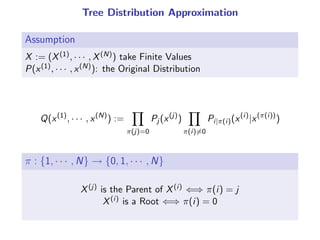
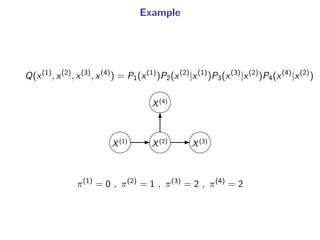
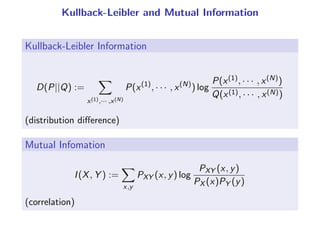
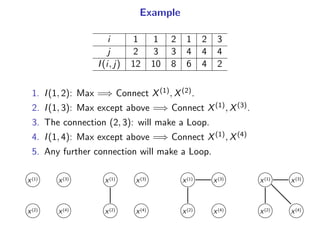
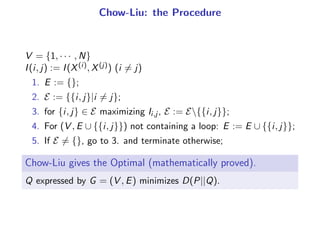
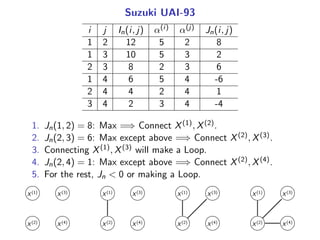
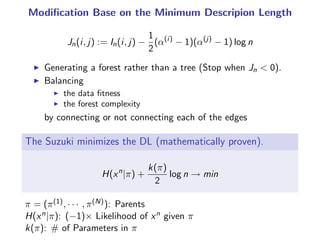
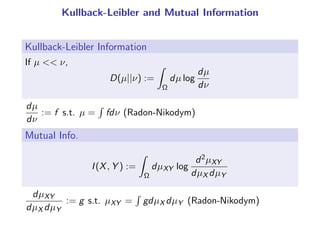
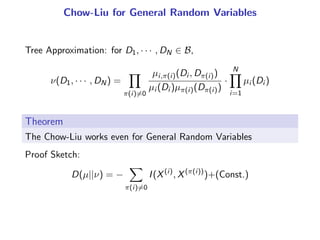
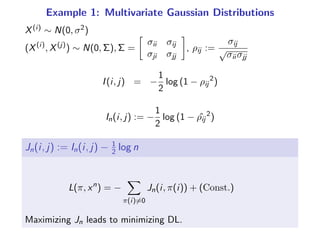
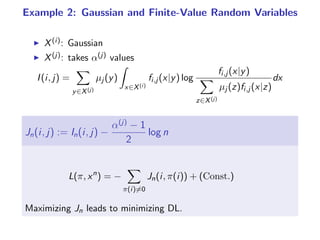
The document presents a generalization of the Chow-Liu algorithm for approximating distributions of general random variables and highlights its applications in artificial intelligence. It discusses the algorithm's methodology for constructing tree and forest structures minimizing Kullback-Leibler divergence by selecting edges based on mutual information. Additionally, the extension to general random variables is mathematically proven through examples involving Gaussian and finite-value random variables.