Embed presentation
Downloaded 124 times



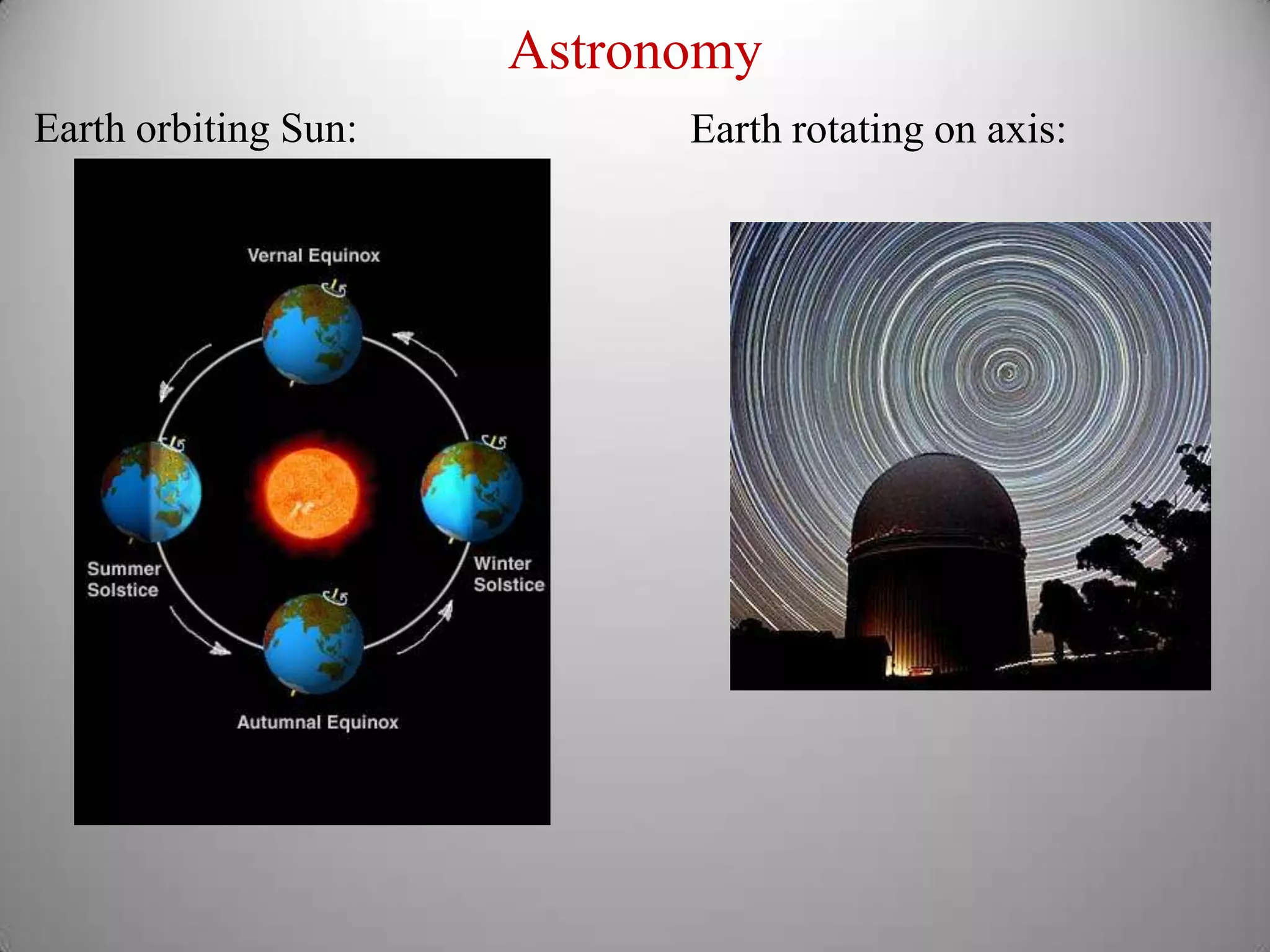
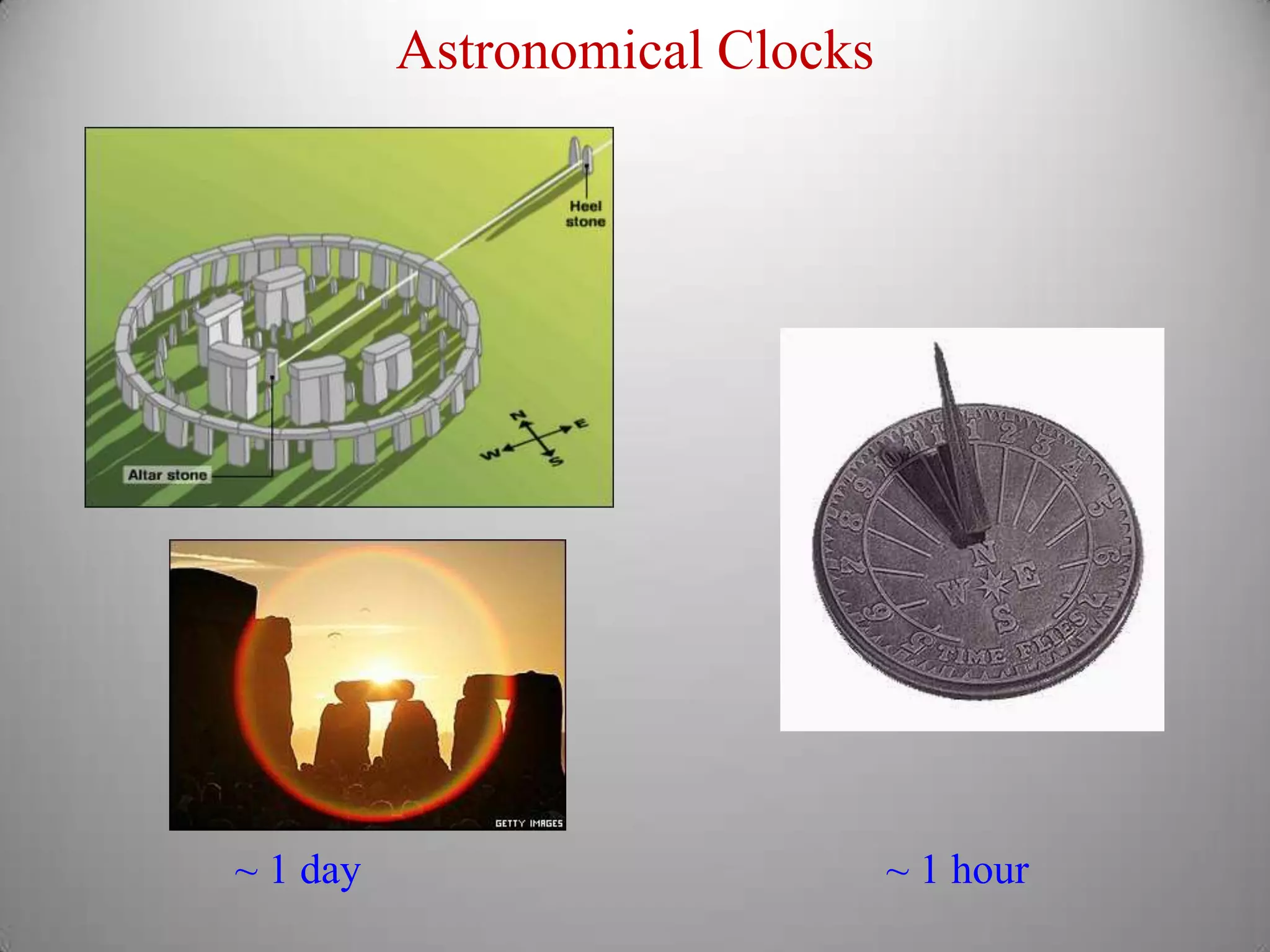
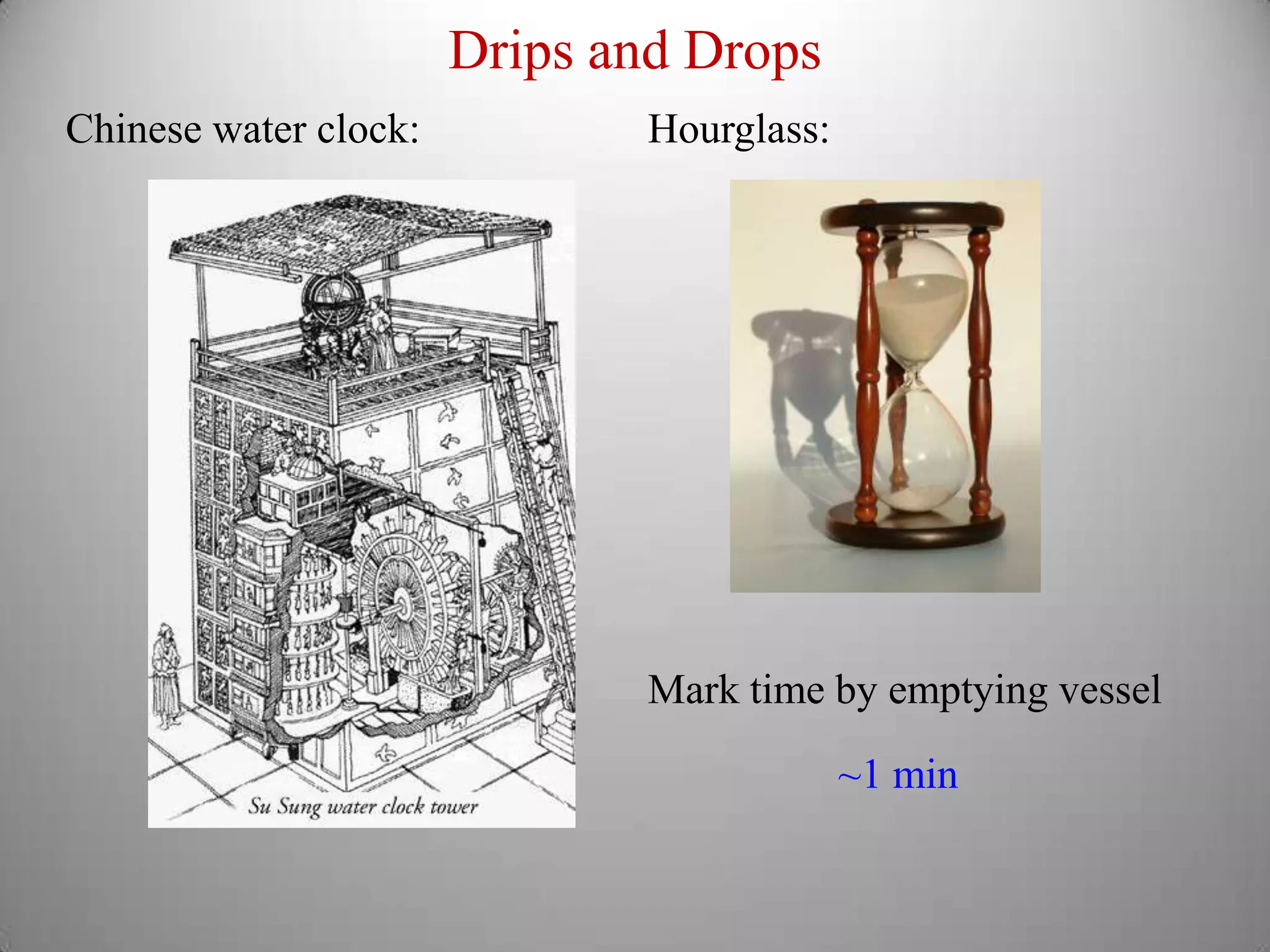


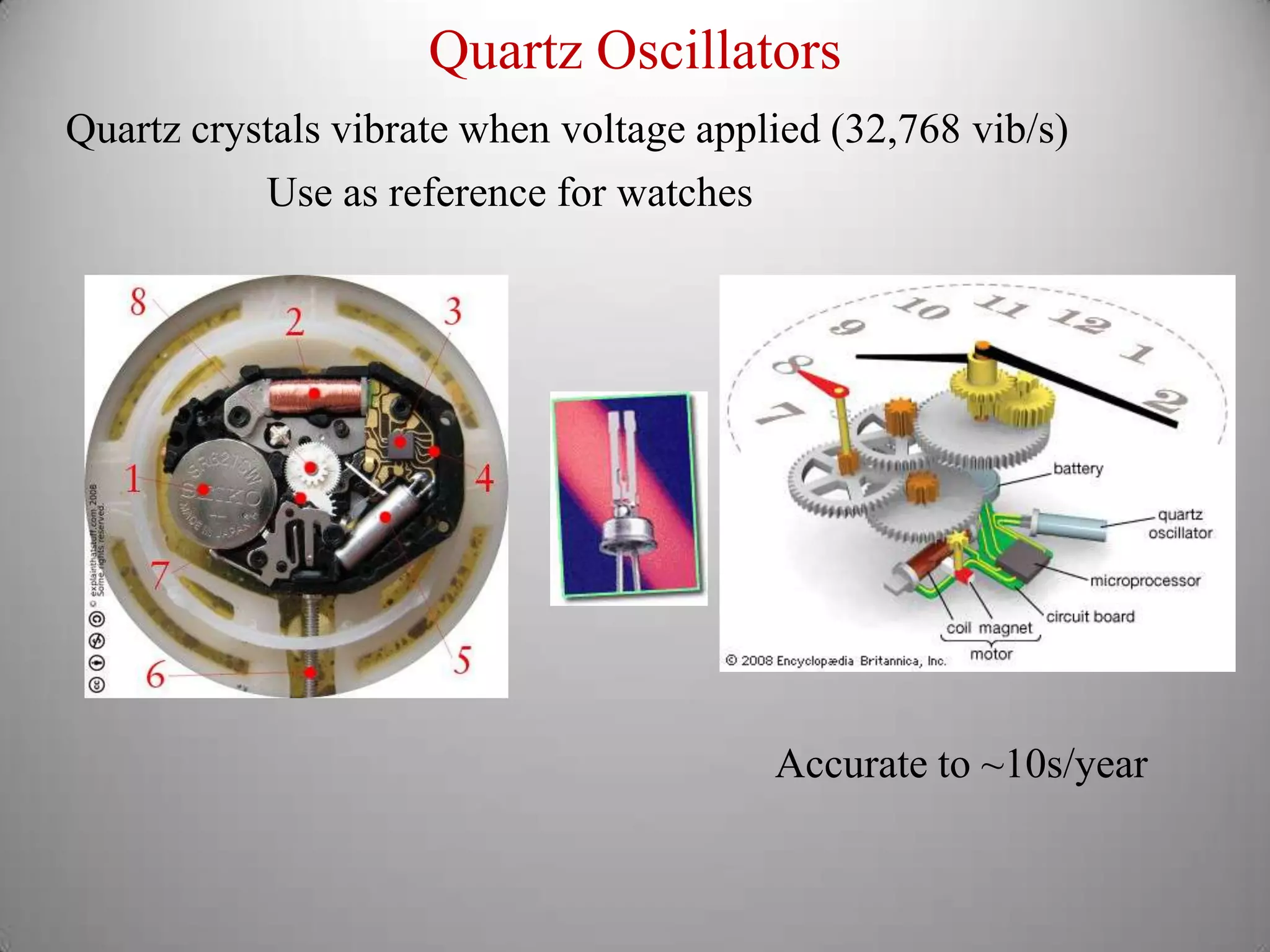
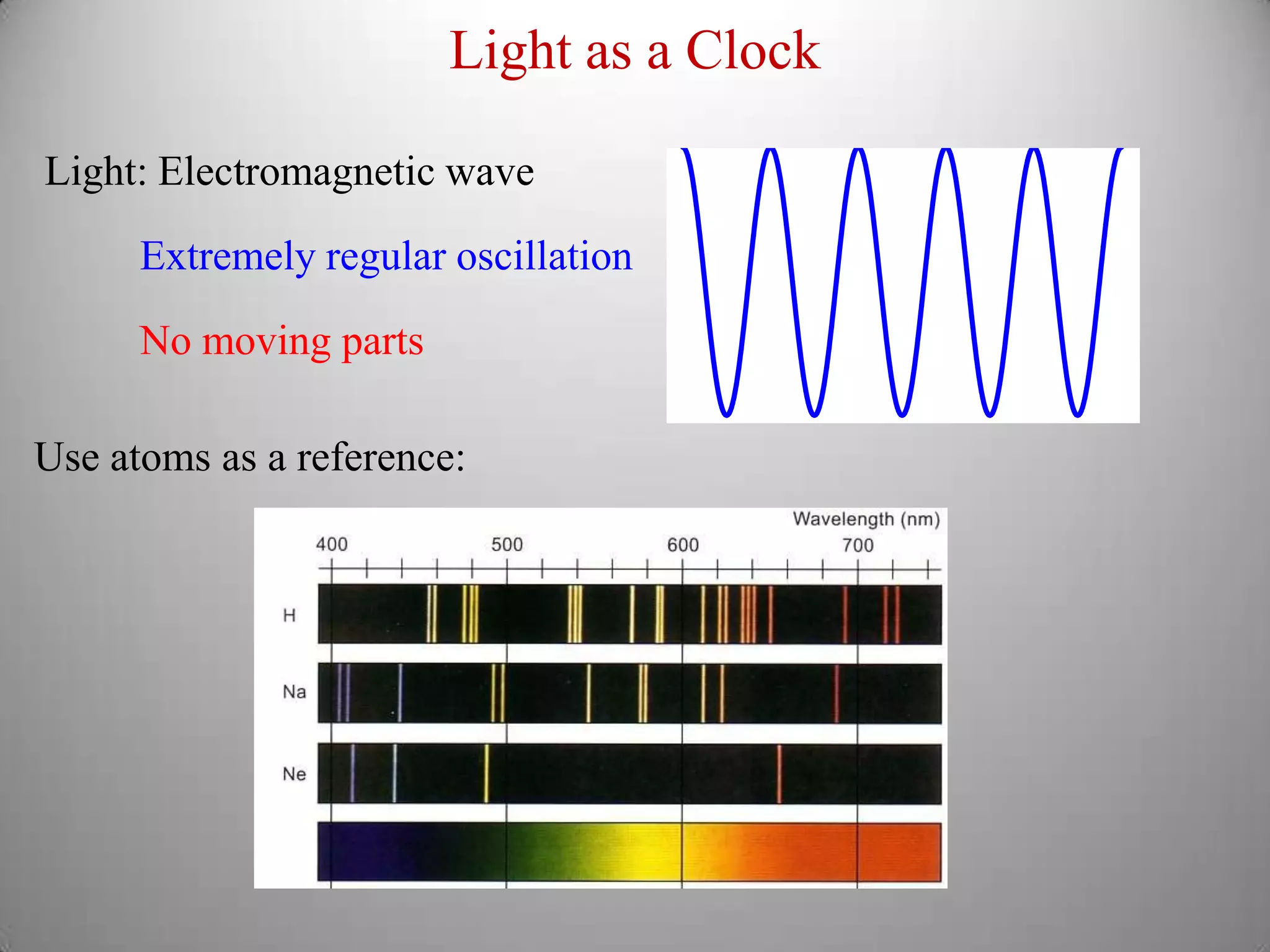




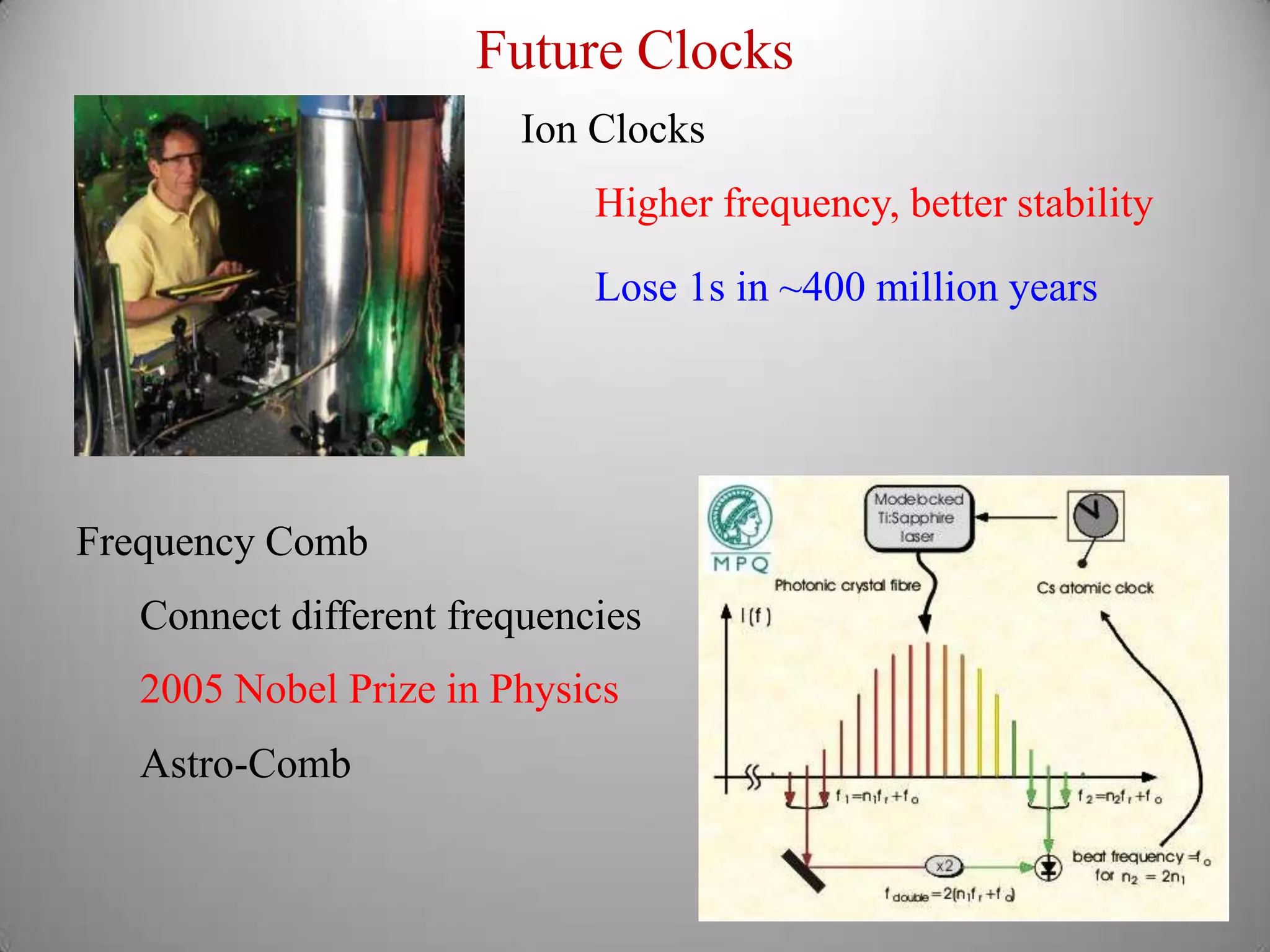

From Stonehenge to NIST F1 provides a brief history of timekeeping. It discusses early astronomical clocks based on the earth's orbit and rotation. It then describes the development of pendulum clocks in the 17th century and John Harrison's sea clocks in the 18th century. Quartz oscillators were developed in the 1920s providing more accurate timekeeping. Atomic clocks were developed in the 1950s using the vibration of cesium atoms as the most accurate clock yet, losing only 1 second every 20-30 million years. Precise timekeeping from atomic clocks is necessary for applications like global positioning systems.















