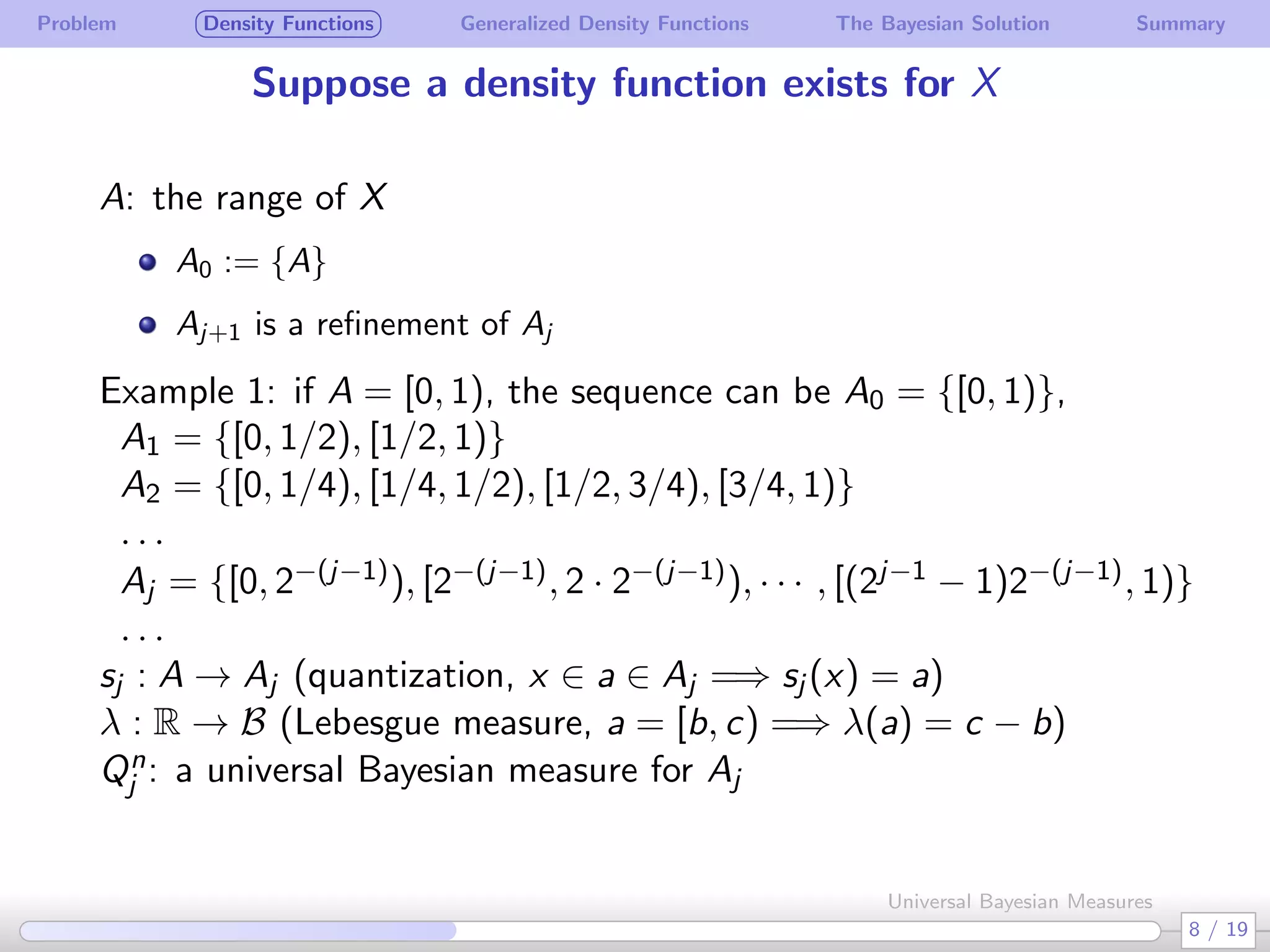
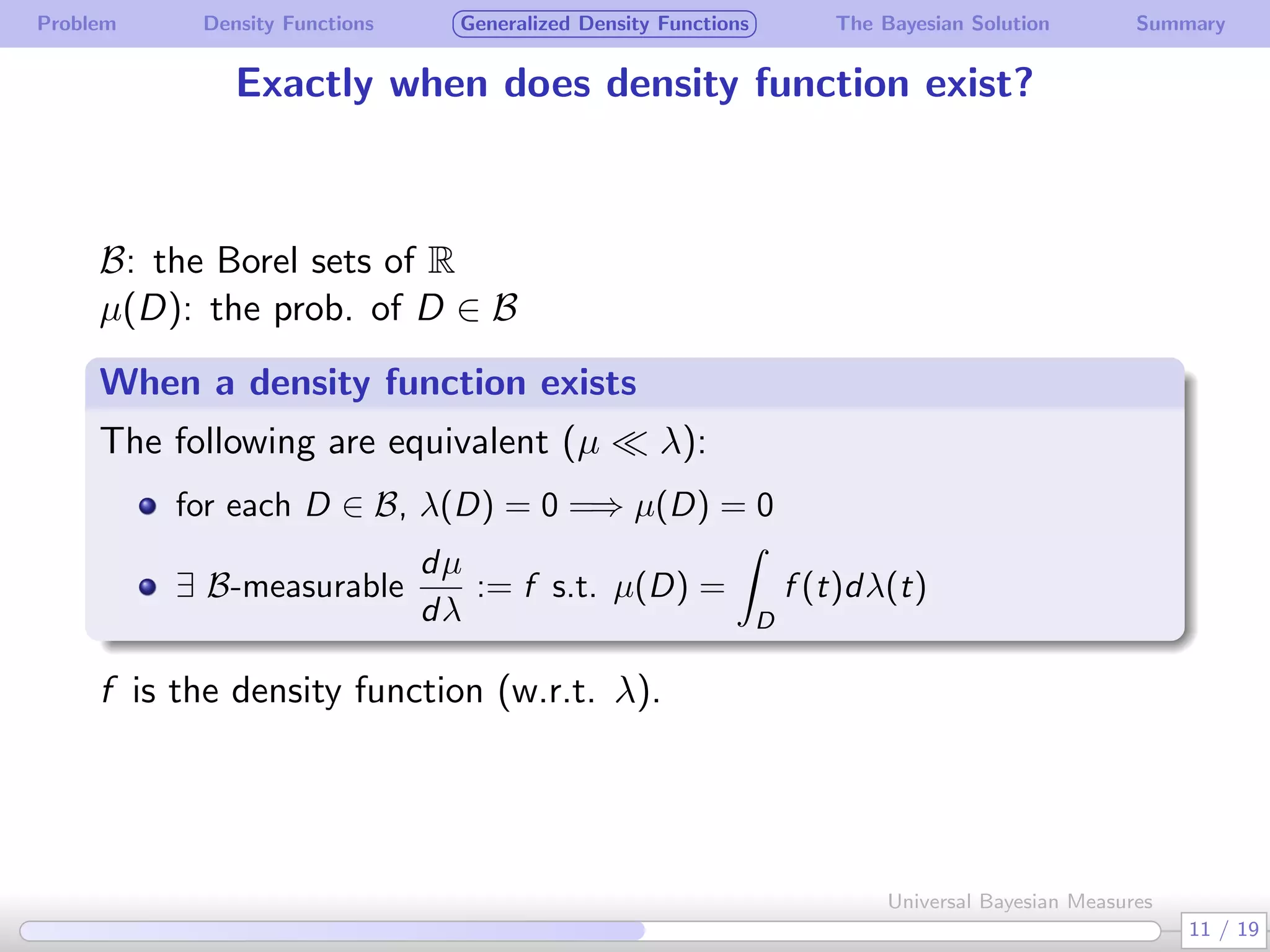
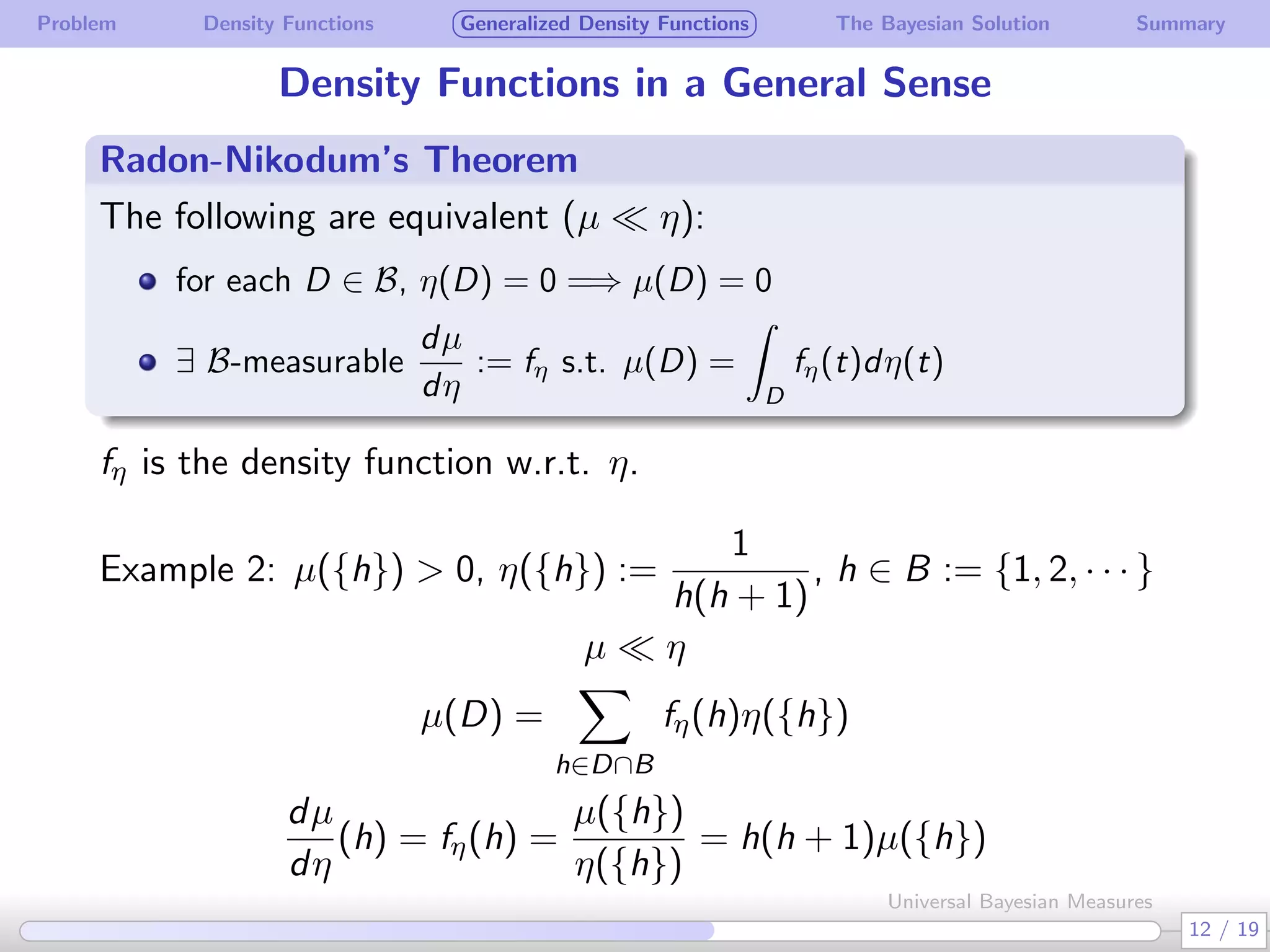
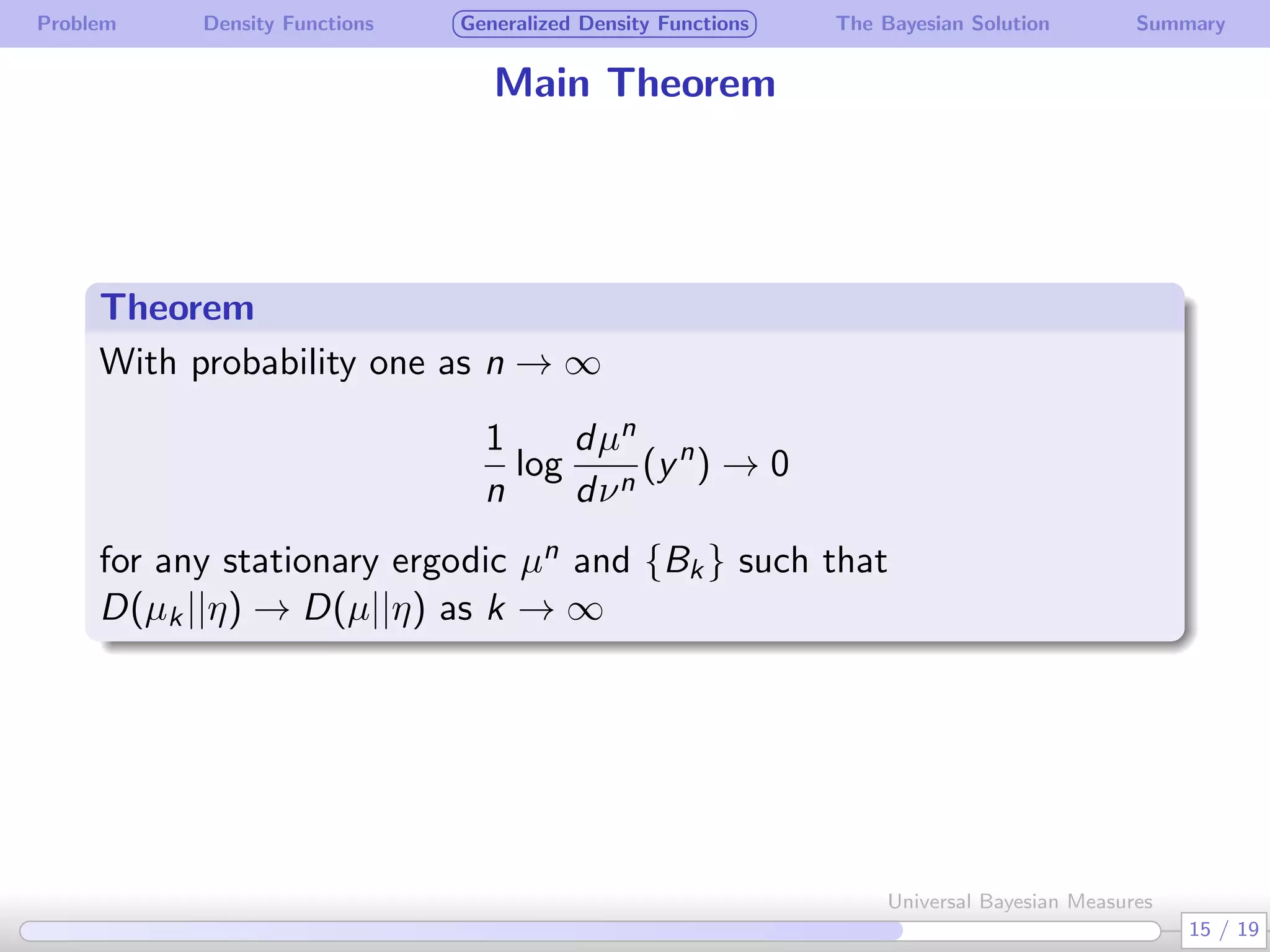
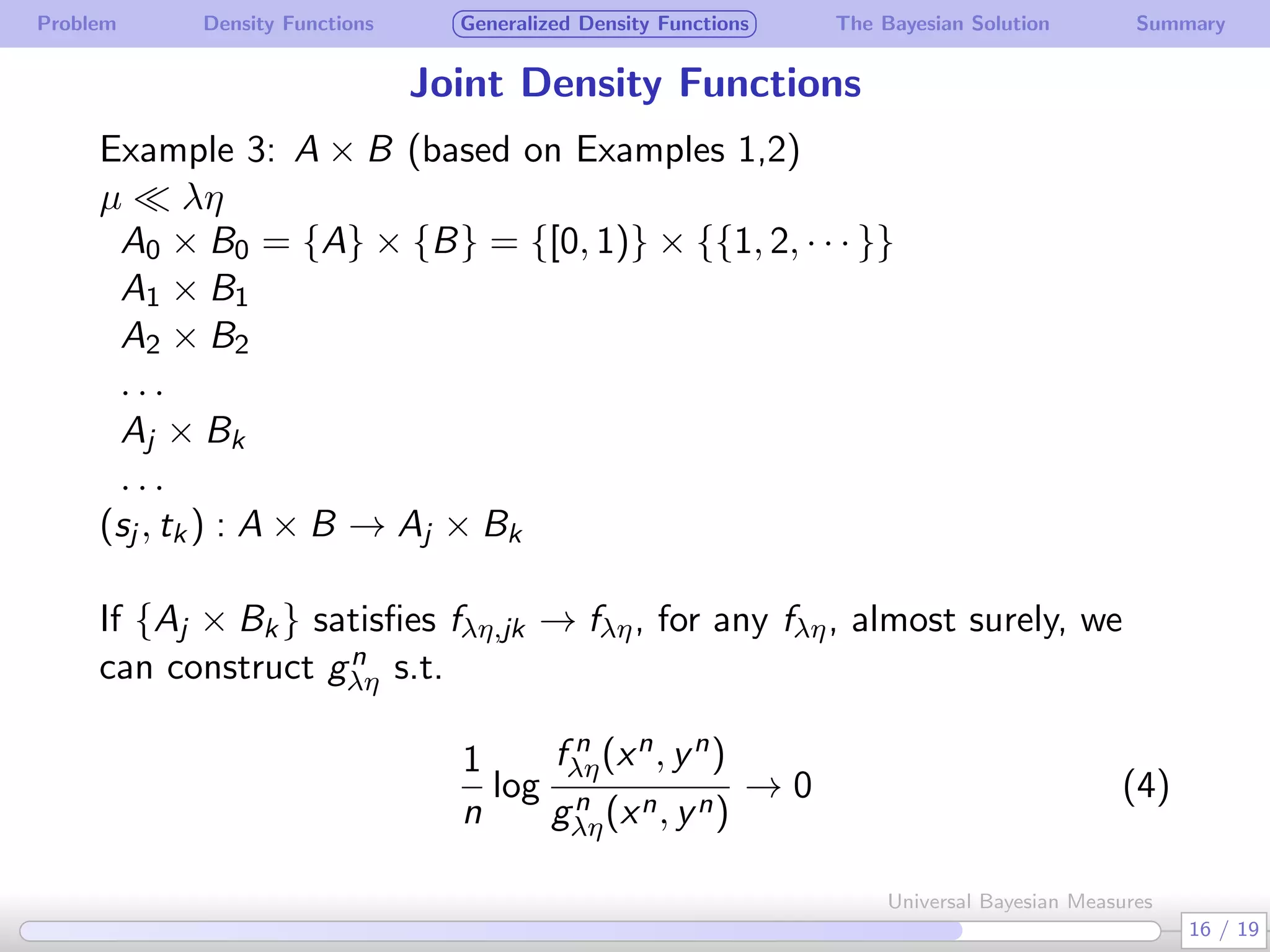
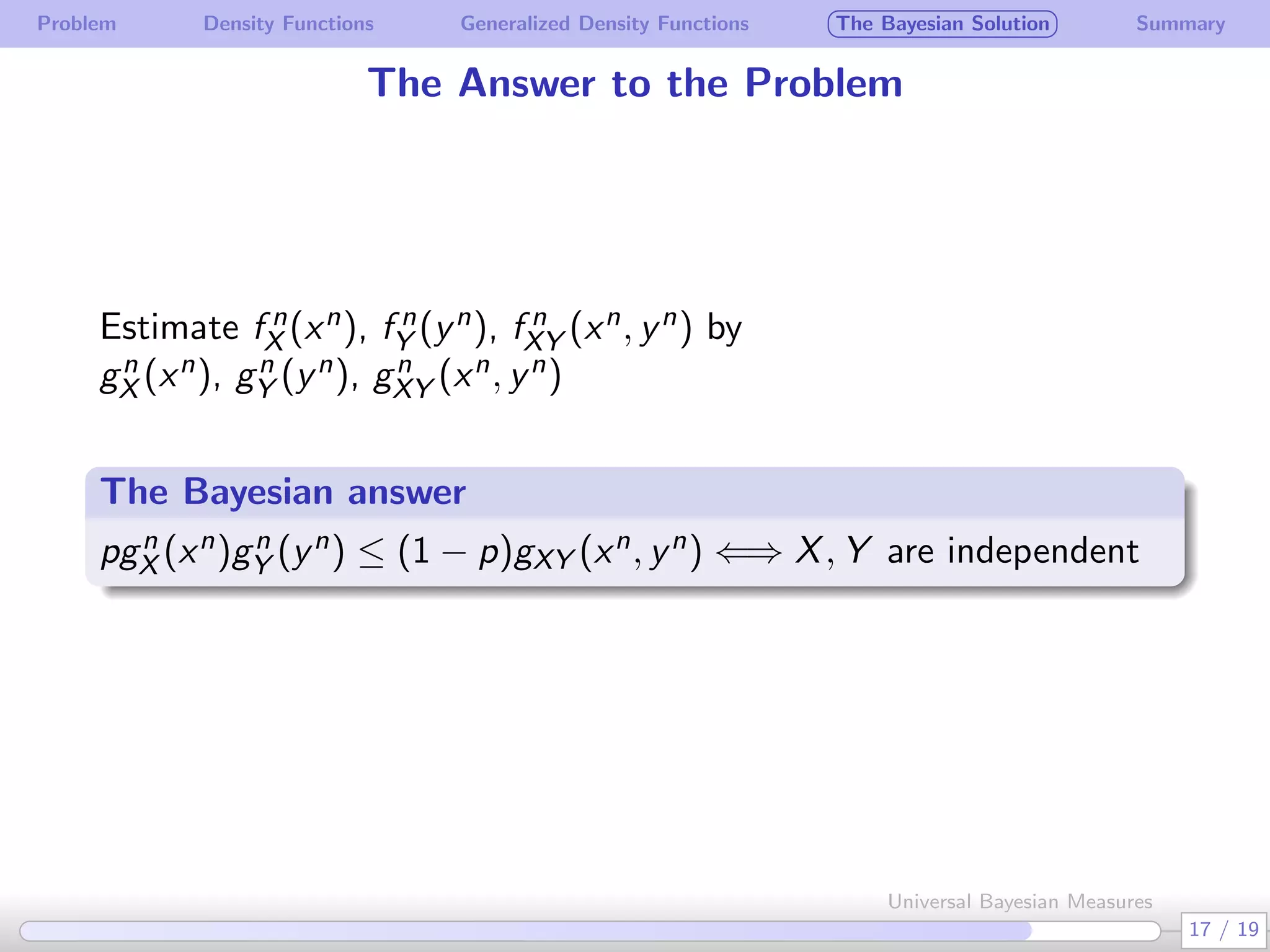
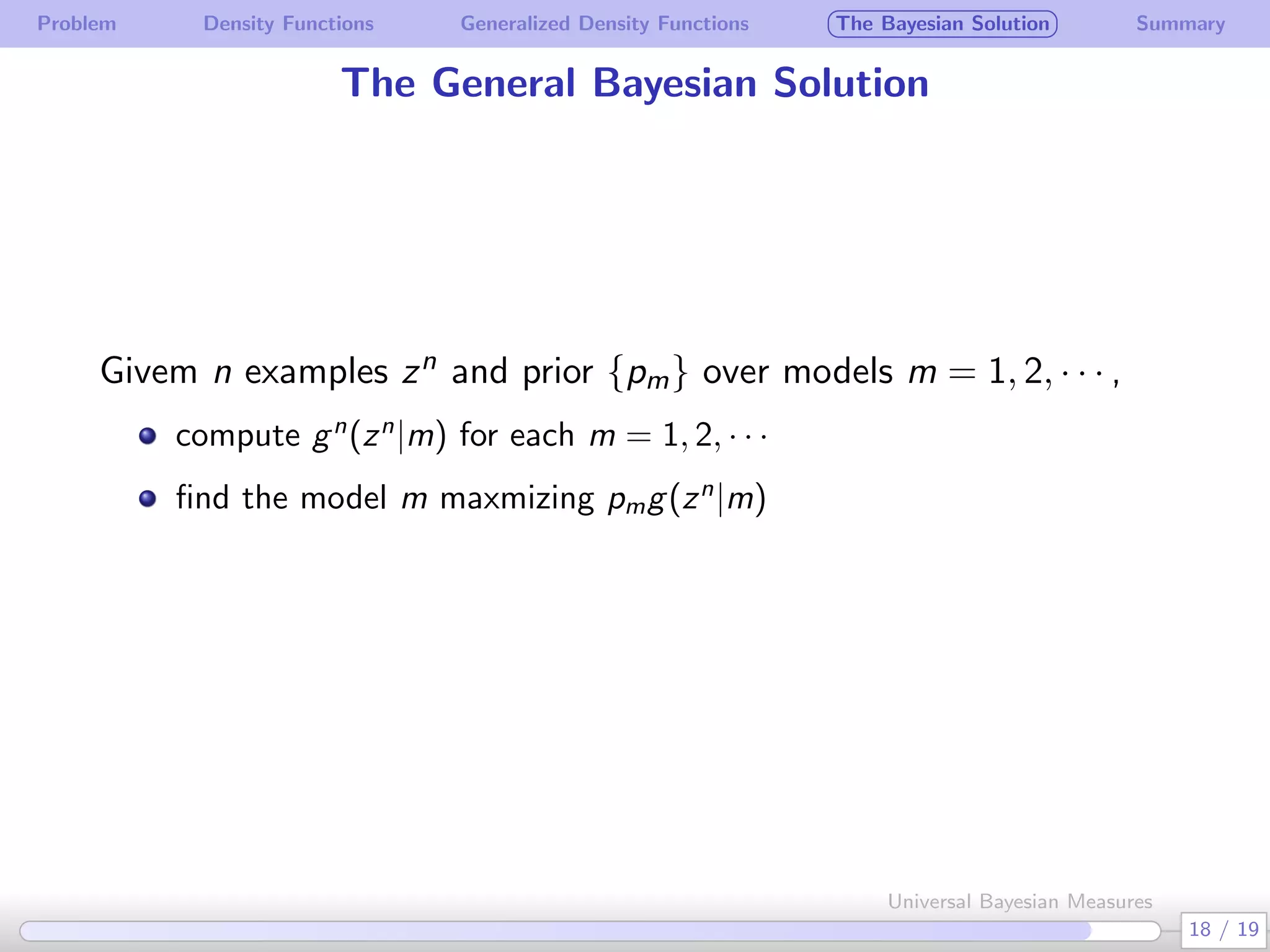
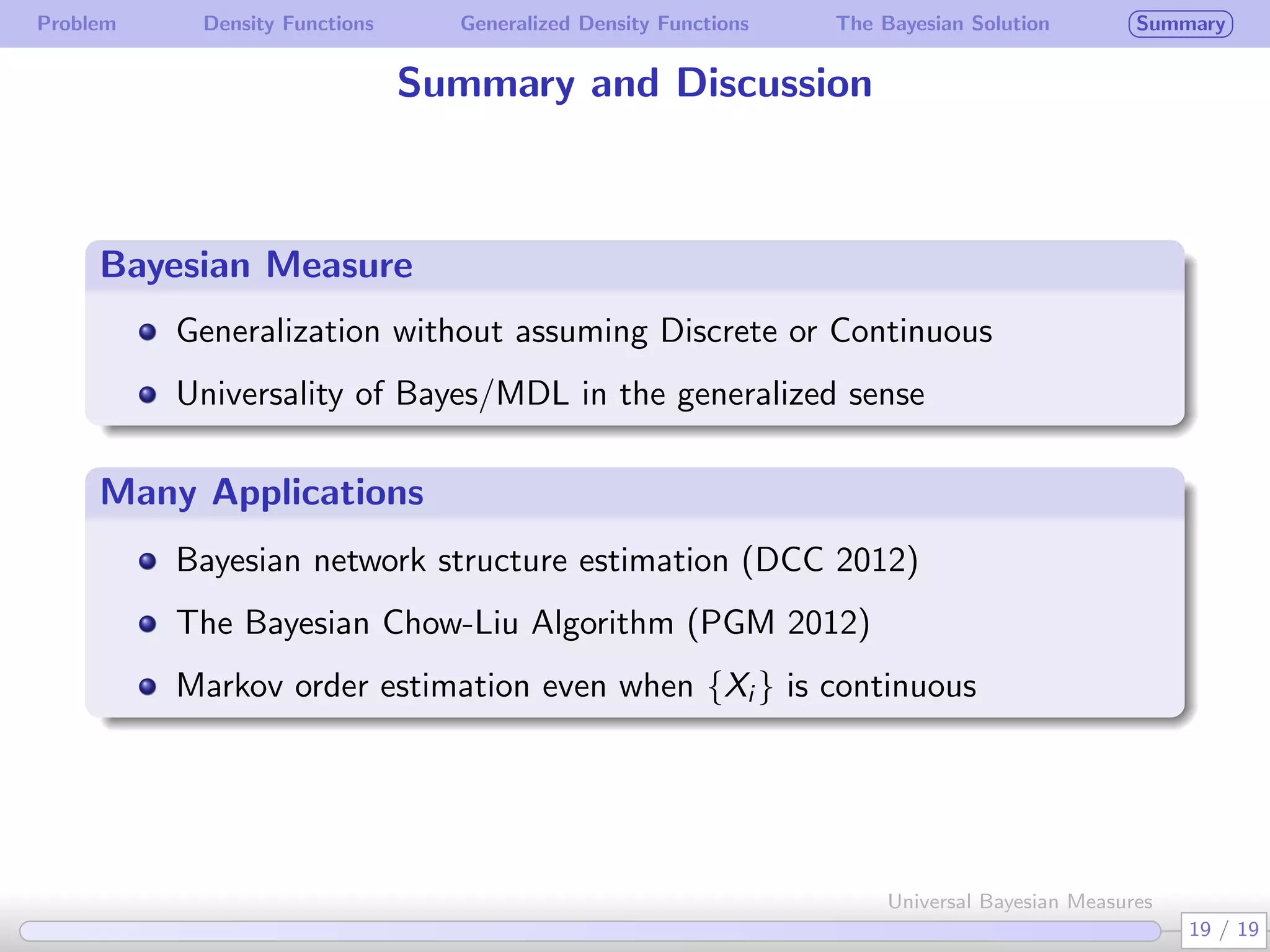
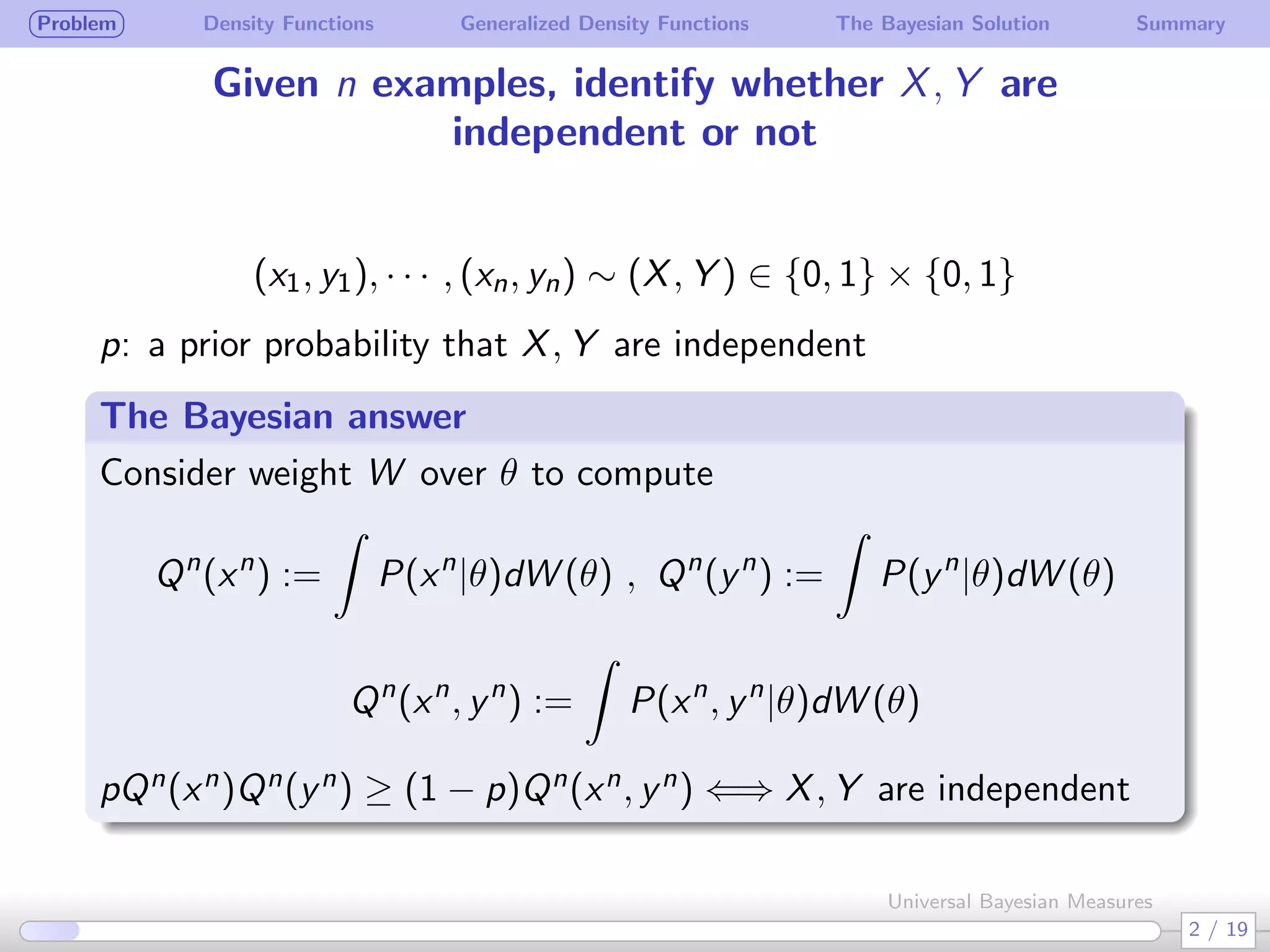
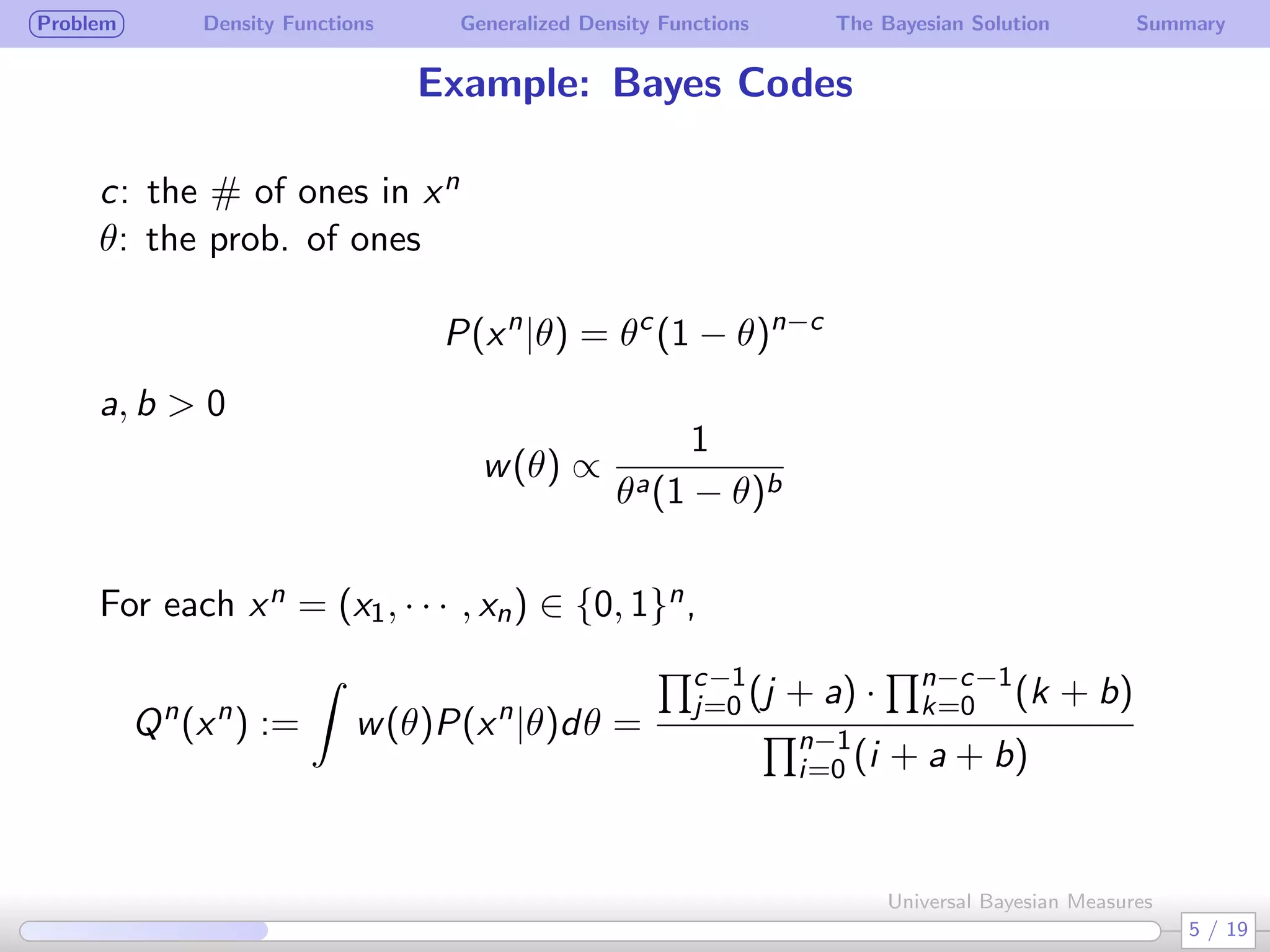
The document discusses generalizing Bayesian measures to situations where random variables may be neither discrete nor continuous. It defines generalized density functions that allow estimating probabilities without assuming an underlying distribution. A main theorem states that universal Bayesian measures gn can estimate densities fn such that the log ratio of fn/gn approaches 0 as n increases, for any stationary ergodic distribution. This generalizes the Bayesian solution to testing independence of random variables without requiring a known distribution.



![Problem Density Functions Generalized Density Functions The Bayesian Solution Summary
Universal Coding/Measures
If we choose
a = b = 1/2
(Krichevsky-Trofimov) and xn is i.i.d. emitted by
Pn
(xn
|θ) =
n∏
i=1
P(xi ) , P(xi ) = θ, 1 − θ
then, for any P, almost surely,
−
1
n
log Qn
(xn
) → H :=
∑
x∈A
−P(x) log P(x)
From Shannon McMillian Breiman, for any P,
−
1
n
log Pn
(xn
|θ) =
1
n
n∑
i=1
− log P(xi ) → E[− log P(xi )] = H
6 / 19
Universal Bayesian Measures](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2013-7-8-130711044407-phpapp01/75/2013-IEEE-International-Symposium-on-Information-Theory-6-2048.jpg)