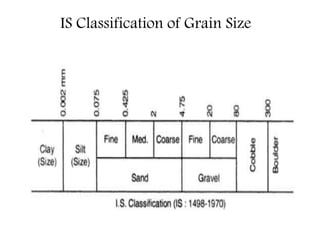
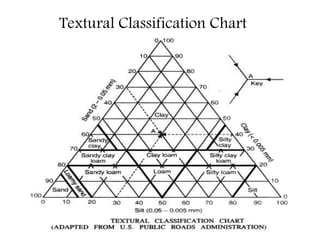
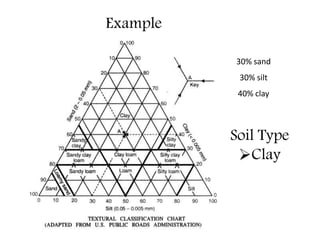
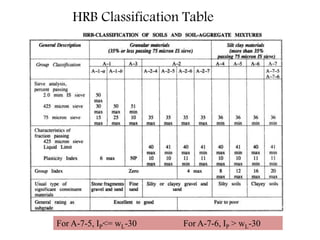
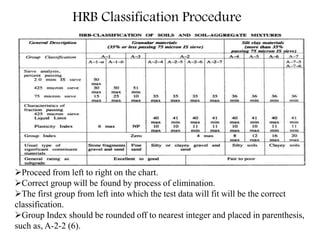
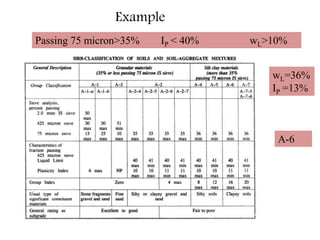
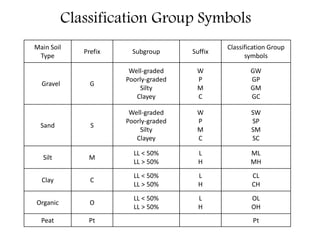
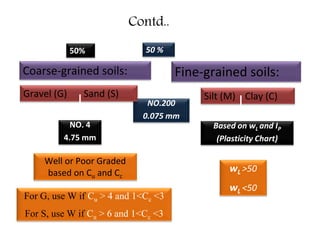
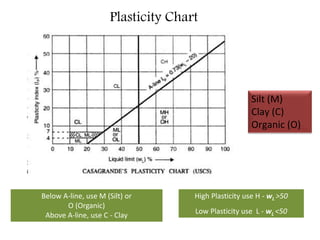
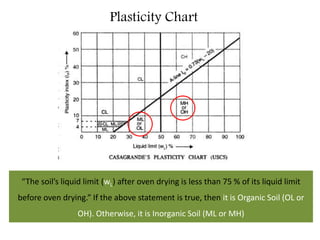
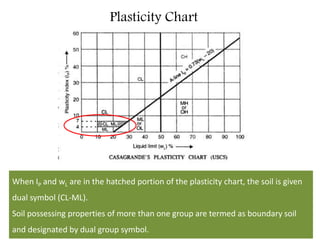
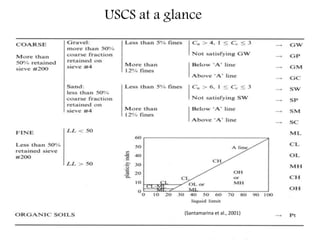
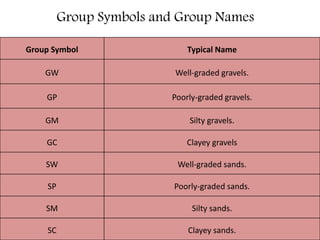
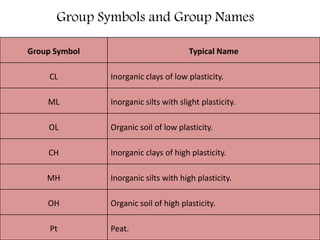
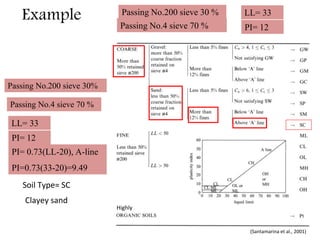
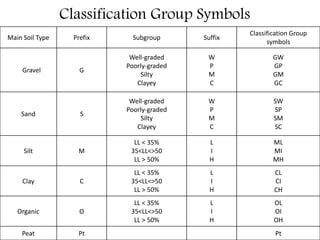
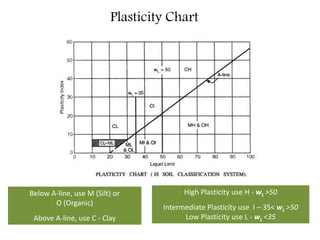
This document provides an overview of different soil classification systems including: particle size classification, textural classification, Highway Research Board (HRB) classification, Unified Soil Classification System (USCS), and Indian Standard Classification System (ISCS). It describes the key aspects of each system such as group name designations, plasticity characteristics, grain size thresholds. Examples are provided to demonstrate how to classify soils according to their particle sizes, plasticity properties and assign them the appropriate group symbol under different systems.