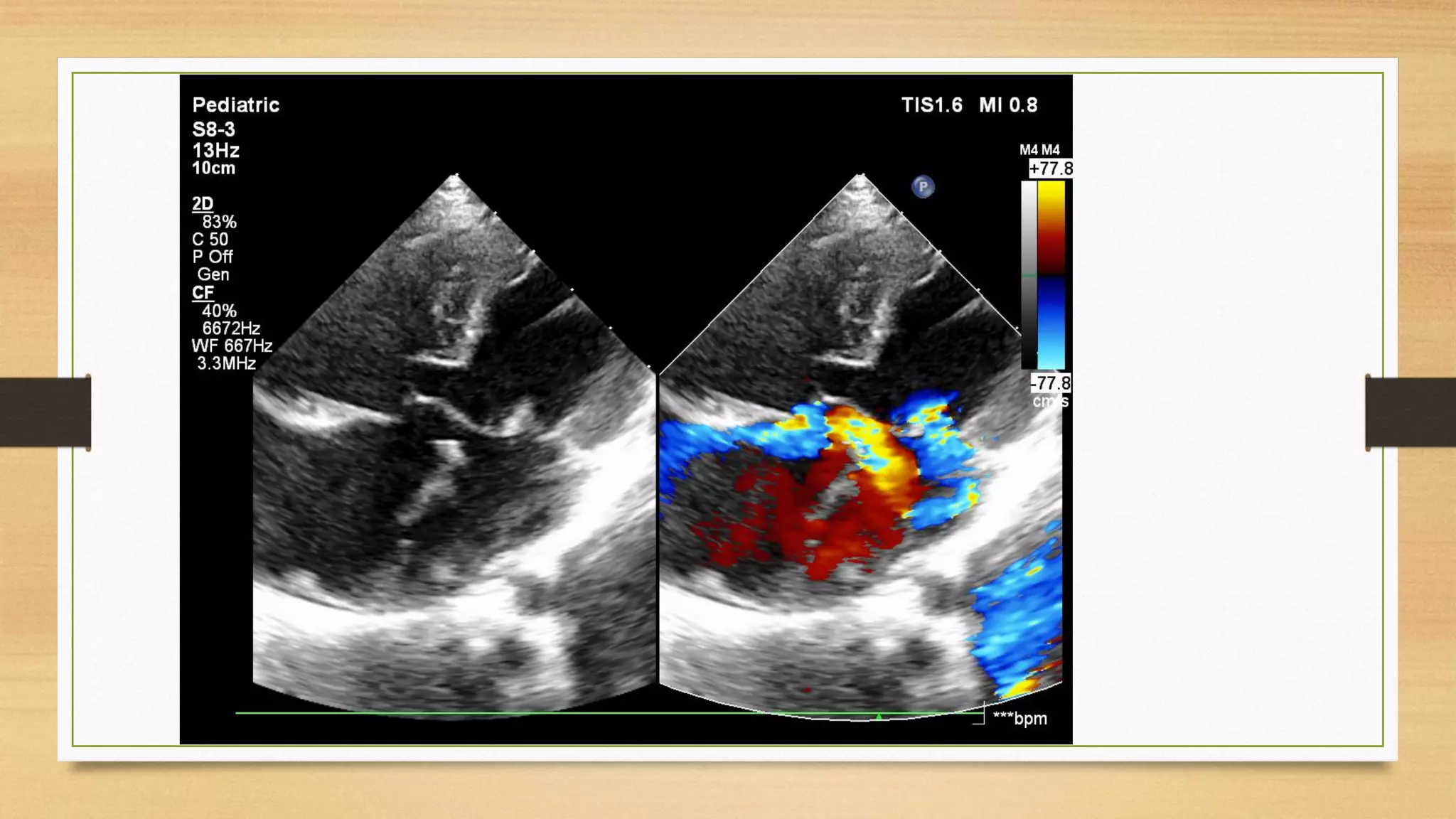
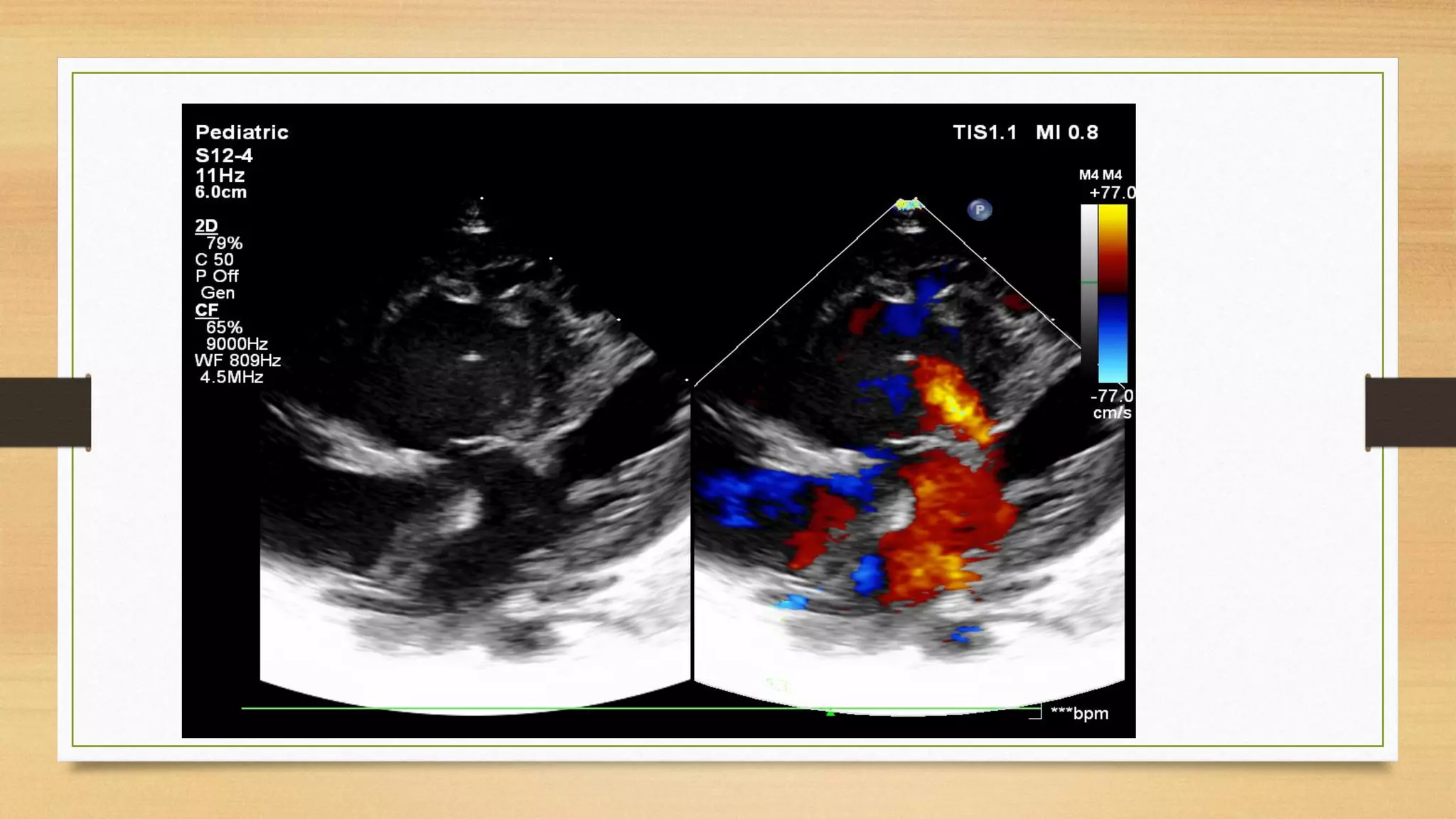
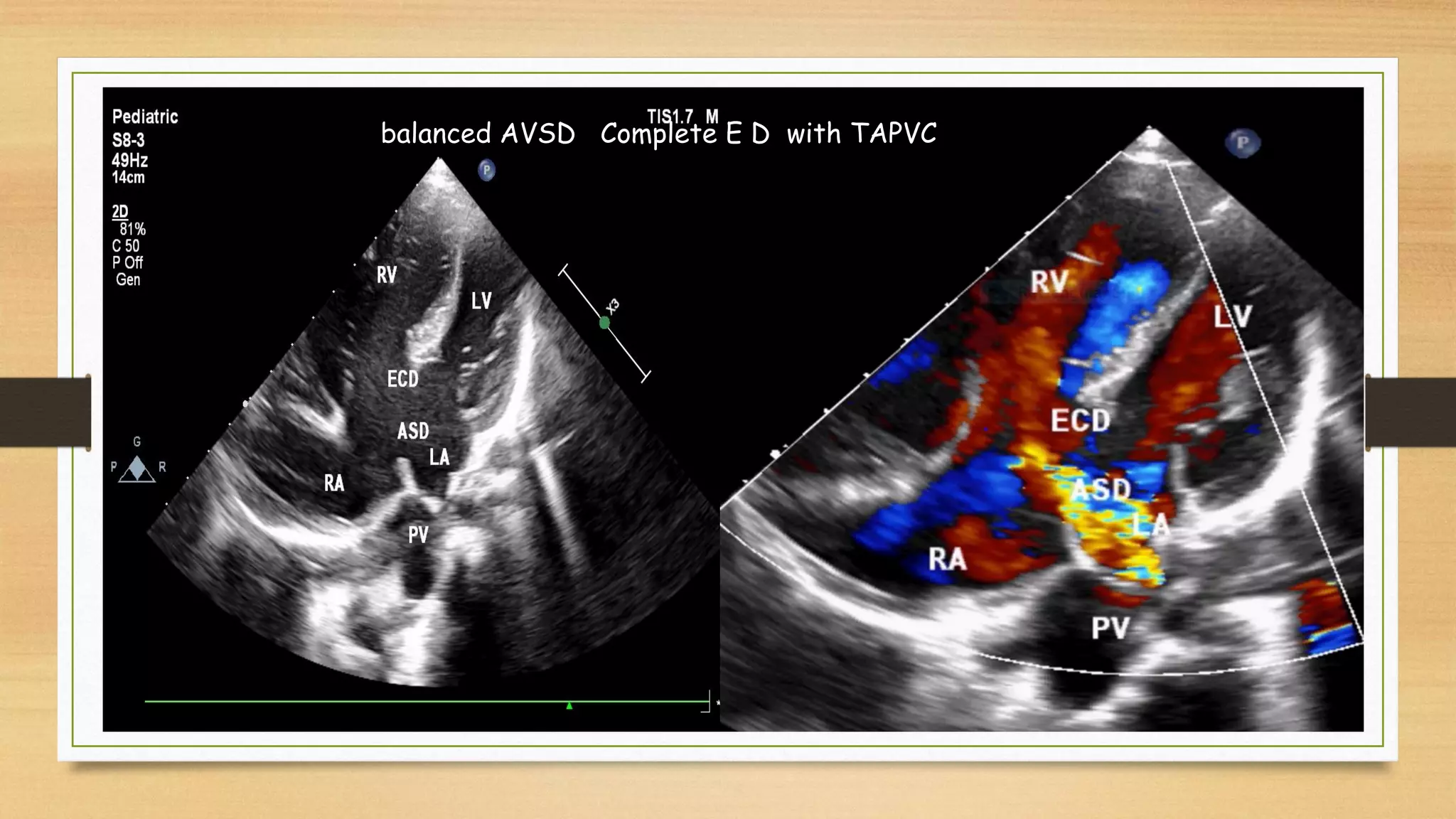
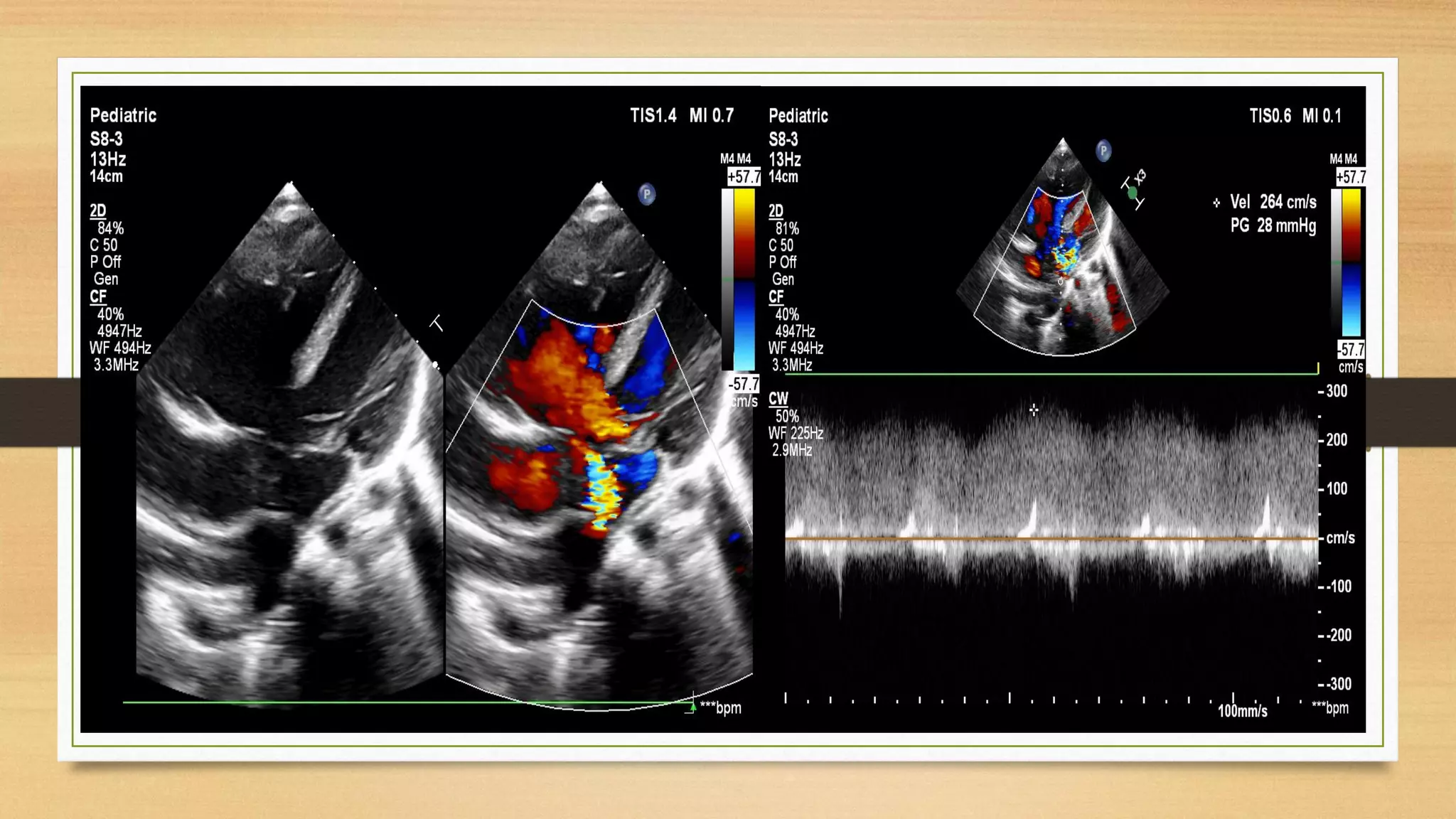
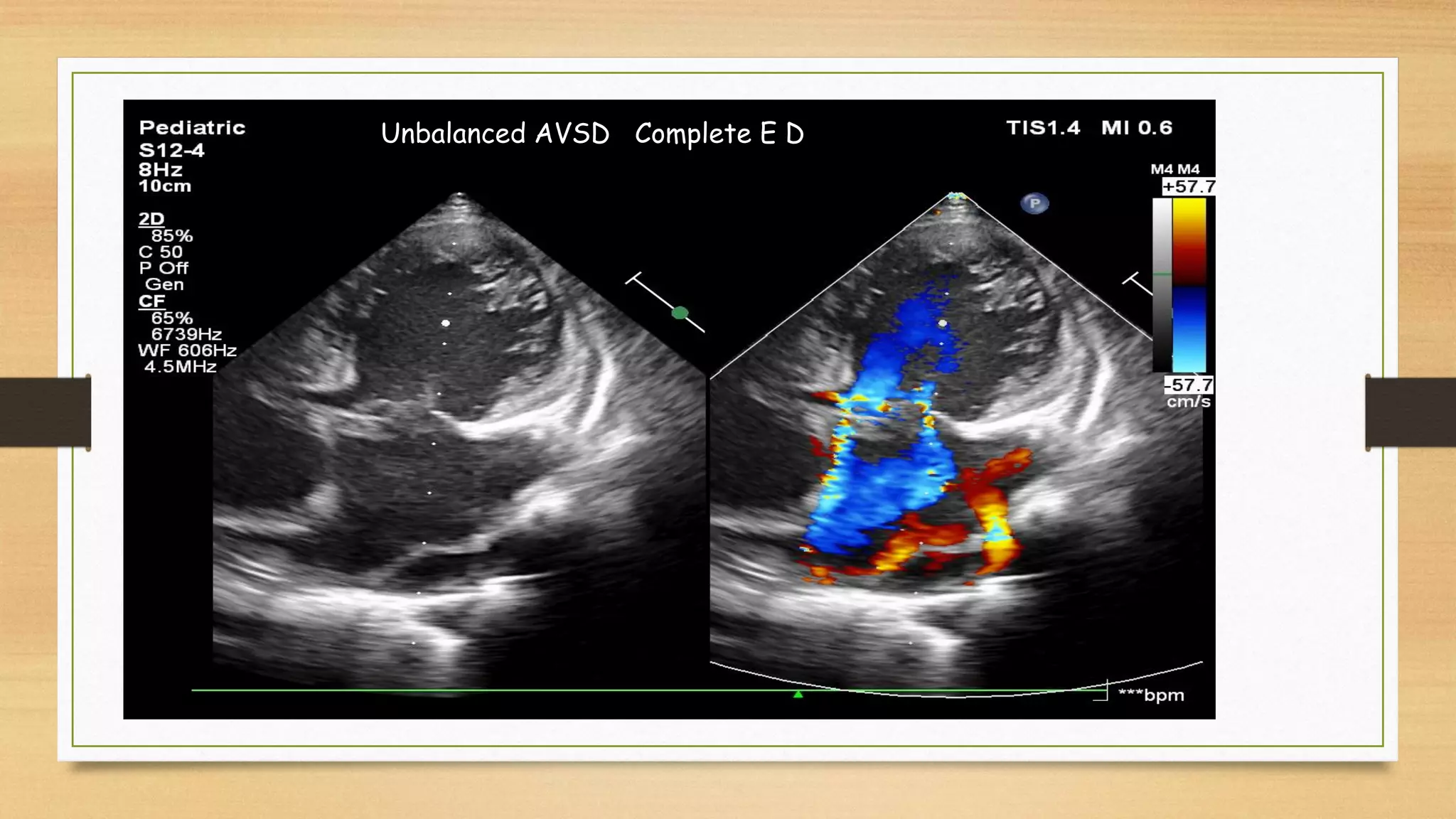
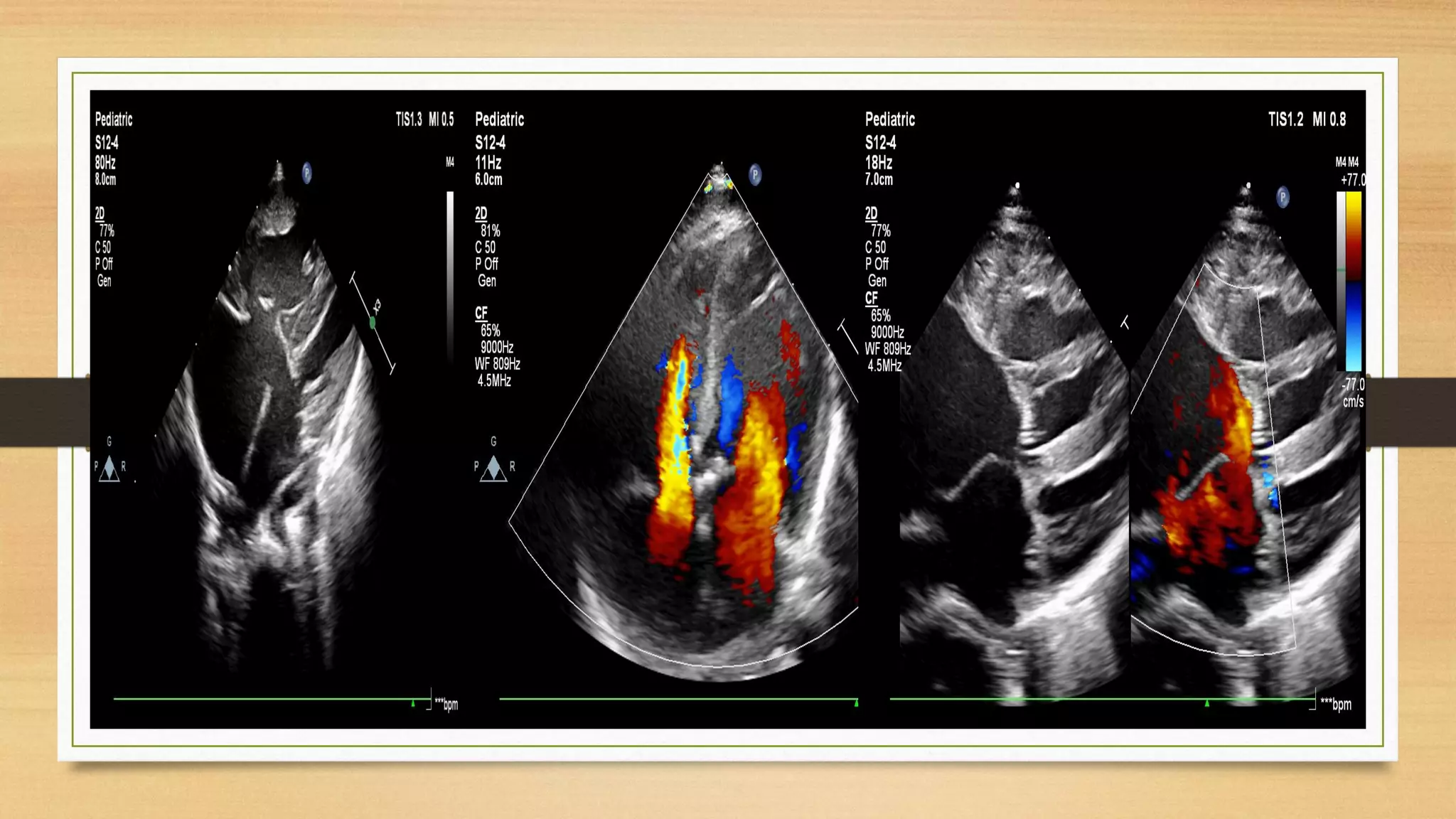
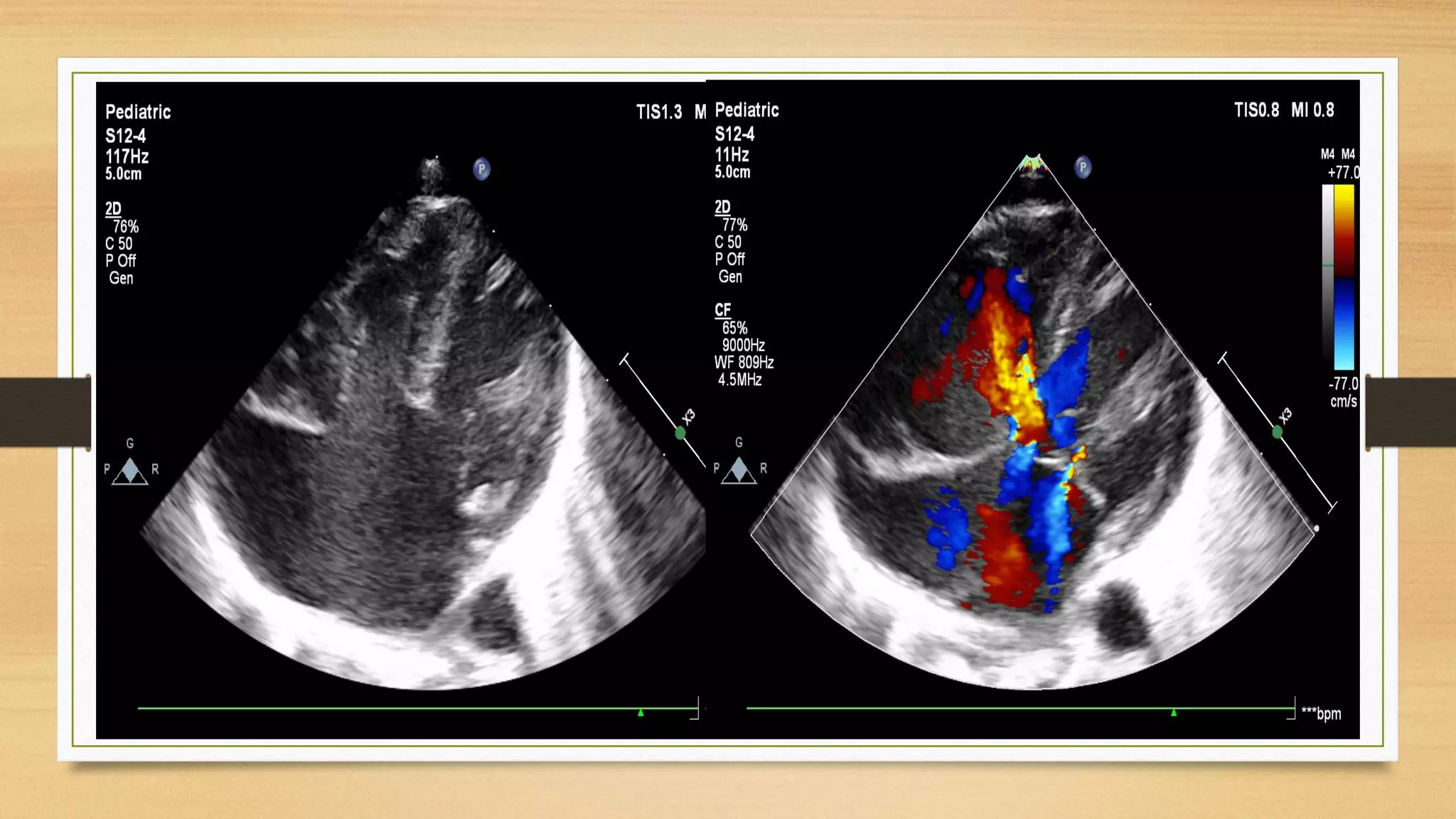
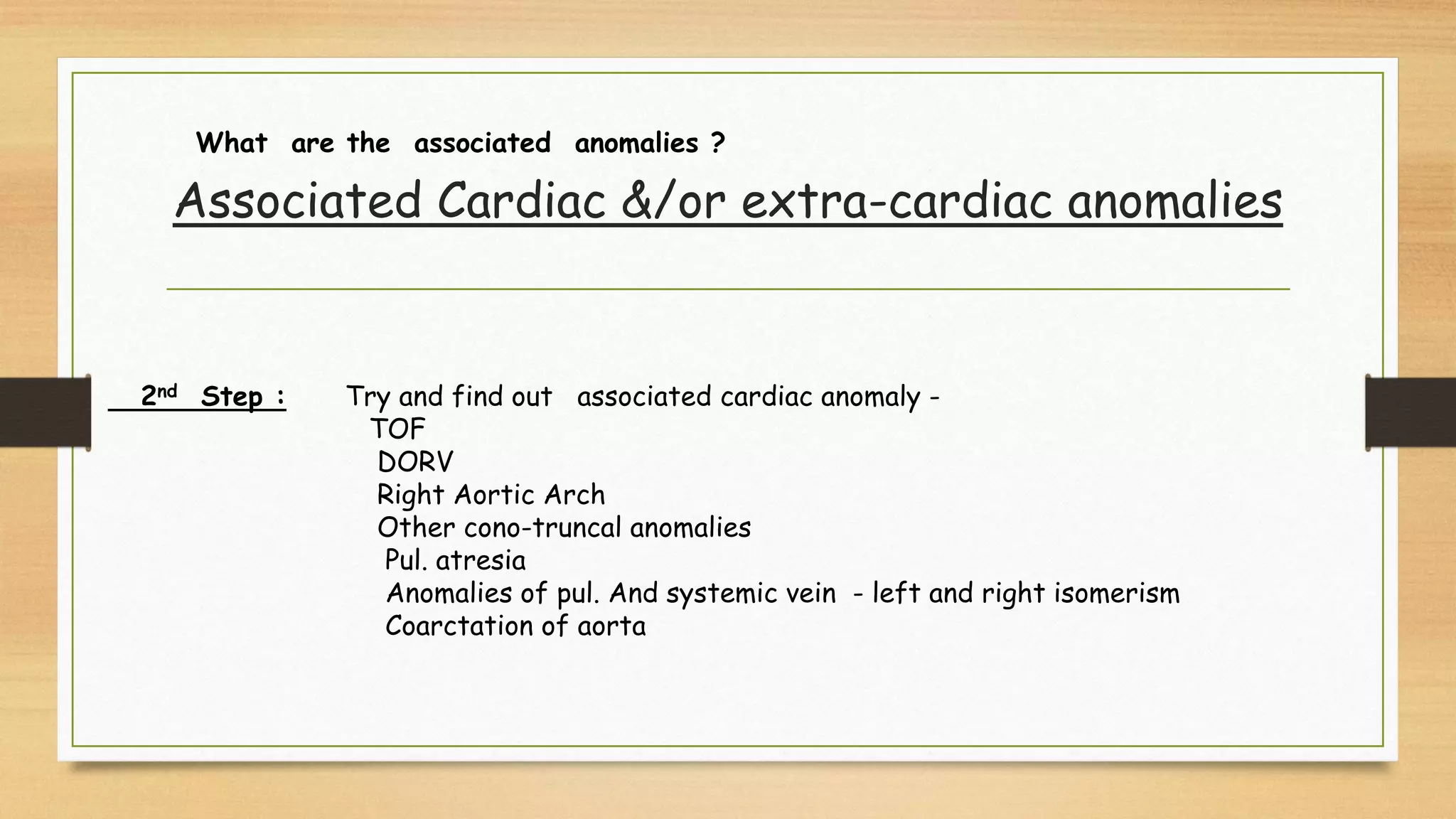
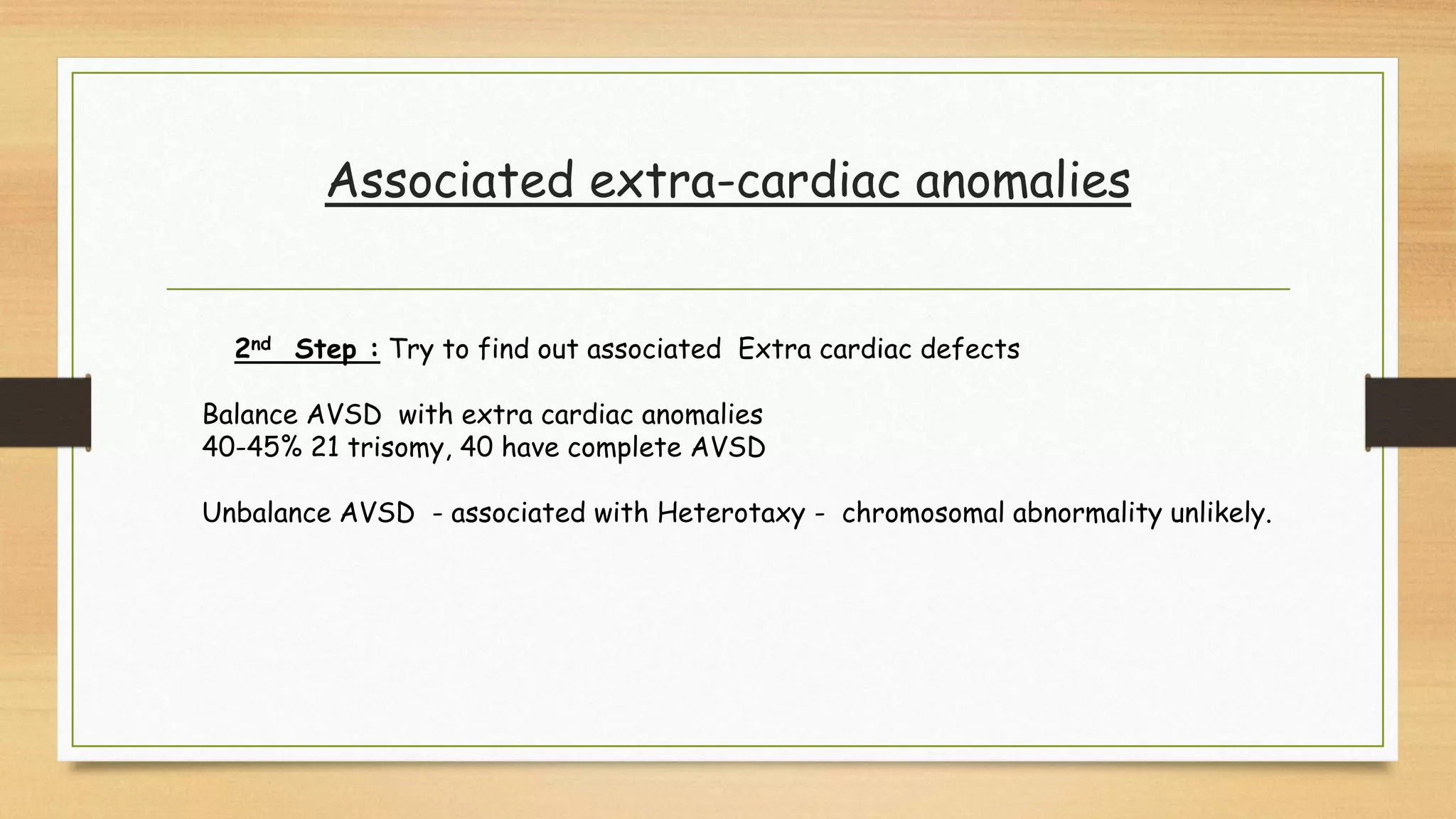
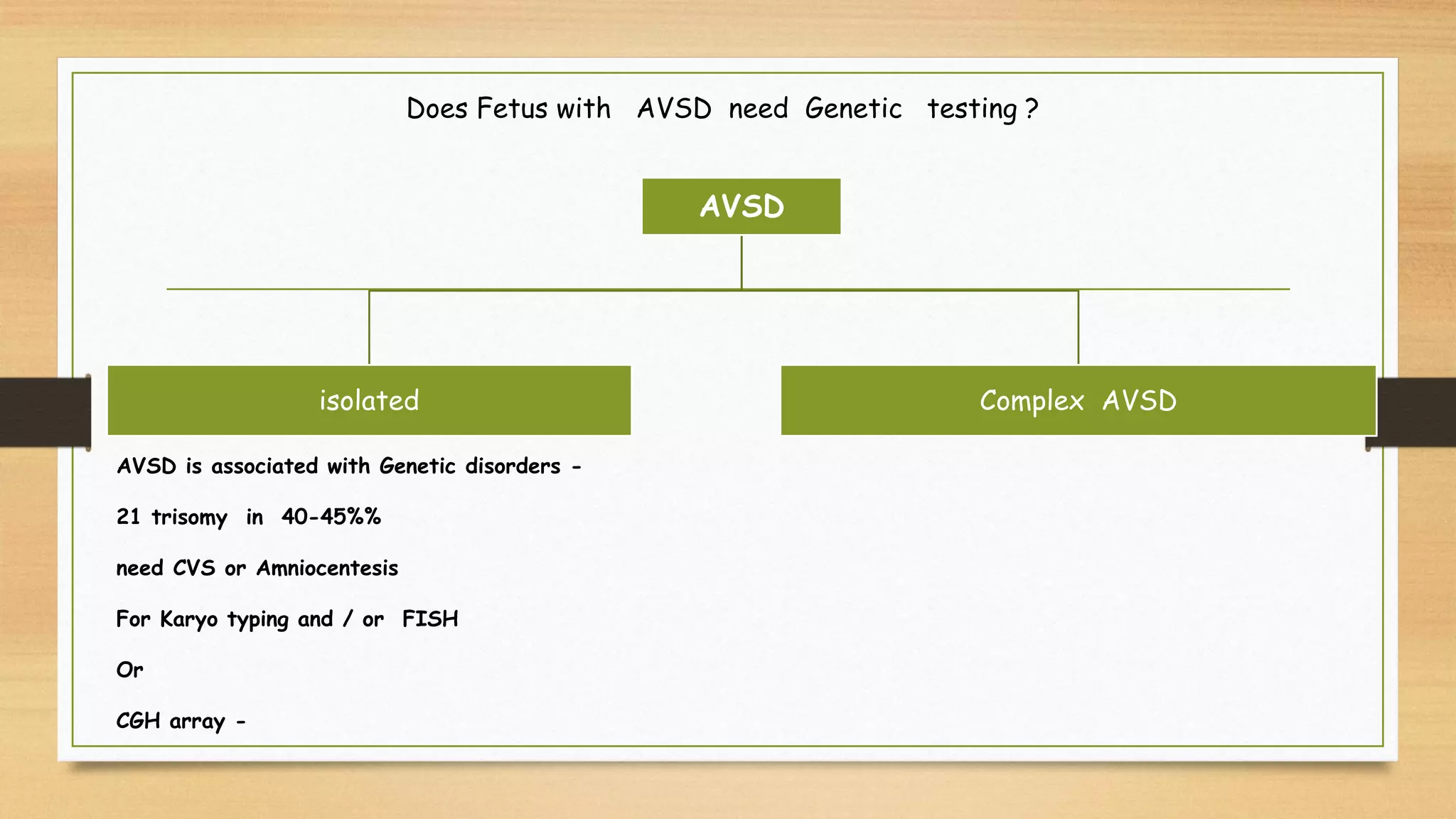
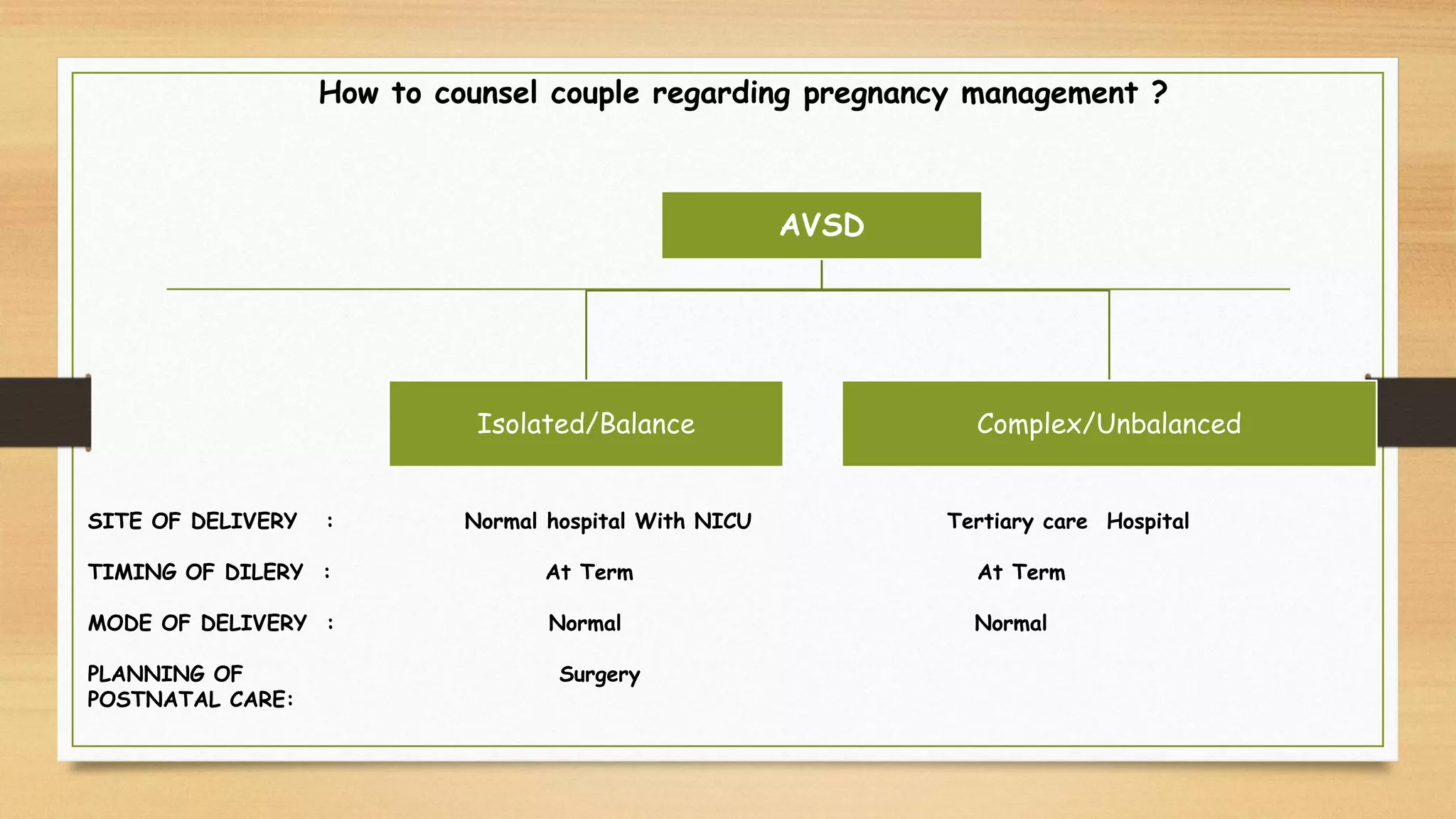
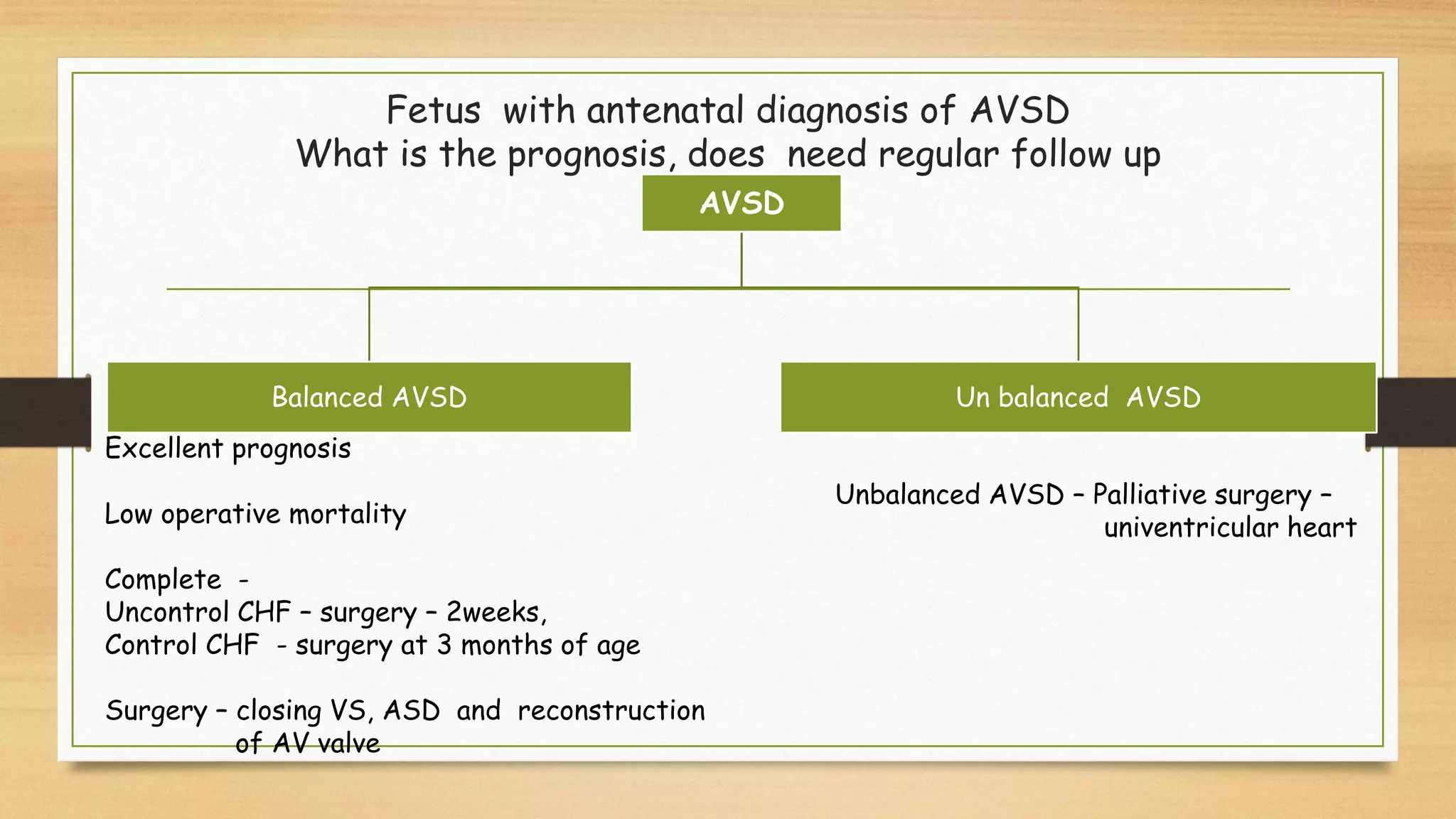
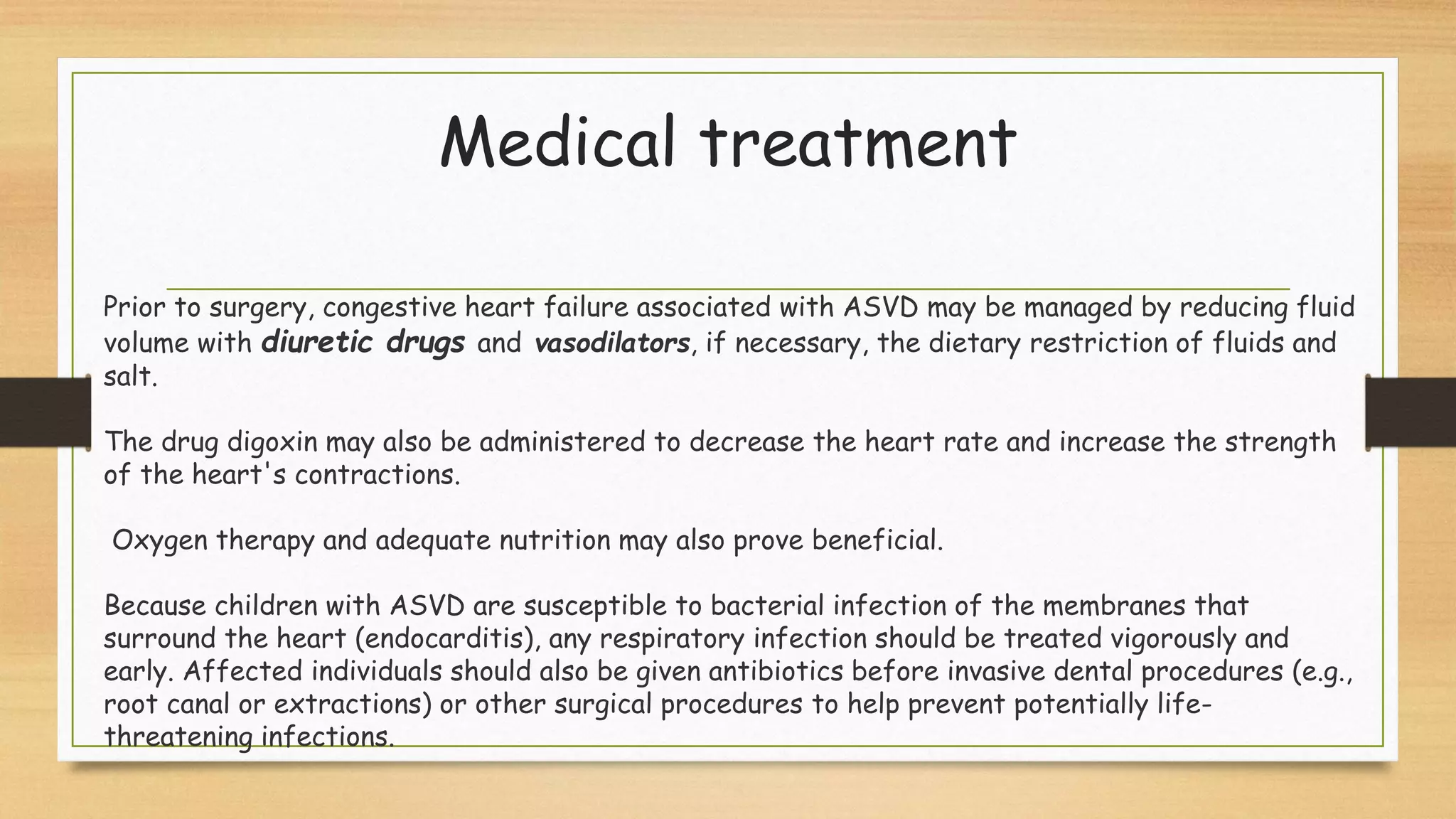
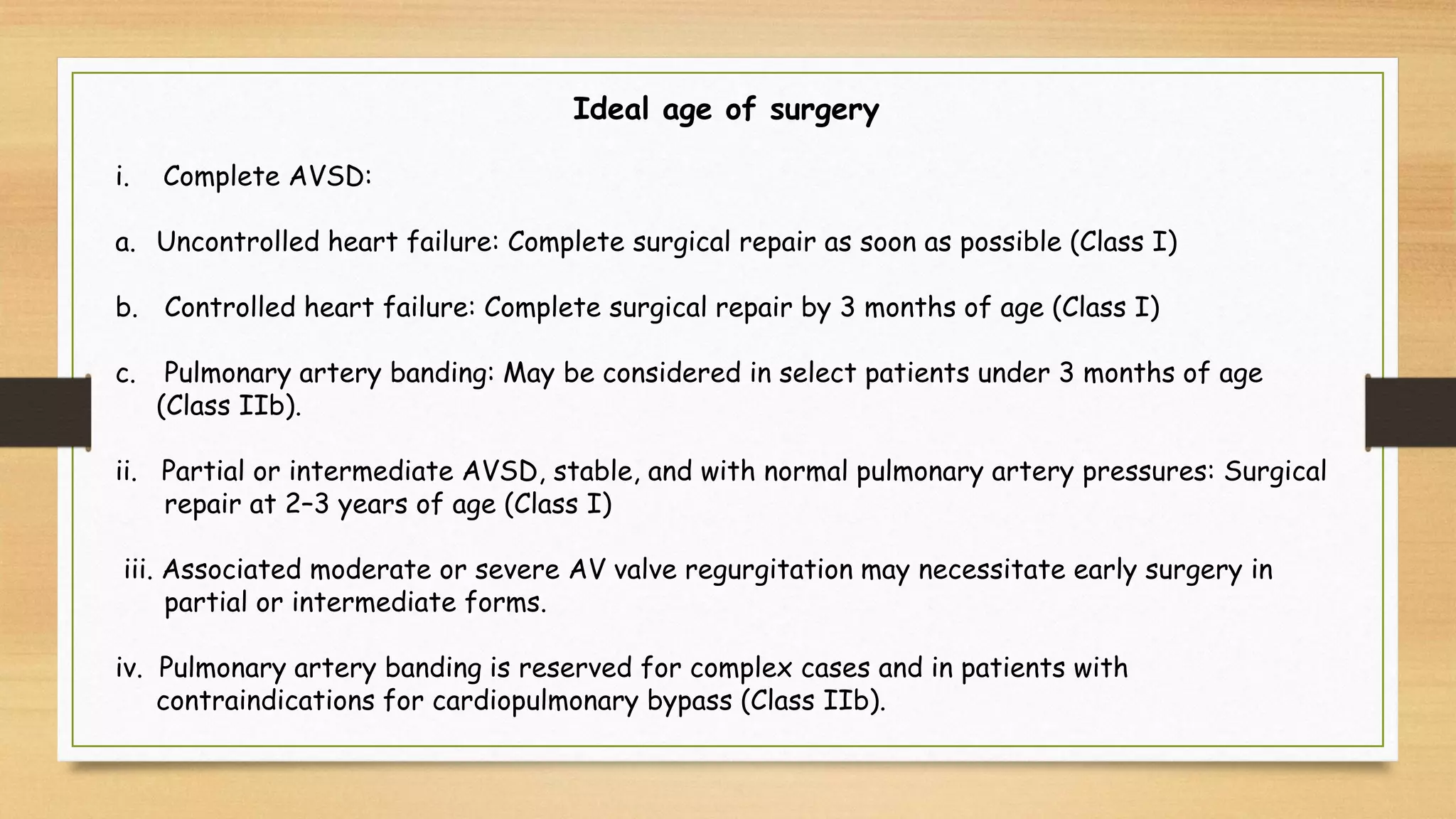
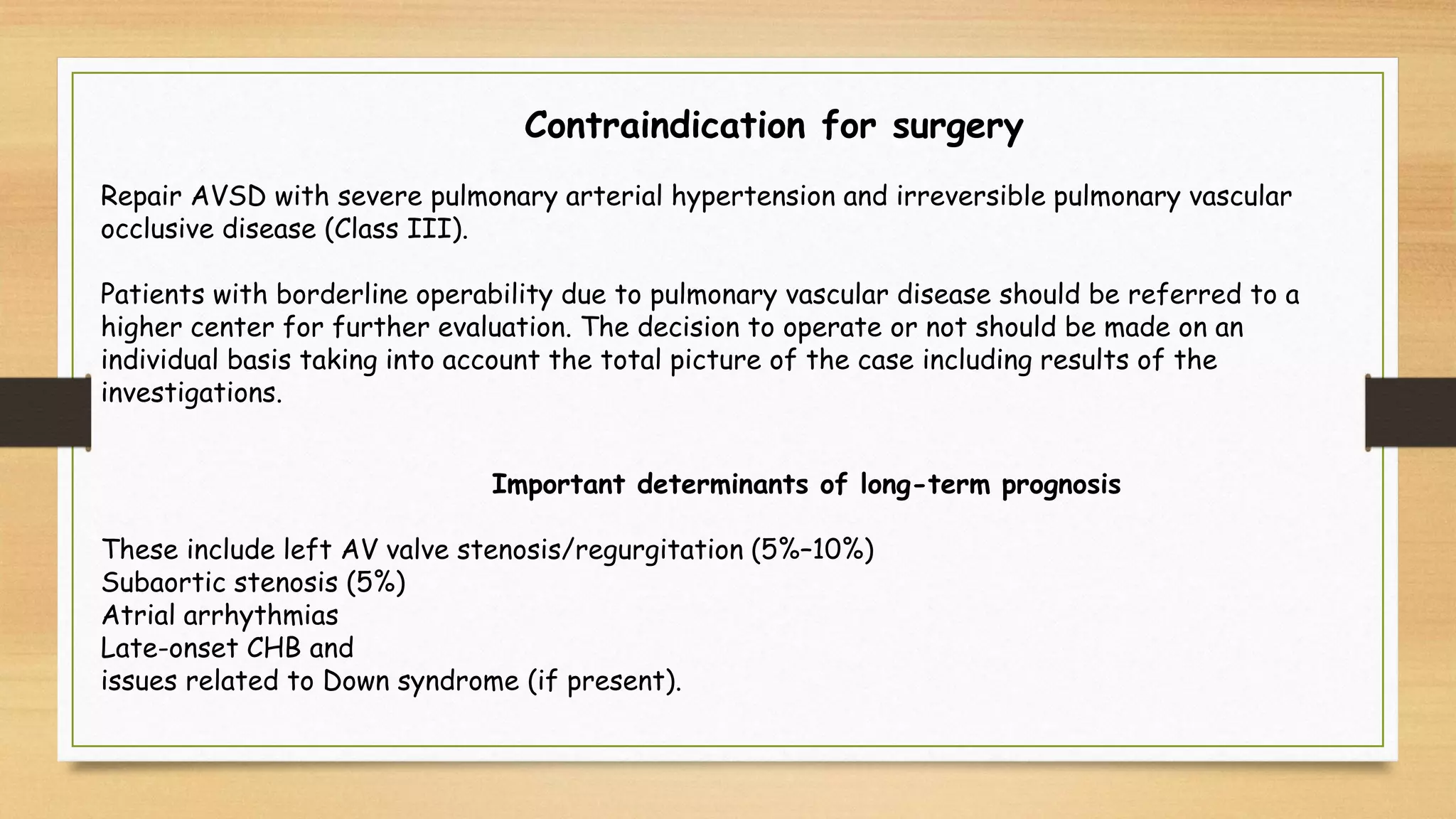
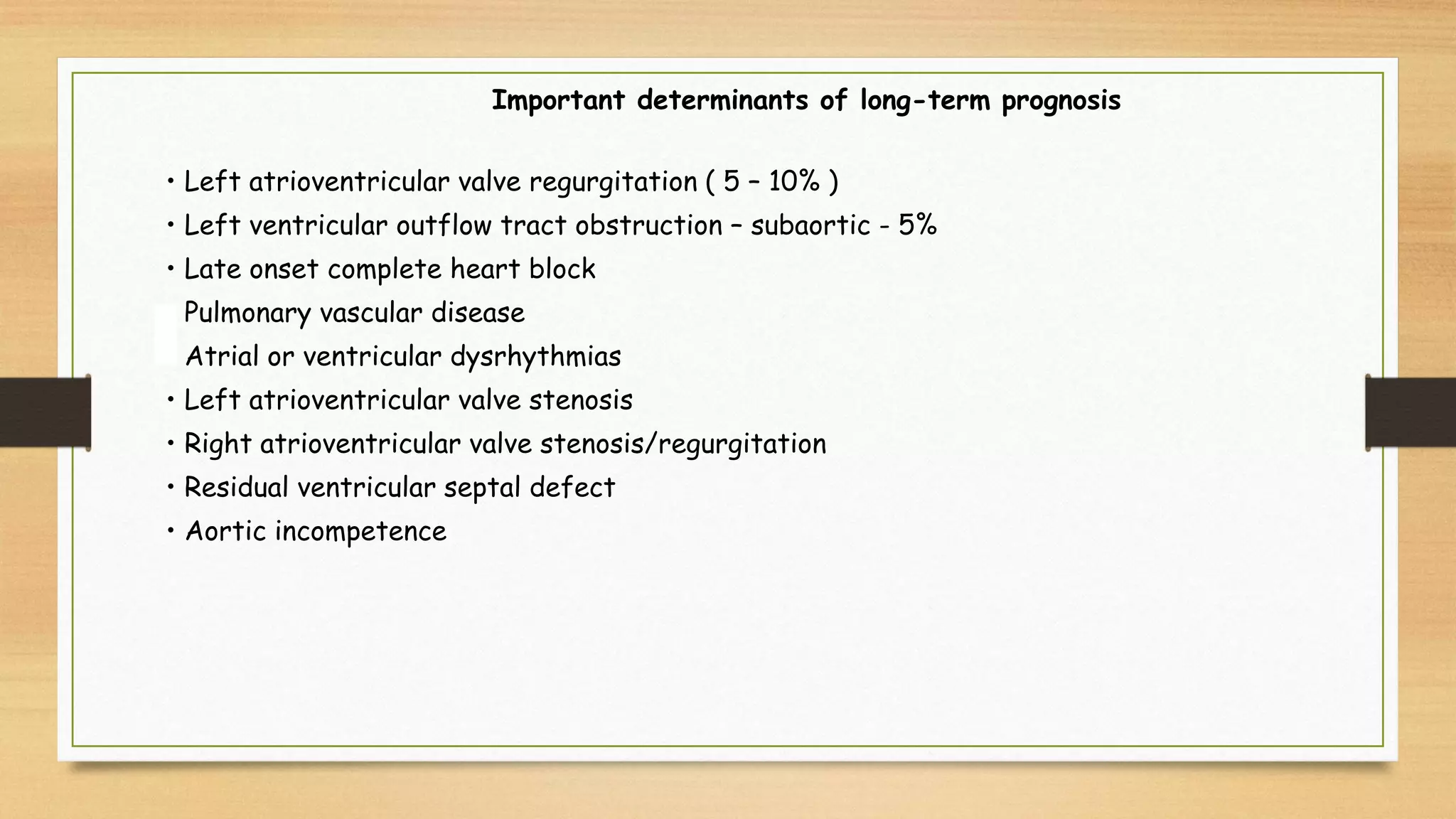
Atrioventricular septal defects (AVSDs) represent a significant portion of congenital heart defects, often associated with Down syndrome, leading to severe pulmonary vascular disease. They can be classified into balanced and unbalanced forms, with varying impacts on heart function and blood flow, particularly in patients with associated anomalies like heterotaxy. Diagnosis relies heavily on echocardiography, assessing structural defects and function to guide treatment strategies.