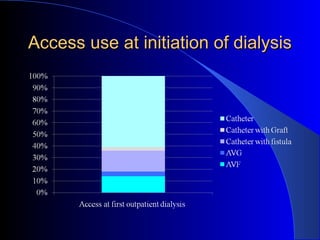
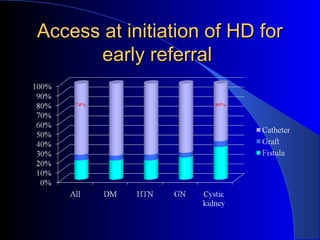
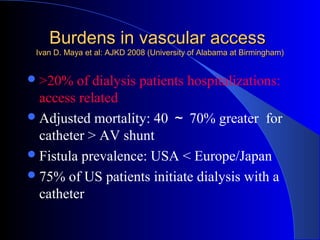
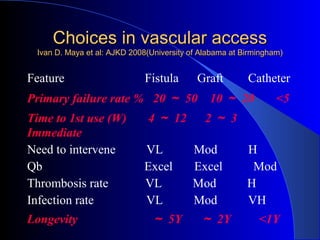
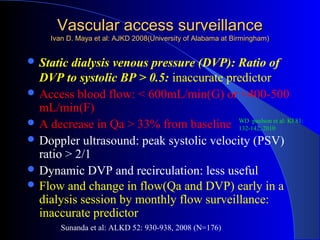
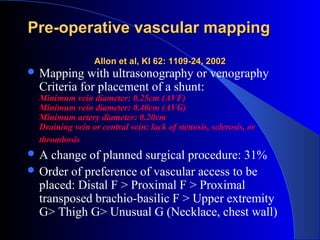
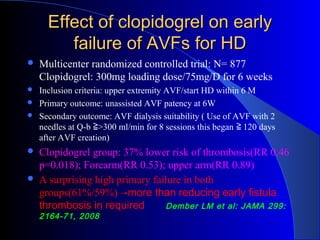
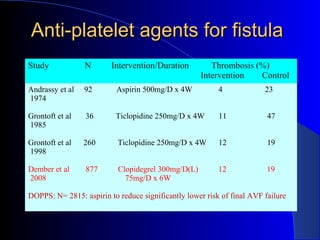
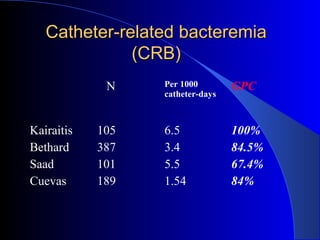
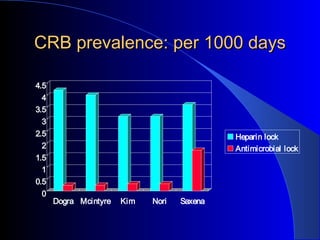
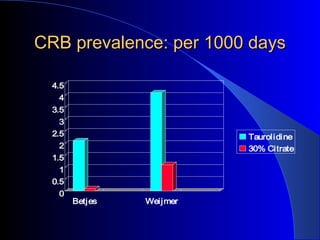
This document summarizes the history and developments in vascular access for hemodialysis. It discusses key milestones like the first hemodialysis in 1924, the Quinton-Scribner shunt in 1960, and the Brescia-Cimino fistula in 1966. It then compares arteriovenous fistulas, grafts, and catheters and their primary failure rates, infection risks, and longevity. The document outlines criteria for successful fistulas and grafts and factors that can lead to stenosis. It also discusses strategies to prevent stenosis and reduce catheter use, such as earlier patient referral and education on permanent access options.