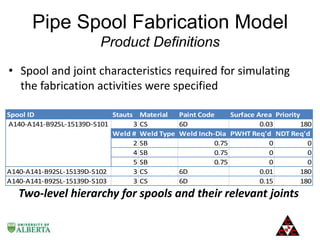
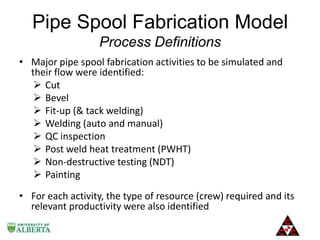
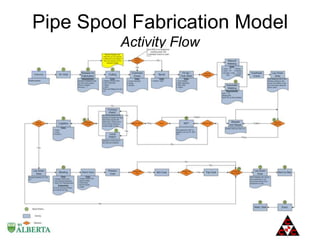
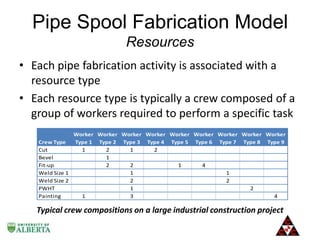
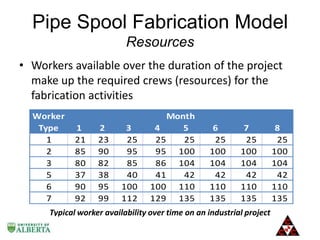
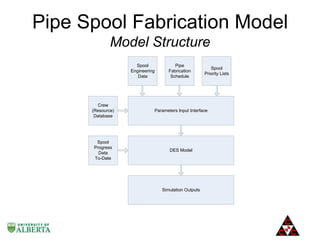
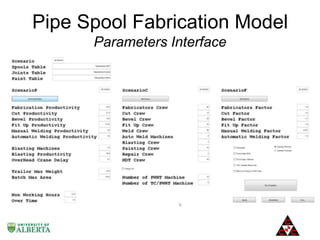
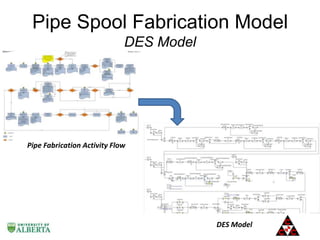
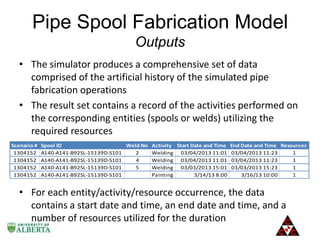
The document discusses a computer modeling and simulation approach designed to improve pipe spool fabrication processes in large industrial projects. It outlines the model's structure, including product and process definitions, resource allocation, and potential benefits such as predictive analysis and optimization during project execution. Future enhancements planned for the model include additional modules for material constraints and installation simulation.